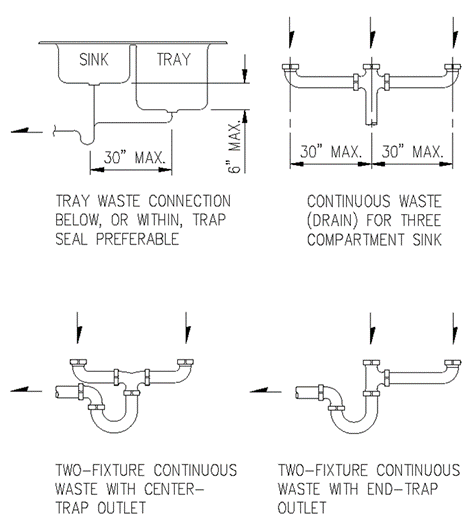
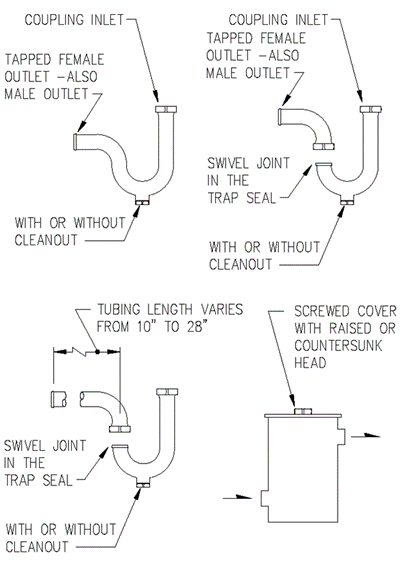
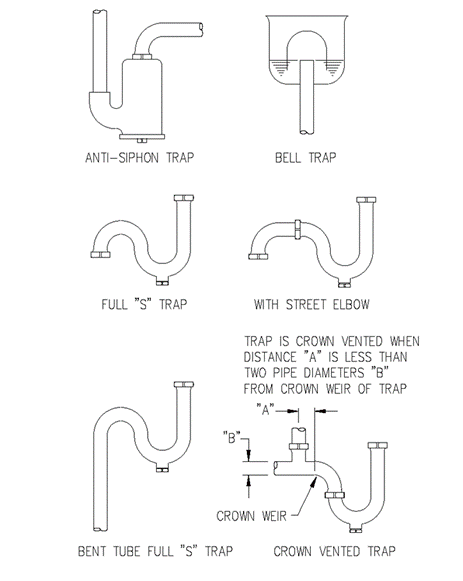
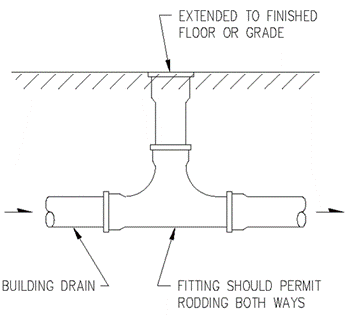
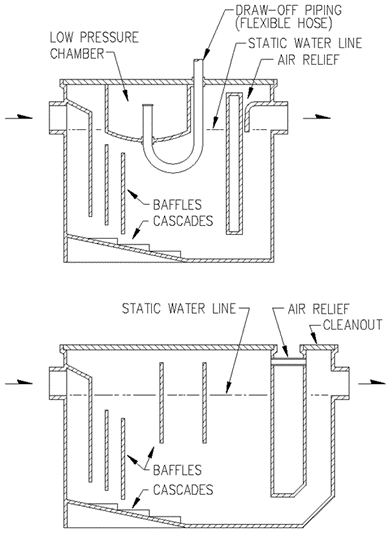
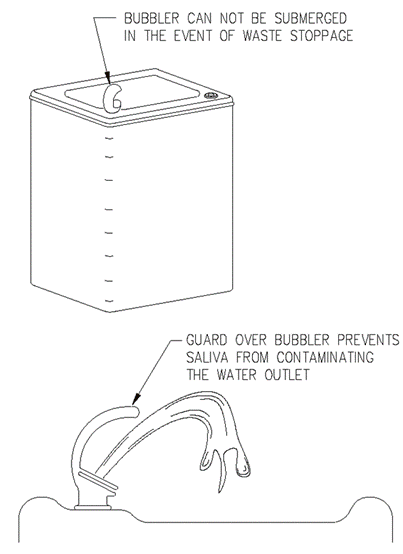
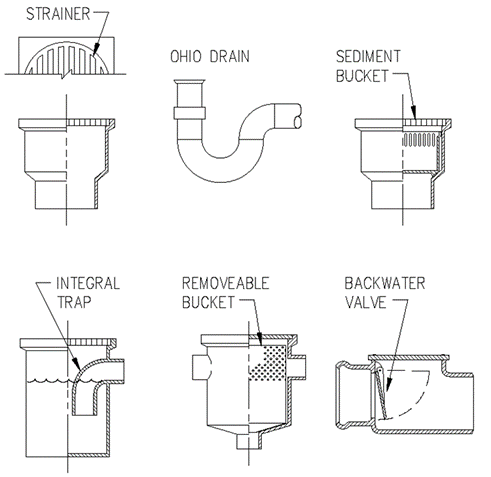
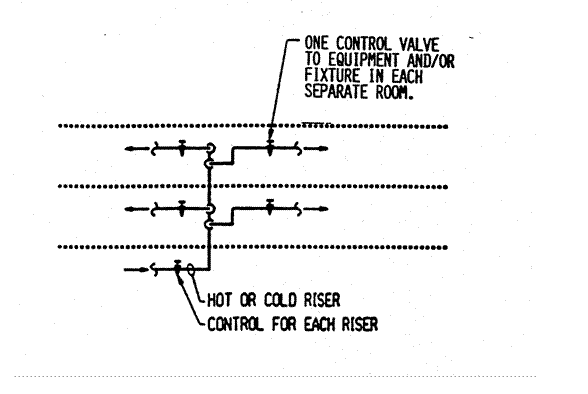
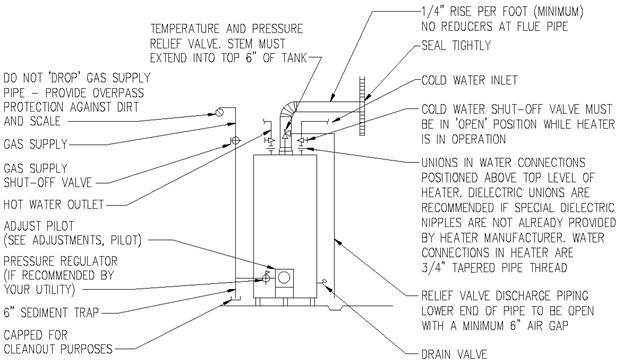
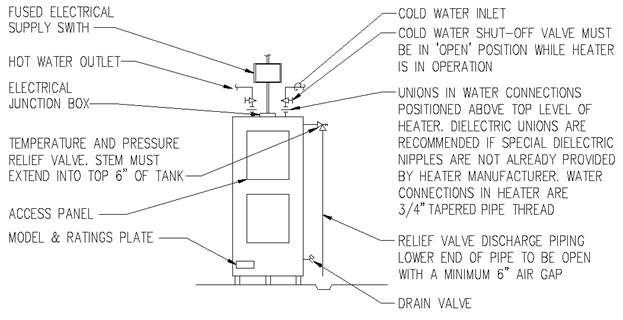
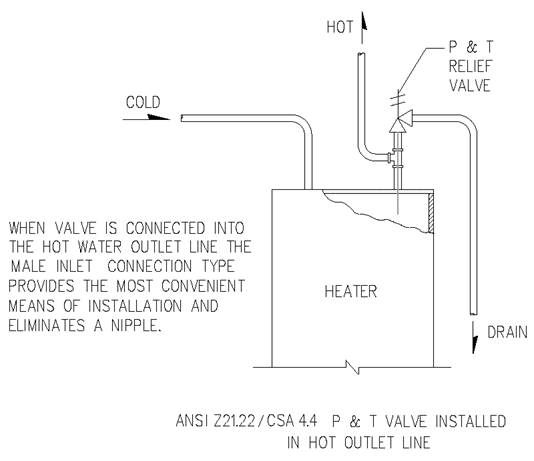
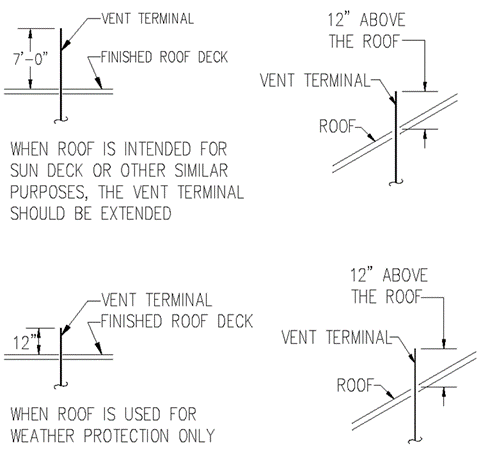
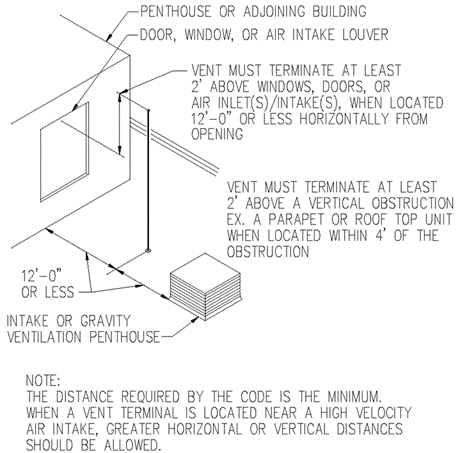
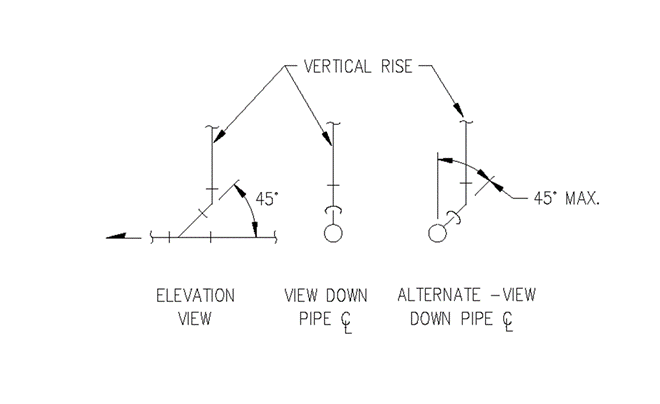
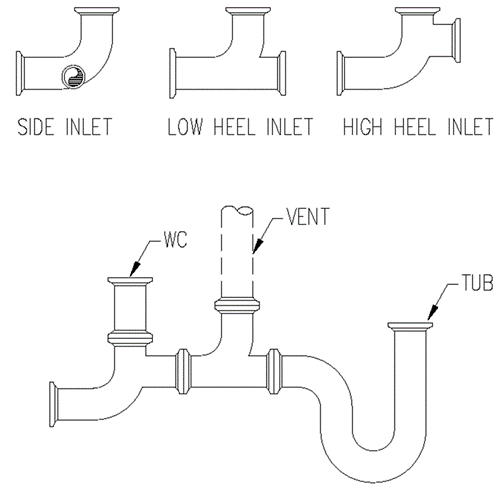
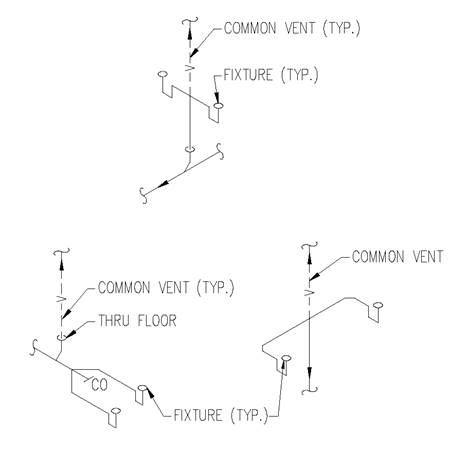
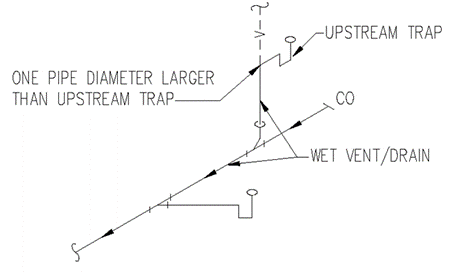
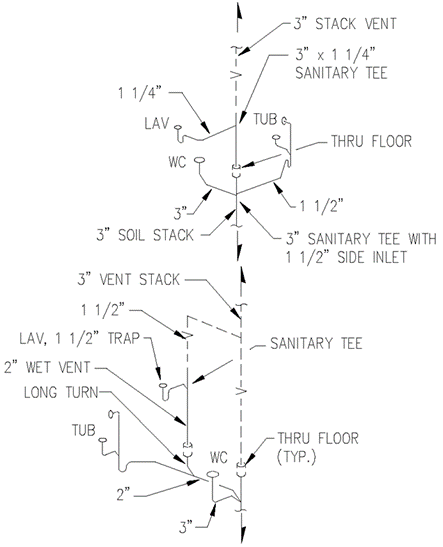
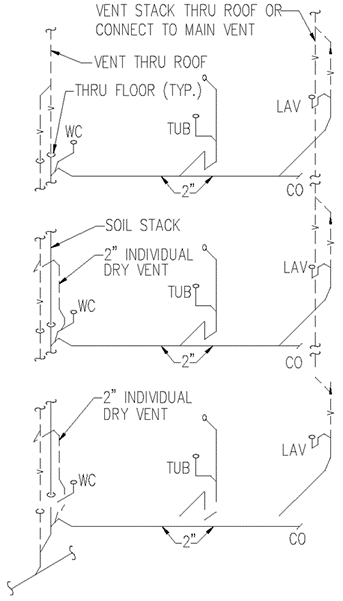
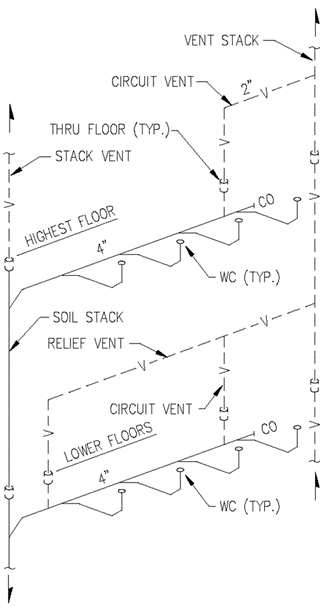
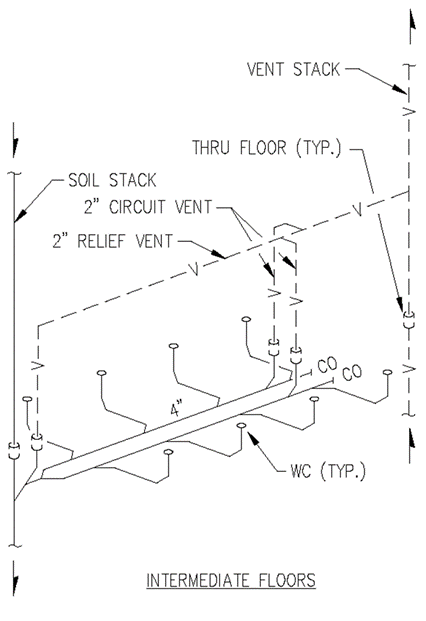
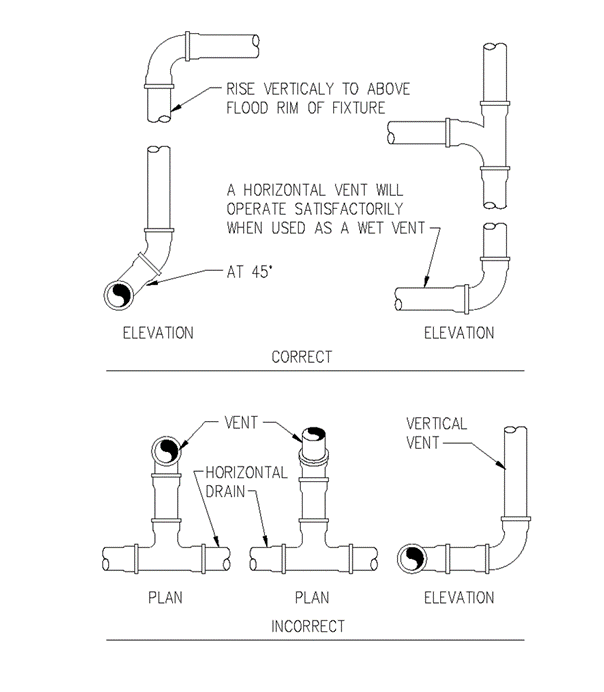
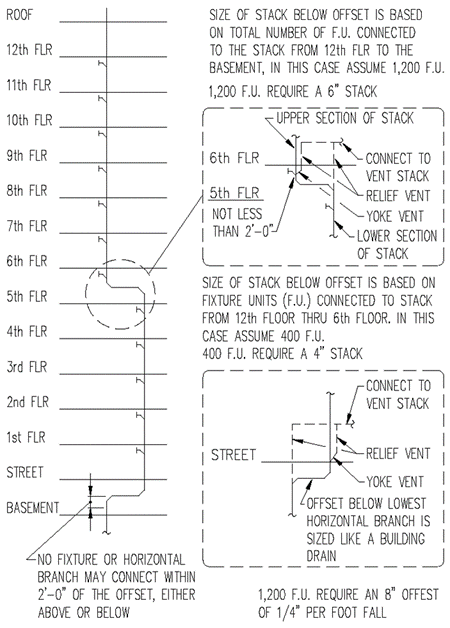
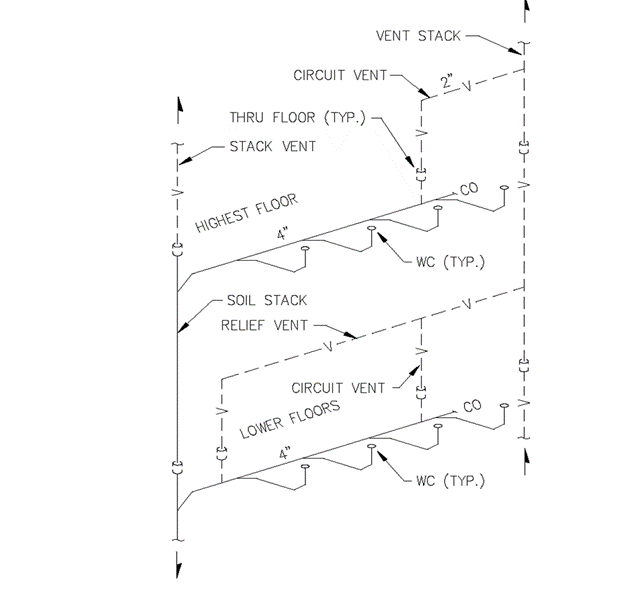
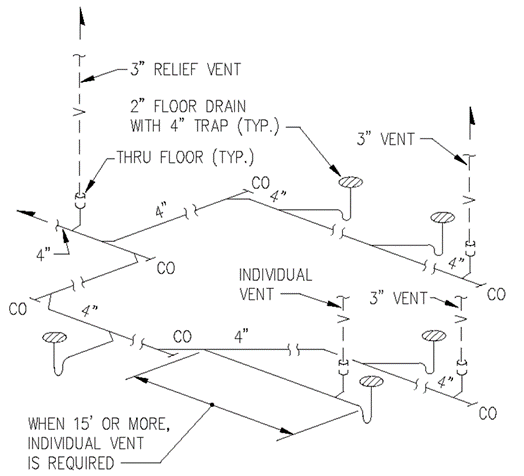
Section 890.1910 Inspections
A plumbing system or any part thereof shall not be enclosed, covered up or used until the system has been inspected and approved by a plumbing inspector. It is the responsibility of the licensed plumber or plumbing contractor on the job to arrange for inspection by the Department or a local plumbing inspector. The plumbing inspector may require tests as listed in Section 890.1930 to determine whether or not the system as installed is in compliance with this Part. Plumbing found not to be in compliance with this Part shall not be approved. A plumbing system not complying with the provisions of this Part shall not be used until such time as it is brought into compliance with this Part. After the plumbing corrections have been made, the plumbing contractor shall arrange for reinspection.
Section 890.1920 Testing of Plumbing Systems
Defective Plumbing. Where there is reason to believe that the plumbing system fails to comply with this Part, the Department or local plumbing inspector may require such tests (see Section 890.1930) and inspections as may be necessary to assure that any defects are found and corrected.
a) Exposure of Work. When plumbing work has been covered or concealed prior to being tested and approved, it shall be exposed for testing. It is the responsibility of the licensed plumber or plumbing contractor to expose plumbing for inspection purposes.
b) Equipment, Material and Labor for Tests. All equipment, material and labor required for inspection and testing a plumbing system or any part thereof is the responsibility of the licensed plumber or plumbing contractor.
Section 890.1930 Test Methods
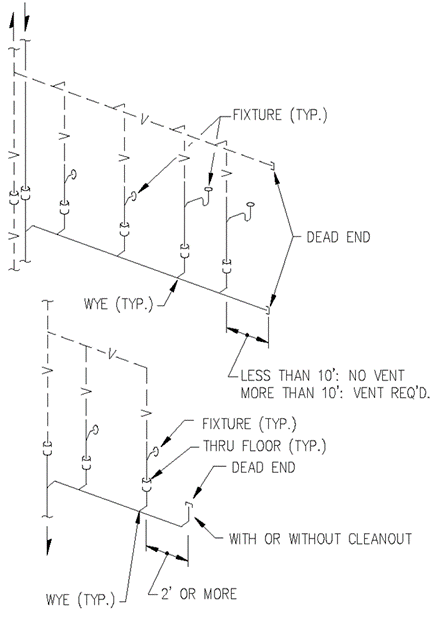
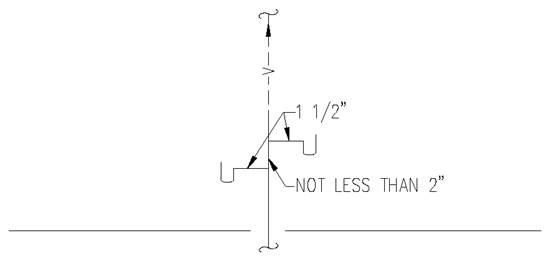
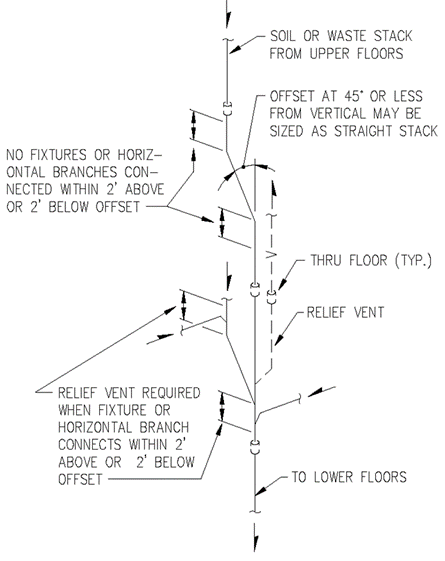
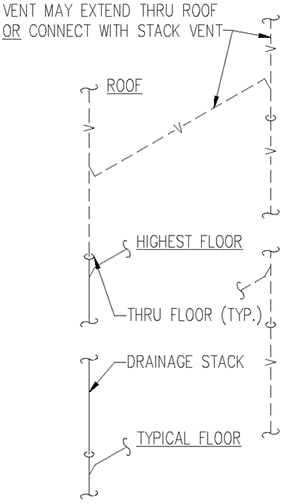
a) Roughed-In Plumbing. The piping of plumbing drainage and venting systems shall be tested upon completion of the roughed-in piping installation by water or air to prove watertight. The Department or local plumbing inspector may require the removal of any cleanout plugs to ascertain if the pressure has reached all parts of the system.
b) Water test. The water test shall be applied to the drainage system either in its entirety or in sections after piping has been roughed-in. If applied to the entire system, all openings in the piping shall be tightly closed, except the highest opening, and the system shall be filled with water to point of overflow. If the system is tested in sections, each opening shall be tightly plugged except the highest opening of the section being tested and each section shall be filled with water; however, a section shall not be tested with less than a ten (10) foot head of water. In testing successive sections, at least the upper ten (10) feet of the next higher section shall be tested, so that every joint or pipe in the building (except the uppermost ten (10) feet of the system) shall be submitted to a test of at least a ten (10) foot head of water. The water shall be kept in the system or in the portion being tested for at least 15 minutes before inspection starts; and inspection or testing of the system shall confirm that the system is tight at all points.
c) Air test. An air test shall be made by attaching an air compressor testing apparatus to any suitable opening and after closing all other inlets and outlets to the system, forcing air into the system until there is a uniform gauge pressure of five (5) pounds per square inch (p.s.i.) or sufficient to balance a column of mercury ten (10) inches in height. This pressure shall be held without introduction of additional air for a period of at least fifteen (15) minutes.
d) Water Supply System. Upon completion of a section, or the entire water supply system, the system shall be tested and proved tight under a water pressure at least one and one-half (1 ½) times the system pressure but at least 100 p.s.i., by air or water. When exceeding 100 p.s.i., the test shall be of the hydrostatic type only. Testing pressure shall be maintained for 15 minutes. The water used for this test shall be from a potable water supply.
e) Finished Plumbing. After the plumbing fixtures have been set and their traps filled with water, their connections shall be tested and proved gas and watertight. The test for gas and water tightness of the completed drainage and vent system shall be made by filling all traps with water, and then introducing into the system a pungent, thick smoke produced by one or more smoke machines. When the smoke appears at stack openings on the roof, the stack opening shall be closed and a pressure equivalent to a one (1) inch water column shall be maintained for the period of the inspection. Where the Department or local plumbing inspector finds that a smoke test cannot be performed, a peppermint test may be substituted. A peppermint test is conducted by introducing two (2) ounces of oil of peppermint into the roof terminal of every line or stack to be tested. Immediately after the oil of peppermint is introduced into the system, ten (10) quarts of hot (160 degrees F.) water shall be added, and each terminal sealed. The detection of the odor of peppermint at any trap or at any other point in the plumbing system denotes a leak. Individuals whose body or clothing have come in contact with oil of peppermint shall be excluded from the area until the test is completed.
f) Building Sewer. The building sewer shall be tested by insertion of a test plug at the point of connection with the public sewer. The building sewer shall be filled with water under a head of at least ten (10) feet of water. The water level at the top of the water column shall not drop for at least 15 minutes.
Section 890.1940 General Administration
The plans and specifications for a plumbing system whose design does not comply with this Part must be submitted to the Department for approval prior to installation of such a plumbing system. Such approval shall be in writing from the Department and shall be based on a determination that the system is expected to perform and exhibit durability as if meeting the requirements of this Part.
Section 890.1950 Violations
a) Notice of Violation
1) Violators of this Part shall be informed of any violation at the time of inspection, followed by a formal notice in writing, including a deadline date for correction of the violation(s).
2) Factors to be considered in establishing deadline dates for correction shall include the nature and complexity of the violation, the stage of construction, the type of violation involved, the weather, and whether or not the violation represents a potential or immediate health hazard.
b) Reinspection. Upon receipt of information from the violator indicating correction of violations or upon expiration of the established deadline date, a reinspection shall be made.
Section 890.APPENDIX A Plumbing Materials, Equipment, Use Restrictions and Applicable Standards
Abbreviations used in Appendix A.Table A refer to the following agencies or organizations:
1) ANSI – American National Standards Institute;
1819 L Street, N.W., 11th Floor, Washington DC 20036.
2) ASHRAE – American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc.;
1791 Tullie Circle, NE, Atlanta, Georgia 30329.
3) ASME – American Society of Mechanical Engineers;
Three Park Avenue, New York, New York 10016-5990.
4) ASPE – American Society of Plumbing Engineers;
6400 Shafer Ct, Suite 350, Rosemont IL 60018.
5) ASSE – American Society of Sanitary Engineering;
18927 Hickory Creek Drive, Suite 220, Mokena IL 60448..
6) ASTM – American Society for Testing and Materials;
100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, Pennsylvania 19428.
7) AWWA – American Water Works Association;
6666 West Quincy Avenue, Denver, Colorado 80235.
8) CISPI – Cast Iron Soil Pipe Institute;
1064 Delaware Avenue SE, Atlanta, Georgia 30316.
9) FM – Factory Mutual Approvals;
1151 Boston-Providence Turnpike,
P.O. Box 9102, Norwood, Massachusetts 02062.
10) NSF (National Sanitation Foundation) International;
789 N. Dixboro Road, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48113.
11) PDI – Plumbing and Drainage Institute;
800 Turnpike Street, Suite 300, North Andover, Massachusetts 01845.
12) UL – Underwriters Laboratories, Inc.;
333 Pfingsten Road, Northbrook, Illinois 60062-2096.
Approved Certification Agencies
1) ASSE – American Society of Sanitary Engineering;
901 Canterbury Road, Suite A, Westlake, Ohio 44145.
2) CSA (Canadian Standards Association) International;
8501 E. Pleasant Valley Road, Cleveland, Ohio 44131-5575.
3) IAPMO – International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials;
4755 E. Philadelphia Street, Ontario, California 91761.
4) ICC − International Code Council;
500 New Jersey Avenue NW, 6th Floor, Washington DC 20001.
5) NSF (National Sanitation Foundation) International;
789 N. Dixboro Road, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48113.
6) PDI − Plumbing and Drainage Institute;
800 Turnpike Street, Suite 300, North Andover, Massachusetts 01845.
7) Truesdail Laboratories, Inc.;
14201 Franklin Avenue, Tustin, California 92780-7008.
8) UL – Underwriters Laboratories, Inc.; 333 Pfingsten Road, Northbrook, Illinois 60062-2096.
(Source: Amended at 38 Ill. Reg. 9940, effective April 24, 2014)
Section 890.APPENDIX A Plumbing Materials, Equipment, Use Restrictions and Applicable Standards
Section 890.TABLE A Approved Materials and Standards
All materials shall meet at least one of the approved standards listed.
Approved Building Drainage/Vent Pipe
|
1) |
Acrylonitrite Butadiene Styrene (ABS) Pipe |
ASTM D 2661-2011 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM F 628-2012 |
|
|
|
CSA B181.1-2011 in B1800 |
||
|
|
Joints |
ASTM D 2235-2011 |
|
|
|
CSA B602-2010 |
||
|
|
Solvent Cement1 |
ASTM D 2235-2011 ASTM D 3138-2011 |
|
|
|
CSA B181.1-2011 in B1800 |
||
|
|
|
||
|
2) |
Brass Pipe |
ASTM B 43-2009 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3) |
Cast Iron Pipe |
ASTM A 74-2009 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM A 888-2011 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM C 564-2012 |
|
|
|
|
CISPI 301-2009 |
|
|
|
CSA B70-2012 FM 1680-1989 |
||
|
|
|
||
|
4) |
Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC) (Pipe and Fittings for Chemical Waste Drainage Systems) |
ASTM F2618-2009 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
5) |
Copper/Copper Alloy Pipe |
ASTM B 42-2010 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM B 302-2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6) |
Copper/Copper Alloy Tubing |
ASTM B 75/B75M-2011 |
|
|
|
(K-L-M or DWV)2 |
ASTM B 88-2009 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM B 251-2010 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM B 306-2009 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7) |
Galvanized Steel Pipe2 |
ASTM A 53/A53M-2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8) |
Glass Fiber Borosilicate Pipe3 |
ASTM C 1053-2010 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9) |
High Silicon Content Cast Iron Pipe3 |
ASTM A 377-2008e1 |
|
|
|
CSA B70-2012 |
||
|
|
|
||
|
10) |
Polypropylene Pipe3 |
|
|
|
|
CSA B137.1-2009 in B137 |
||
|
|
|
||
|
11) |
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Pipe and Fittings |
ASTM D 2665-2012 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM D 2949-2010 |
|
|
|
CSA B137.2-2009 in B137 |
||
|
|
CSA B181.2-2011 in B1800 |
||
|
|
|
||
|
12) |
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Pipe with Cellular Core4 |
ASTM F891-2010 ASTM F1760-2011 |
|
|
|
Joints |
ASTM D 2855-2010 |
|
|
|
Primer |
ASTM F 656-2010 |
|
|
|
Solvent Cement1 |
ASTM D 2564-2012 ASTM D 3138-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13) |
Polyvinylidene Fluoride3 |
ASTM D 3222-2010 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14) |
Solder |
ASTM B 32-2008 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15) |
Stainless Steel – types 304 and 316L |
ASME A112.3.1-2007 (R2012) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16) |
Stainless Steel Buttweld Fittings |
ASTM A 403/A 403M-2012 ASTM A 774/A 774M-2009 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17) |
Stainless Steel Flanges |
ASTM A 2400/A 240M-2012a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18) |
Identification of Piping Systems |
ASME A13.1-2007 |
|
Agency Notes:
1 Solvent cement must be handled in accordance with ASTM F 402-1993.
2 Type M copper tubing, DWV copper tubing, and galvanized steel pipe are approved for above-ground uses only.
3 Approved for corrosive waste or corrosive soil conditions.
4 PVC pipe with cellular core is approved only for gravity drainage and venting.
5 ASME B.1.20.1-1983
Approved Materials for Building Sewer
|
1) |
Acrylonitrite Butadiene Styrene (ABS) Pipe |
ASTM D 2661-2011 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM D 2751-2005 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM F 628-2012 |
|
|
|
|
CSA B181.1-2011 in B1800 |
|
|
|
Joints |
ASTM D 2235-2011 |
|
|
|
|
CSA B602-2010 |
|
|
|
Solvent Cement1 |
ASTM D 2235-2011 ASTM D 3138-2011 |
|
|
|
CSA B181.1-2011 in B1800 |
||
|
|
|
||
|
2) |
Asbestos Cement Pipe |
ASTM C 428/C 428M-2011e1 |
|
|
|
|
CSA B127.1-1999 (R2009) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3) |
Cast Iron Soil Pipe/Fittings |
ASTM A 74-2009 |
|
|
|
CSA B70-2012 |
||
|
|
Hubless Soil Pipe |
CISPI 301-2009 |
|
|
|
|
CISPI 310-2011 |
|
|
|
CSA B70-2012 FM 1680-1989 |
||
|
|
Rubber Gaskets |
ASTM C 564-2012 ASTM D 4161-2010 |
|
|
|
|
CSA B70-2012 |
|
|
|
|
CSA B602-2010 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4) |
Copper/Copper Alloy Tubing |
ASTM B 88-2009 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5) |
Concrete Pipe |
ASTM C 14-2011 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM C 76-2013 ASTM C 443-2012 |
|
|
|
CSA B602-2010 |
||
|
|
|
||
|
6) |
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Pipe |
ASTM D 3350-2012 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
7) |
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Pipe |
ASTM F 1866-2007 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM D 2665-2012 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM D 2949-2010 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM D 3034-2008 |
|
|
|
CSA B182.1-2011 in B1800 |
||
|
|
|
CSA B182.2-2011 in B1800 |
|
|
|
|
CSA B182.4-2011 in B1800 |
|
|
|
|
CSA B181.2-2011 in B1800 |
|
|
|
Joints |
ASTM D 2855-2010 ASTM D 3212-2013 |
|
|
|
CSA B602-2010 |
||
|
|
Primer |
ASTM F 656-2010 |
|
|
|
Solvent Cement1 |
ASTM D 2564-2012 ASTM D 3138-2011 |
|
|
|
CSA B181.2-2011 in B1800 |
||
|
|
|
||
|
8) |
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Pipe with Cellular Core2 |
ASTM F 891-2010 |
|
|
|
Joints |
ASTM D 2855-2010 ASTM D 412-2006ae2 |
|
|
|
Primer |
ASTM F 656-2010 |
|
|
|
Solvent Cement1 |
ASTM D 2564-2012 ASTM D 3138-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9) |
Solder |
ASTM B 32-2008 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10) |
Vitrified Clay Pipe2 |
ASTM C 4-2009 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM C 700-2013 ASTM C 425-2009 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11) |
Polypropylene Pipe2 |
ASTM F 2389-2010 AWWA C901-2008 AWWA C906-2012 (Material Code PE3408)3 (Material Codes PE2406 and PE3406)4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12) |
Identification of Piping Systems |
ASME A13.1-2007 |
|
Agency Notes:
1 Solvent cement must be handled in accordance with ASTM F 402-1988.
2 PVC pipe with cellular core and vitrified clay pipe are approved only for gravity drainage.
3 Dimension Ratio (DR) 17 or less.
4 Dimension Ratio (DR) 13.5 or less.
Approved Materials for Water Service Pipe
|
1) |
Acrylonitrite Butadiene Styrene (ABS) Pipe2 |
ASTM D 1527-2005 |
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Joints |
ASTM D 2235-2011 |
||
|
|
Solvent Cement1 |
ASTM D 2235-2011 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2) |
Brass Pipe2 |
ASTM B 43-2009 |
||
|
|
|
|||
|
3) |
Cast Iron (ductile iron)2 |
ASTM A 377-2008e1 |
||
|
|
Water Pipe |
CSA B70-2012 AWWA C151-2009 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4) |
Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC) Pipe2 |
ASTM D 2846/D 2846M-2009be1 |
||
|
|
|
ASTM F 441/F 441M-2012 |
||
|
|
|
ASTM F 442/F 442M-2012 |
||
|
|
CSA B137.6-2009 in B137 |
|||
|
|
Joints |
ASTM D 2846/D 2846M-2009be1 |
||
|
|
|
CSA B137.6-2009 in B137 |
||
|
|
Solvent Cement1 |
ASTM F 493-2010 |
||
|
|
|
CSA B137.6-2009 in B137 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5) |
Copper/Copper Alloy Pipe2, 3 |
ASTM B 42-2010 |
||
|
|
|
ASTM B 302-2012 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6) |
Copper/Copper Alloy Tubing2,3 |
ASTM B 88-2009 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7) |
Galvanized Steel Pipe2 |
ASTM A 53/A 53M-2012 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8) |
Poly Butylene (PB) Pipe/Tubing2 |
CSA B137.8-2009 in B137 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9) |
Polyethylene (PE) Pipe2 |
ASTM D 2239-2012a AWWA C901-2008 AWWA C906-2012 (Material Code PE3408)4 (Material Codes PE2406 and PE3406)5 |
||
|
|
|
|||
|
10) |
Polyethylene (PE) Tubing2 |
ASTM D 2737-2012a |
||
|
|
CSA B137.1-2009 in B137 |
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
11) |
Polypropylene Pipe2 |
ASTM F 2389-2010 |
||
|
|
|
|||
|
12) |
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Pipe2 |
ASTM D 1785-2012 |
||
|
|
|
ASTM D 2241-2009 |
||
|
|
|
ASTM D 2672-2009 ASTM F 477-2010 AWWA C900-2007 |
||
|
|
CSA B137.3-2009 in B137 |
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Joints |
ASTM D 2855-2010 ASTM D 3139-2011 |
||
|
|
CSA B137.2-2009 in B137 |
|||
|
|
CSA B137.3-2009 in B137 |
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Primer |
ASTM F 656-2010 |
||
|
|
Solvent Cement1 |
ASTM D 2564-2012 |
||
|
|
|
CSA B137.3-2009 in B137 |
||
|
|
|
|||
|
13) |
Stainless Steel Pipe2 |
ASTM A 312/A 312M-2012a ASTM A 403/A 403M-2012 ASTM A 511/A 511M-2012 |
||
|
|
|
|||
|
142) |
Welded Copper Water Tube2 |
ASME B31.1-2012 ASTM B 447-2012a WK and WL |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15) |
Solder |
ASTM B 32-2008 |
||
Agency Notes:
1 Solvent cement must be handled in accordance with ASTM F 402-1988.
2 Water service pipe must meet the appropriate NSF standard for potable water.
3 Type K or L copper may be installed underground.
4 Dimension Ratio (DR) 17 or less.
5 Dimension Ratio (DR) 13.5 or less.
6 ASME B.1.20.1-1983.
Approved Materials for Water Distribution Pipe
|
1) |
Brass Pipe2 |
ASTM B 43-2009 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
2) |
Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride2 (CPVC) Pipe/Tubing |
ASTM D 2846/D 2846M-2009be1 |
|||
|
|
ASTM F 441/F 441M-2012 |
||||
|
|
|
ASTM F 442/F 442M-2012 |
|||
|
|
CSA B137.6-2009 in B137 |
||||
|
|
Joints |
ASTM D 2846/D 2846M-2009be1 |
|||
|
|
CSA B137.6-2009 in B137 |
||||
|
|
Solvent Cement1 |
ASTM F 493-2010 |
|||
|
|
|
CSA B137.6-2009 in B137 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
3) |
Copper/Copper Alloy Pipe2 |
ASTM B 42-2010 |
|||
|
|
|
ASTM B 302-2012 AWWA C606-2011 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
4) |
Copper/Copper Alloy Tubing2 |
ASTM B 88-2009 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
5) |
Cross Linked Polyethylene2 |
ASTM F 876-2013a |
|||
|
|
Distribution Systems
Joints |
ASTM F 877-2011a ASTM F 1807-2012 ASTM F 1960-2012 ASTM F 2080-2012 ASTM F 2098-2008 ASTM F 2159-2011 ASSE 1061-2011 |
|||
|
|
CSA B137.5-2009 in B137 |
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
6) |
Galvanized Steel Pipe2 |
ASTM A 53-2012 AWWA C606-2011 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
7) |
Poly Butylene (PB) Pipe/Tubing2 |
|
|||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
CSA B137.8-2009 in B137 |
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
8) |
Polypropylene Pipe2 |
ASTM F 2389-2010 |
|||
|
|
|
||||
|
9) |
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Pipe2, 3 |
ANSI/NEMA Z535.1-2006 (R2011) ASTM D 1785-2012 |
|||
|
|
|
ASTM D 2241-2009 |
|||
|
|
|
ASTM D 2672-2009 |
|||
|
|
|
CSA B137.3-2009 in B137 |
|||
|
|
Joints |
ASTM D 2855-2010 ASTM F 441/F 441M-2012 |
|||
|
|
|
CSA B137.2-2009 in B137 |
|||
|
|
|
CSA B137.3-2009 in B137 |
|||
|
|
Primer |
ASTM F 656-2010 |
|||
|
|
Solvent Cement1 |
ASTM D 2564-2012 |
|||
|
|
|
CSA B137.3-2009 in B137 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
10) |
Stainless Steel Pipe2 |
ASTM A 312/A 312M-2012 ASTM A 403/A 403M-2012 ASTM A 511/A 511M-2012 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
11) |
Welded Copper Water Tube2 |
ASTM B 447-2012a WK, WL and WM |
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
12) |
Solder |
ASTM B 32-2008 |
|||
Agency Notes:
1 Solvent cement must be handled in accordance with ASTM F 402-1988.
2 Water distribution pipe must meet the appropriate NSF standard for potable water. Plastic shall be rated at 160 psi at 73.4 degrees Fahrenheit.
3 Use for cold or tempered water only.
4 ASME B.1.20.1-1983.
5 Safety Color.
Approved Materials and Standards for
Plumbing Fixtures and Fixture Fittings
|
1) |
Bathtub Liners (plexiglass/ABS or acrylic/plastic) |
IAPMO/ANSI Z124.8-2013 |
|
|
|
|
|
2) |
Bathtubs, Plastic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CSA B45.5-2011/IAPMO Z124-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
3) |
Bidets |
ASME A112.19.2-2013/CSA B45.1-2013 |
|
|
|
|
|
4) |
Enameled Cast Iron and Enameled Steel Plumbing Fixtures |
ASME A112.19.1-2008/CSA B45.2-2008 |
|
|
|
|
|
5) |
Fittings: |
|
|
|
Plumbing Fixture Fittings (metering valves, faucets, etc.) |
ASME A112.18.1-2012/CSA B125.1-2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Suction Fittings for Use in Swimming Pools, Wading Pools, Spas, Hot Tubs and Whirlpool Bathtub Appliances |
ANSI/APSP 16-2011 CSA C22.2 No. 218.1-M1989 (R2011) CSA C22.2 No. 218.2-1993 (R2008) |
|
|
|
|
|
6) |
Floor Drains and Trench Drains |
ASME A112.6.3-2001 (R2007) |
|
|
CSA B79-2008 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
7) |
Flushometer Bowls |
ASME A112.19.2-2013/CSA B45.1-2013 |
|
|
CSA B125.3-2011 |
|
|
|
Flushometers |
ASSE 1037-1990 |
|
|
CSA B125.3-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8) |
Grease Interceptors |
ASME A112.14.3-2000 (R2004) |
|
|
|
|
|
9) |
Low Consumption (1.6 gpf) Water Closets1 |
ASME A112.19.2-2013/CSA B45.1-2013 ASME A112.19.14-2006 (R2-11) |
|
|
|
|
|
10) |
Plastic Lavatory |
|
|
|
CSA B45.5-2011/IAPMO Z124-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
11) |
Plastic Shower Receptors/Shower Stalls |
|
|
|
CSA B45.5-2011/IAPMO Z124-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
12) |
Plastic Water Closets Bowls/Tanks |
|
|
|
CSA B45.5-2011/IAPMO Z124-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
13) |
Plastic Urinals Fixtures |
CSA B45.5-2011/IAPMO Z124-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
14) |
Porcelain Enameled Formed Steel Plumbing Fixtures, including Bathtub Liners |
ASME A112.19.1-2008/CSA 45.2-2008 |
|
|
|
|
|
15) |
Stainless Steel Plumbing Fixtures (Residential) |
ASME A112.19.3-2008/CSA B45.4-2008 |
|
|
|
|
|
16) |
Vitreous China Plumbing Fixtures |
ASME A112.19.2-2013/CSA B45.1-2013 |
|
|
|
|
|
17) |
Vitreous China Nonwater Urinals |
ASME A112.19.19-2006 (R2011) |
|
|
|
|
|
18) |
Whirlpool Bathtub Appliances |
ASME A112.19.7-2012/CSA B45.10-2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 218.2-1993 (R2008) |
Agency Note:
The water pressure at each fixture installation shall meet the manufacturer's minimum recommended level for the fixture.
Approved Standards for Plumbing
Appliances/Appurtenances/Devices
|
1) |
Anti-Backflow Freezeless Wall Hydrants |
ASSE 1019-2011 |
|
|
ASME A112.18.1-2012/CSA B125.1-2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2) |
Anti-Scald Control Valve |
ASSE 1016-2011/ASME A112.1016-2011/CSA B125.16-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
3) |
Anti-siphon Self-Drain Frost Proof Sillcock |
ASSE 1019-2011 CSA B125.3-2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
4) |
Automatic Ice Making Equipment |
NSF/ANSI 12-2009 |
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 120-M1991 (R2008) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
5) |
Automatic Storage Type Water Heater Less Than 75,000 BTU/HR |
ANSI Z21.10.1-2009/CSA 4.1-2009 ASHRAE 90.1 2010 ASHRAE 90.2-2007 ANSI Z21.10.1a-2009/CSA 4.1a-2009 |
|
ANSI Z21.10.1b-2011/CSA 4.1b-2011 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
6) |
Back Water Valves |
ASME A112.14.1-2003 (R2012) |
|
|
CSA B181.1-2011 in B1800 |
|
|
|
CSA B181.2-2011 in B1800 |
|
|
|
CSA B182.1-2011 in B1800 |
|
|
|
CSA B70-2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
7) |
Circulating Tank, Instantaneous |
ANSI Z21.10.1-2009/CSA 4.1-2009 ANSI Z21.10.1a-2009/CSA 4.1a-2009 ANSI Z21.10.1b-2011/CSA 4.1b-2011 |
|
|
ANSI Z21.10.3-2011/CSA 4.3-2011 |
|
|
|
ANSI Z21.13-2010/CSA 4.9-2010 ANSI Z21.13a-2010/CSA 4.9a-2010 ANSI Z21.13b-2012/CSA 4.9b-2012 |
|
|
|
CSA B140.12-2003 (R2008) |
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 110-1994 (R2009) UL 499-2005 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8) |
Circulating Tank, Instantaneous, Automatic |
ANSI Z21.10.3-2011/CSA 4.3-2011 ANSI Z21.13-2010/CSA 4.9-2010 ANSI Z21.13a-2010/CSA 4.9a-2010 ANSI Z21.13b-2012/CSA 4.9b-2012 UL 174-2004 |
|
|
CSA 4.1-2011 |
|
|
|
|
CSA B140.12-2003 (R2008) |
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 110-1994 (R2009) |
|
|
|
|
|
9) |
Detergent/Chemical Feeders for Commercial Use |
ASSE 1055-2009 |
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 0-2010 |
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 0.4-2004 (R2009) |
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 68-1992 (R2008) |
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 142-M1987 (R2009) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10) |
Dishwashing Machine (Commercial) |
ASSE 1004-2008 ANSI Z83.21-2005/CSA C22.2 No. 168-2005 ANSI Z83.21a-2012/CSA C22.2 No. 168a-2012 |
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 0-2010 |
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 0.4-2004 (R2009) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
11) |
Dishwashing Machine (Residential) |
ASSE 1006-1986 (R1989) |
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 167-2008 |
|
|
|
|
|
12) |
Diverters for Residential – Anti-Siphon |
|
|
|
ASME 1112.18.1-2012/CSA B125.1-2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
13) |
Double Check Detector Assembly |
ASSE 1048-2011 |
|
|
CSA B64-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
14) |
Double Check With Atmospheric Vent |
ASSE 1012-2009 |
|
|
CSA B64-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
15) |
Double Check Valve Assembly |
ASSE 1015-2011 |
|
|
CSA B64-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
16) |
Drinking Fountains |
ASHRAE 18-2008 (R2013) UL 399-2008 ASME A112.19.2-2013/CSA 45.1-13 |
|
|
|
|
|
17) |
Drinking Water Treatment Units – Health Effects |
NSF/ANSI 53-2011a |
|
|
|
|
|
18) |
Drinking Water Treatment Units – Aesthetic Effects |
NSF/ANSI 42-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
19) |
Drinking Water Treatment Chemicals |
NSF/ANSI 60-2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
20) |
Dual Check Valve |
ASSE 1024-2004 |
|
|
CSA B64-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
21) |
Duel Check Valve (Carbonated Beverage) (Relief Port Required) |
ASSE 1022-2003 CSA B64-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
22) |
Food Waste Disposal (Commercial) |
ASSE 1009-1990 |
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 1-2010 |
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 68-1992 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
23) |
Food Waste Disposal (Residential) |
ASSE 1008-2006 |
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 0-2010 |
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 68-2008 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
24) |
Gas Water Heater Above 75,000 BTU |
ANSI Z21.10.3-2011/CSA 4.3-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
25) |
Gas Water Heater 75,000 BTU or Less |
ANSI Z21.10.1-2009/CSA 4.1-2009 ANSI Z21.10.1a-2009/CSA 4.1a-2009 |
|
|
ANSI Z21.10.1b-2011/CSA 4.1b-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
26) |
Gas Water Heater (Continuous Use) |
ANSI Z21.10.1-2009/CSA 4.1-2009 ANSI Z21.10.1a-2009/CSA 4.1a-2009 |
|
|
ANSI Z21.10.1b-2011/CSA 4.1b-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
27) |
Gas Water Heater – Space Heating |
ANSI Z21.10.1-2009/CSA 4.1-2009 ANSI Z21.10.1a-2009/CSA 4.1a-2009 |
|
|
ANSI Z21.10.1b-2011/CSA 4.1b-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
28) |
Grease Interceptors |
PDI-G 101-2010 ASME A112.14.3-2000 (R2004) |
|
|
|
|
|
29) |
Handheld Showers |
ASSE 1014-2005 ASSE 1016-2011/ASME A112.1016-2011/CSA B125.16-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
30) |
Home Laundry Equipment |
ASSE 1007-1986 (R1992) |
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 0-2010 |
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 0.4-2004 (R2009) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 169-1997 (R2012) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
31) |
Hot Water Dispensers-Electrical |
ASSE 1023-1979 |
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 64-2010 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
32) |
Hot Water Generating/Heat Recovery Equipment |
NSF/ANSI 5-2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
33) |
Ice Makers |
UL 563-2009 |
|
|
CSA B45-2008 |
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 0-2010 |
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 0.4-2004 (R2009) |
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 63-1993 (R2008) |
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 120-M1991 (R2008) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
34) |
Individual Pressure Balancing In-line valves for individuals fixture fittings |
ASSE 1066-1997 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35) |
Mixing Valves
Automatic Compensating Valves for Individual Shower and Tub/Shower Combinations |
ASSE 1016-2011/ASME
A112.1016-2011/CSA B125.16-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Temperature Actuated Mixing Valves for Hot Water Distribution |
ASSE 1017-2009
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Automatic Temperature Control Mixing Valves |
ASSE 1069-2005 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Water Temperature Limiting Devices |
ASSE 1070-2004 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mixing Valves for Plumbed Emergency Equipment |
ASSE 1071-2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
36) |
Oil Fired Water Heaters |
UL 732-2010 |
|
|
CSA B140.0-2003 (R2008) |
|
|
|
CSA B140.12-2003 (R2008) |
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 0-2010 |
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 3-M1988 (R2009) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
37) |
Pressure Relief Valve |
ANSI Z21.22-1999 (R2008)/CSA 4.4-M1999 (R2008) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ANSI Z21.22a-2000 (R2008)/CSA 4.4a-2000 (R2008) |
|
|
|
ANSI Z21.22b-2001 (R2008)/CSA 4.4b-2001 (R2008) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
38) |
Pressurized Flushing Device |
ASSE 1037-1990 |
|
|
|
|
|
39) |
Reduced Pressure Detector Assembly |
ASSE 1047-2011 |
|
|
CSA B64-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
40) |
Reduced Pressure Principle Backflow Preventer |
ASSE 1013-2011 |
|
|
CSA B64-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
41) |
Refuse Compactors/Compactor System |
NSF/ANSI 13-2012 |
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 0-2010 |
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 68-2008 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
42) |
Relief Valves For Hot Water System |
ANSI Z21.22-1999 (R2008)/CSA 4.1-M1999 (R2008) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ANSI Z21.22a-2000 (R2008)/CSA 4.4a-2000 (R2008) |
|
|
|
ANSI Z21.22b-2001 (R2008)/CSA 4.4b-2001 (R2008) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
43) |
Reverse Osmosis Drinking Water Treatment System |
NSF/ANSI 58-2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
44) |
Spray Type Dishwashing Machine for Commercial Use |
NSF/ANSI 3-2012 CSA C22.2 No. 0-2010 |
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 0.4-2004 (R2009) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ANSI Z83.21-2005/CSA C22.2 No. 168-2005 ANSI Z83.21a-2012/CSA C22.2 No. 168a-2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
45) |
Trap Seal Primer Valve |
ASSE 1018-2001 |
|
|
CSA B125.3-2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
46) |
Vacuum Breakers, Anti-siphon |
ASSE 1001-2008 |
|
|
CSA B64-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
47) |
Vacuum Breakers Hose Connection |
ASSE 1011-2004 |
|
|
CSA B64-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
48) |
Vacuum Breaker (Laboratory Faucet) |
ASSE 1035-2008 |
|
|
CSA B64-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
49) |
Vacuum Breakers Pressure Type |
ASSE 1020-2004 |
|
|
CSA B64-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
50) |
Vacuum Relief Valve |
ANSI Z21.22b-2001 (R2008) |
|
|
CSA B64-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
51) |
Vending Machine for Food/Beverage |
NSF/ANSI 25-2012 |
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 0-2010 |
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 120-M1991 (R2008) |
|
|
|
CSA C22.2 No. 128-1995 (R2009) ASSE 1002-2008 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
52) |
Water Closet Personal Hygiene Devices |
ASME A112.4.2-2009 |
|
|
|
|
|
53) |
Water Closet Tank Ballcock |
ASSE 1002-2008 CSA B64-2011 |
|
|
CSA B125.3-2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
54) |
Water Hammer Arresters |
ASSE 1010-2004 |
|
|
|
|
|
55) |
Water Heater Drain Valve |
ASME A121.18.1-2011/CSA B125.1-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
56) |
Water Pressure Reducing Valves (Domestic) |
ASSE 1003-2009 |
|
|
CSA B356-2010 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
57) |
Water Softener and Treatment Devices |
NSF/ANSI 44-2012 |
Approved Standards for Fittings
|
1) |
Cast Iron Threaded Drainage Fittings |
ASME B16.12-2009 |
|
|
|
|
|
2) |
Cast Copper Alloy Solder Pressure Fittings |
ASME B16.18-2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
3) |
Cast Copper Alloy Solder Drainage Fitting (DWV) |
ASME B16.23-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
4) |
Copper Fittings |
ASME B16.15-2011 |
|
|
|
ASME B16.51-2011 |
|
|
|
ASME B16.18-2012 |
|
|
|
ASME B16.22-2012 |
|
|
|
ASME B16.23-2011 |
|
|
|
ASME B16.26-2011 |
|
|
|
ASME B16.29-2012 |
|
|
|
NSF/ANSI 61-2012
|
|
5) |
Forged Steel Fittings, Socket, Welded, Threaded |
ASME B16.11-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
6) |
Gray Iron/Ductile Iron |
AWWA C 110-2009 |
|
|
|
AWWA C 151-2009 |
|
|
|
|
|
7) |
Malleable Iron |
ASME B 16.3-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
8) |
Plastic |
ASTM D 2466-2006 |
|
|
|
ASTM D 2467-2006 |
|
|
|
ASTM D 2564-2012 |
|
|
|
ASTM F409-2012 |
|
|
|
ASTM F438-2009 |
|
|
|
ASTM F439-2012 |
|
|
CSA B137.3-2009 in B137 |
|
|
|
CSA B181.2-2011 in B1800 |
|
|
|
CSA B182.1-2011 in B1800 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CSA B137.6-2009 in B137 |
|
|
|
CSA B137.6-1999 in B137 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
9) |
Plumbing Fixture Fittings (Metering valves, faucets, etc.) |
ASME A112.18.1-2012/CSA B125.1-2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
10) |
Steel |
ASME B 16.9-2012 |
|
|
|
ASME B 16.11-2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
11) |
Wrought Copper/Bronze Solder Pressure Fitting |
ASME B 16.22-2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
12) |
Wrought Copper and Wrought Copper Alloy Solder (Drainage Fittings) |
ASME B16.29-2012 |
|
ASME B16.22-2012 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
13) |
Wrought Steel Buttwelding Fittings |
ASME B16.9-2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
14) |
Wrought Steel Buttwelding Short Radius Ells |
ASME B16.9-2012 |
(Source: Amended at 38 Ill. Reg. 9940, effective April 24, 2014)
Section 890.APPENDIX A Plumbing Materials, Equipment, Use Restrictions and Applicable Standards
Section 890.TABLE B Minimum Number of Plumbing Fixtures
|
Type of Building |
|
All Facilities for Employee Use |
Single Dwelling or Unit of Multiple Dwelling; Condo. or Apartment; or Hotel/Motel Unit |
||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
Male |
Female |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Water closets (Fixtures per person) |
For 1-5 Total Employees See Section 890.810(b)(1) |
1 per dwelling or unit |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
1: |
1-15 |
1: |
1-15 |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
2: |
16-35 |
2: |
16-35 |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
3: |
36-55 |
3: |
36-55 |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
4: |
56-80 |
4: |
56-80 |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
5: |
81-110 |
5: |
81-110 |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
Over 110, add 1 fixture per restroom for each additional 40 males/females. |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
(See Footnote #1) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Urinals |
See footnote #2 |
See footnote #2 |
None |
||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Lavatories3 |
1: |
1-15 |
1: |
1-15 |
|
1 per dwelling or unit |
|||||||||
|
(Fixtures per person) |
2: |
16-35 |
2: |
16-35 |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
3: |
36-60 |
3: |
36-60 |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
Over 60, add 1 fixture per restroom for each additional 45 males/females. |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Bathtubs/Showers |
1 per 107 |
1 per 107 |
1 per dwelling or unit |
||||||||||||
|
|
(If Required) |
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Drinking fountains4 |
1 per 100 |
None |
|||||||||||||
|
(Fixtures per person) |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Other Fixtures5 |
None |
1 Double Kitchen Sink; or 1 Single Bowl − 24 inches x 21 inches x 6½ inches minimum 1 Laundry Tray or 1 Clothes Washer connection for each 10 units5 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
Type of Building |
Dormitories |
Assembly Places: Sports Arenas, Stadiums, Convention Halls, Etc. |
|||||
|
|
|||||||
|
|
Male |
Female |
Male |
Female |
|||
|
|
|||||||
|
Water Closet (Fixtures per person) |
1 per 10 |
1 per 8 |
1: |
1-100 |
2: |
1-100 |
|
|
Add 1 fixture for each additional 25 males over 10; and 1 for each additional 20 females over 8. |
2: |
101-200 |
3: |
101-150 |
|||
|
3: |
201-400 |
4: |
151-200 |
||||
|
4: |
400-800 |
5: |
201-300 |
||||
|
|
|
6: |
301-400 |
||||
|
|
|
7: |
401-500 |
||||
|
|
|
8: |
501-650 |
||||
|
|
|
9: |
651-800 |
||||
|
|
Over 800, add 1 fixture for each additional 700 males and 1 for each 150 females. See Footnote #1 |
||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
Urinals |
1 per 25 |
See Footnote #2 |
1: |
1-100 |
See Footnote #2 |
||
|
(Fixtures per person) |
Over 150, add 1 fixture for each 50 males added; over 400, add 1 for each 200 males added.2 |
2: |
101-200 |
||||
|
3: |
201-400 |
||||||
|
4: |
401-600 |
||||||
|
Over 600, add 1 fixture for each additional 250 persons. |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Lavatories3 |
1 per 12 |
1 per 12 |
1: |
1-200 |
1: |
1-200 |
|
|
(Fixtures per person) |
Over 12, add 1 fixture for each additional 20 males and 1 for each 15 females. |
2: |
201-400 |
2: |
201-400 |
||
|
3: |
401-750 |
3: |
401-750 |
||||
|
|
|
|
Over 750, add 1 fixture per restroom for each added 400 males/females. |
||||
|
|
|||||||
|
Bathtubs, Showers |
1 per 8 |
None |
|||||
|
(Fixtures per person) |
See Footnote #13. |
|
|
||||
Type of Building |
Dormitories |
Assembly Places: Sports Arenas, Stadiums, Convention Halls, Etc. |
|||||||
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
Male |
Female |
Male |
Female |
|||||
|
Drinking Fountains4 |
1 per 75 |
|
|
|||||
|
(Fixtures per person) |
|
|
1 per each set of male and female public restrooms (High-Low) |
|
||||
|
|
|
|||||||
|
Other Fixtures (Fixtures per person) |
1 service sink per floor |
1 service sink per floor |
|
|||||
Type of Building |
Assembly Places: Theaters, Auditoriums, Other Facilities for Spectator Events |
Mercantile Units, Malls, Stores, Etc. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Male |
Female |
Male |
Female |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Water Closet (Fixtures per person) |
1: |
1-100 |
2: |
1-100 |
|
1: |
1-100 |
1: |
1-50 |
|
|||||||||||||
|
2: |
101-200 |
3: |
101-150 |
|
2: |
101-200 |
2:
|
51-100
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
3: |
201-400 |
4: |
151-200 |
|
3: |
201-400 |
3: |
101-150 |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
4: |
401-800 |
5: |
201-300 |
|
4: |
401-800 |
4: |
151-250 |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
6: |
301-400 |
|
|
|
5: |
251-350 |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
7: |
401-500 |
|
|
|
6: |
351-500 |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
8: |
501-650 |
|
|
|
7: |
501-650 |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
9: |
651-800 |
|
|
8: |
651-800 |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
Over 800, add 1 fixture for each additional 400 males and 1 for each 150 females. See Footnote #1 |
Over 800, add 1 fixture for each additional 500 males and 1 for each 150 females. See Footnote #1 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Urinals (Fixtures per person) |
1: |
1-100 |
See Footnote #2 |
|
1: |
51-200 |
See Footnote #2 |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
2: |
101-200 |
|
2: |
201-400 |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
3: |
201-400 |
|
3: |
401-600 |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
4: |
401-600 |
|
4: |
601-800 |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
Over 600, add 1 fixture for each additional 300 males. |
Over 800, and 1 fixture for each additional 300. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lavatories3 (Fixtures per person) |
1: |
1-200 |
1:1-200 |
|
1: |
1-200 |
1: |
1-200 |
|
||||||||||||||
|
2: |
201-400 |
2:201-400 |
|
2: |
201-400 |
2: |
201-400 |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
3: |
401-750 |
3:401-750 |
|
3: |
401-750 |
3: |
401-750 |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
Over 750, add 1 fixture per restroom for each added 400 males/females. |
Over 750, add 1 fixture per restroom for each added 350 males/females. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Drinking Fountains4 (Fixtures per person) |
1: |
1-100 |
|
|
|
1: |
1-100 |
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
1 High-Low for each set of male and female restrooms. |
1 High-Low for each set of male and female restrooms. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Other Fixtures (Fixtures per person) |
1 service sink per floor |
1 service sink per floor |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Type of Building |
Worship Places and Funeral Homes |
Businesses Selling Motor Fuel to the Public10 |
|||||
|
|
|||||||
|
|
Male |
Female |
Male |
Female |
|||
|
|
(See Footnote #1) |
|
|
||||
|
|
|||||||
|
Water Closets (Fixtures per person) |
1 per 250 |
1 per 125 |
1 per station |
1 per station |
|||
|
|
|||||||
|
Urinals (Fixtures per person) |
1 per 250 |
See Footnote #2 |
None |
||||
|
|
|||||||
|
Lavatories3 (Fixtures per person) |
1 per 125 |
1 per 125 |
1 per station |
1 per station |
|||
|
|
|||||||
|
Other Fixtures (Fixtures per person) |
1 service sink |
1 service sink where public restrooms are required. |
|||||
Type of Building |
Office Buildings/Public Buildings |
Food Service Establishments, Pubs, Lounges, Nightclubs, and Places Serving Food or Liquid to be Consumed on the Premises8 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
Male |
Female |
|
Male |
Female |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Water Closet (Fixtures per person) |
1: |
1-15 |
1: |
1-15 |
|
1: |
1-100 |
1: |
1-50 |
|||
|
2: |
16-35 |
2: |
16-35 |
|
2: |
101-300 |
2: |
51-100 |
||||
|
3: |
36-55 |
3: |
36-55 |
|
|
|
3: |
101-150 |
||||
|
|
4: |
56-80 |
4: |
56-80 |
|
|
|
4: |
151-300 |
|||
|
|
5: |
81-110 |
5: |
81-110 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Over 110, add 1 fixture per restroom for each additional 50 males/females. See Footnote #1 |
|
Over 300, add 1 fixture for each additional 200 males and 1 fixture per each 100 females. See Footnotes #1. |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Urinals (Fixtures per person) |
See Footnote #2 |
|
1: |
1-150 |
See Footnote #2 |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Over 150, add 1 fixture for each added 150 males. |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Lavatories3 (Fixtures per person) |
1: |
1-15 |
1: |
1-15 |
|
1: |
1-100 |
1: |
1-100 |
|||
|
2: |
16-35 |
2: |
16-35 |
|
2: |
101-200 |
2: |
101-200 |
||||
|
3: |
36-60 |
3: |
36-60 |
|
3: |
201-400 |
3: |
201-400 |
||||
|
|
4: |
61-90 |
4: |
61-90 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
5: |
91-125 |
5: |
91-125 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Over 125, add 1 fixture per restroom for each additional 50 males/females. See Footnote #1 |
|
Over 400, add 1 fixture per restroom for each additional 200 males/females. See Footnotes #1 and #6 |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
Drinking Fountains4 (Fixtures per person) |
1 per 75
|
|
See Footnote #12 |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
Other Fixtures (Fixtures per person) |
1 service sink per floor on which restrooms are located |
|
1 service sink and 1 3-Compartment Sink as required by 77 Ill. Adm. Code 750 See Footnote #6 |
|
||||||||
Type of Building |
Schools-Student Use: Elementary |
Schools-Student Use: Secondary, Colleges, Universities, Adult Centers, Etc. |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
Male |
Female |
|
Male |
Female |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Water Closets (Fixtures per person) |
1: |
1-20 |
1: |
1-20 |
|
1 per 40 |
1 per 20 |
||||
|
2: |
21-50 |
2: |
21-50 |
|
See Footnote #1 |
||||||
|
|
Over 50, add 1 fixture per restroom for each additional 50 persons. See Footnote #1 |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Urinals (Fixtures per person) |
See Footnote #2 |
See Footnote #2 |
|
1 per 40 See Footnote #2 |
See Footnote #2 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Lavatories3 (Fixtures per person) |
1: |
1-25 |
1: |
1-25 |
|
1 per 40 |
1 per 40 |
||||
|
2: |
26-50 |
2: |
26-50 |
|
1 per exercise room |
||||||
|
|
Over 50, add 1 fixture per restroom for each additional 50 persons. See Footnote #1 |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
Drinking Fountains4 (Fixtures per person) |
1 per 75 |
|
1 per 75 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
Other Fixtures (Fixtures per person) |
1 service sink per floor and kitchen area. |
|
1 service sink per floor and kitchen area. |
||||||||
|
Type of Building |
Day Care, Nursery and Preschool Center Toddlers 16-36 Months Excludes Infants (0-15 Months) |
||||
|
|
|||||
|
|
Male |
Female |
|||
|
Water Closets (Fixtures per person) |
1: |
1-10 |
1: |
1-10 |
|
|
2: |
11-25 |
2: |
11-25 |
|
|
|
|
3: |
26-50 |
3: |
26-50 |
|
|
|
4: |
51-75 |
4: |
51-75 |
|
|
|
5: |
76-100 |
5: |
76-100 |
|
|
|
6: |
101-125 |
6: |
101-125 |
|
|
|
7: |
126-150 |
7: |
126-150 |
|
|
|
8: |
151-175 |
8: |
151-175 |
|
|
|
Over 175: Add a fixture per restroom for each additional 50 males/females. See Footnotes #1 and #11 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Urinals (Fixtures per person) |
See Footnote #2 |
See Footnote #2 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Lavatories3 (Fixtures per person) |
1: |
1-10 |
1: |
1-10 |
|
|
2: |
11-25 |
2: |
11-25 |
|
|
|
|
3: |
26-50 |
3: |
26-50 |
|
|
|
4: |
51-75 |
4: |
51-75 |
|
|
|
5: |
76-100 |
5: |
76-100 |
|
|
|
6: |
101-125 |
6: |
101-125 |
|
|
|
7: |
126-150 |
7: |
126-150 |
|
|
|
8: |
151-175 |
8: |
151-175 |
|
|
|
Over 175: Add a fixture per restroom for each additional 50 males/females. See Footnotes #1 and #11 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Drinking Fountains4 (Fixtures per person) |
1 per 75 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Other Fixtures |
1 service sink per facility and kitchen area. |
||||
Type of Building |
Hospital Individual Room |
Hospitals Ward Room |
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
Water Closets |
1 per room |
1 per 8 patients |
||
|
(Fixtures per person) |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
Urinals |
None |
None |
||
|
(Fixtures per person) |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
Lavatories3 |
1 per room |
1 per 8 patients |
||
|
(Fixtures per person) |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
Bathtubs, Showers |
1 per room |
1 per 8 patients |
||
|
(Fixtures per person) |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
Drinking Fountains4 |
None |
1 per 75 |
||
|
(Fixtures per person) |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
Other Fixtures |
1 service sink |
1 service sink |
||
|
(Fixtures per person) |
per floor |
per floor |
||
Type of Building |
Institutional – Other than Hospitals or Penal Institutions (on each floor) |
Penal Institutions For Prisoner Use Cell or Dormitories |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Male |
Female |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Water Closets |
1 per 25 |
1 per 20 |
1 per cell |
|
(Fixtures per person) |
|
|
1 per 8 in a dormitory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Urinals |
1 per 50 (#2) |
See Footnote #2 |
None |
|
(Fixtures per person) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lavatories3 |
1 per 10 |
1 per 10 |
1 per cell |
|
(Fixtures per person) |
|
|
1 per 8 prisoners in a dormitory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bathtubs, Showers |
1 per 8 |
1 per 8 |
1 per 8 prisoners |
|
(Fixtures per person) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Drinking Fountains4 |
1 per 75 |
1 per 75 prisoners |
|
|
(Fixtures per person) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other Fixtures |
1 service sink per floor |
1 service sink per floor |
|
|
(Fixtures per person) |
|
|
|
Instructions/Footnotes For Table B
The numbers of fixtures required for employees are included in the numbers shown in Table B for all building types/uses except Hospital Rooms, Penal Institutions, and Other Institutions. The entry in Table B entitled "All Facilities for Employee Use" shall be used to determine the minimum number of fixtures required for employees in hospitals, penal/other institutions, and all other buildings/facilities that do not appear in Table B.
Questions concerning the minimum numbers of fixtures required for building types not listed in Appendix A, Table B, shall be referred to the Department in writing prior to construction for a decision concerning the minimum numbers (and types) of plumbing fixtures required.
Footnotes:
1. The figures shown are the minimum number of fixtures required for the number of persons indicated or any fraction of that number. Based on the total occupant load determined, the number of fixtures shall be calculated assuming 50 percent of the occupants are male and 50percent are female. The total male/female occupants shall be calculated first; then the number of fixtures for each (males/females) shall be determined from the appropriate table.
2. Urinals may be substituted for water closets for males, not to exceed half of the required total number of water closets. Comparable fixtures for females may be substituted for water closets for females, not to exceed half of the required total number of water closets.
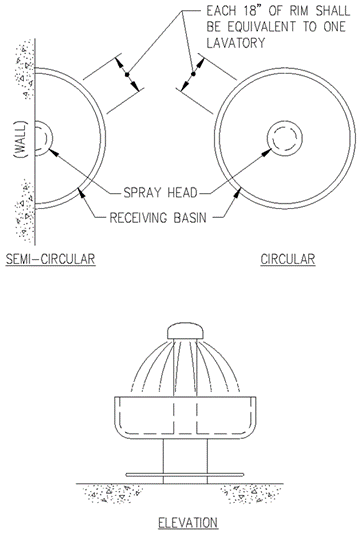
3. 18 lineal inches of wash sink or 18 inches of a circular basin, when provided with water outlets for space of this kind, shall be considered equivalent to one lavatory.
4. Whenever a drinking fountain is required by this Part, bottled drinking water or a water dispensing faucet (water station) may be substituted for a drinking fountain, provided drinking water is accessible to the public. When bottled drinking water is provided in lieu of a drinking fountain, the bottled water used must be commercially sealed in accordance with the Illinois Bottled Water Act and with the Illinois Safe Bottled Water Act.
5. The kitchen sink and laundry tray or connection for the washer are not required for the hotel/motel unit.
6. In addition to providing separate hand-washing facilities in the kitchen for employees, all food service establishments shall provide a minimum of one service/utility sink and one three-compartment sink to sanitize dishes and eating utensils; however, a mechanical dishwasher may be substituted for a three-compartment sink to sanitize dishes and utensils. (See 77 Ill. Adm. Code 750.)
7. Bathtubs/showers that are required for employees by OSHA requirements, collective bargaining agreements, etc., shall be provided at the rate of one per 10 employees.
8. Food Service Establishments with no more than 10 combined employees and seats (for patrons) at any one time need not provide public restrooms, provided that the employee restrooms are accessible and made available to the public.
9. Bed and Breakfast facilities with more than five sleeping rooms shall meet the minimum requirements of this Part for Hotel/Motel units. Bed and Breakfast facilities with five or fewer sleeping rooms, in compliance with the Bed and Breakfast Act, need not provide individual restrooms for each sleeping room.
10. Businesses that sell motor fuel but do not have any employees working as attendants are not required to provide public restrooms.
11. In Day Care Centers providing restroom training facilities for occupants ages three and younger where continuous adult supervision is provided, restrooms are not required to be separated into facilities for males and females, and are allowed to contain multiple lavatories and water closets as required by this Part. Public restrooms shall be required for everyone over the age of three separate from the restroom training facilities as required by this Part.
12. Drinking water shall be provided in accordance with Section 890.720(f).
13. The total number of bathing facilities shall include one bathtub for males and one bathtub for females or one individual user restroom with a bathtub.
(Source: Amended at 38 Ill. Reg. 9940, effective April 24, 2014)
Section 890.APPENDIX A Plumbing Materials, Equipment, Use Restrictions and Applicable Standards
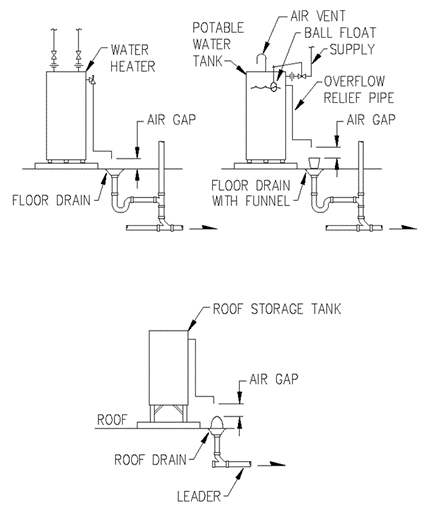
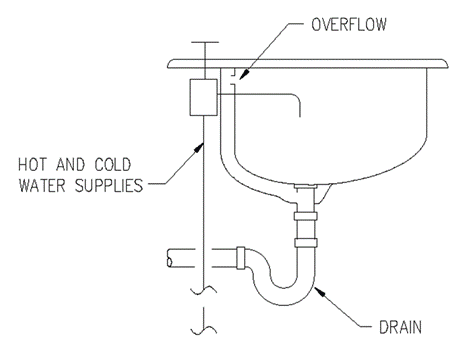
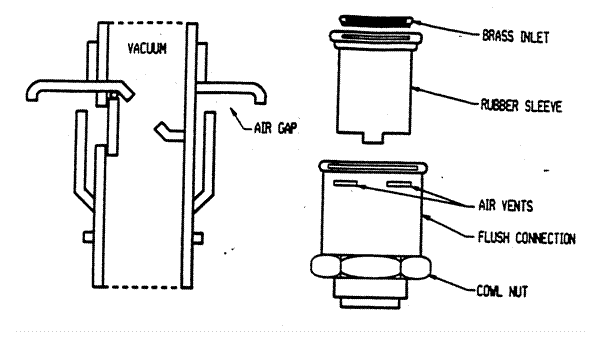
Section 890.TABLE C Minimum Air Gaps for Plumbing Fixtures
|
|
Minimum Air Gap (Inches) |
|
|
|
When Not Affected by Near Wall1 |
When Affected by Near Wall2 |
|
Lavoratories and other fixtures with effective opening not greater than ½ inch diameter. |
1 |
1½ |
|
Drinking water fountains, single orifice not greater than 7/16 (0.437) inch diameter or multiple orifices having total area of 0.150 square inches (area of circle 7/16 inch diameter). |
1 |
1½ |
|
Sink, laundry trays, goose neck bath faucets and other fixtures with effective opening not greater than one inch diameter. |
1½ |
2¼ |
|
Stills, sterilizers and other appliances, fixtures, devices and water and waste connections used for preparation of sterile material. |
2 |
3 |
|
Over rim bath fillers and other fixtures with effective openings not greater than one inch diameter. |
2 |
3 |
|
Effective openings greater than one inch. |
2 X Diameter of effective opening |
3 X Diameter of effective opening |
|
|
|
|
|
1 Side walls, ribs or other similar obstructions do not affect air gaps when spaced from inside edge of spout opening a distance greater than three times the diameter of the effective opening for a single wall, or a distance greater than four times the diameter of the effective opening for two intersecting walls. |
||
|
2 Vertical walls, ribs or similar obstructions extending from the water surface or to above the horizontal plane of the spout opening require a greater air gap when spaced closer to the nearest inside edge of spout opening than specified in Footnote 1 above. The effect of three or more such vertical walls or ribs has not been determined. In such cases, the air gap shall be measured from the top of the wall. |
||
Section 890.APPENDIX A Plumbing Materials, Equipment, Use Restrictions and Applicable Standards
Section 890.TABLE D Minimum Water Distribution Pipe Size
|
Type of Fixture or Device (See Footnotes 1 & 2) |
|
Pipe Size (inches) |
|
|
|
|
|
Bathtubs |
|
½ |
|
Combination sink and tray |
|
½ |
|
Drinking fountain |
|
⅜ |
|
Dishwasher (domestic) |
|
½ |
|
Dishwasher (commercial) |
|
¾ |
|
Kitchen sink (residential) |
|
½ |
|
Kitchen sink (commercial) 1 Faucet |
|
½ |
|
Kitchen sink (commercial) 2 Faucets |
|
¾ |
|
Lavatory |
|
⅜ |
|
Laundry tray (1, 2 or 3 compartment) |
|
½ |
|
Shower (single head) |
|
½ |
|
Sinks (service/slop) |
|
½ |
|
Sinks (flushing rim) |
|
¾ |
|
Urinal (flush tank) |
|
½ |
|
Urinal (direct flush valve) |
|
¾ |
|
Urinal (siphon jet) |
|
1 |
|
Washing machine (automatic) |
|
½ |
|
Water closet (tank type) |
|
⅜ |
|
Water closet (flush valve type) |
|
1 |
|
Hose bibbs |
|
½ |
|
Wall hydrant |
|
½ |
|
1 For fixtures not listed, the minimum supply branch shall be installed in the diameters required for similar type fixtures. |
||
|
2 The fixture supply pipe shall be extended to within 12 inches of the point of connection to fixture and be within the same area and physical space as the point of connection to the fixture. |
||
(Source: Amended at 38 Ill. Reg. 9940, effective April 24, 2014)
Section 890.APPENDIX A Plumbing Materials, Equipment, Use Restrictions and Applicable Standards
Section 890.TABLE E Drainage Fixture Units (D.F.U.) Per Fixture Group
|
Type of Fixture
|
D.F.U./Fixture (Load) |
Minimum Size of Trap2 (inches) |
|
|
|
|
|
Bathroom groups: 1 tank water closet, 1 lavatory with 1¼ inch trap and 1 bathtub1 or shower stall |
7 |
1¼ |
|
1 water closet with flush valve, 1 lavatory with 1¼ inch trap and 1 bathtub or shower1 |
11 |
|
|
Bathtub (with or without overhead shower)1 |
2 |
1½ |
|
Bathtub1 |
3 |
2 |
|
Bidet |
2 |
1½ |
|
Clothes washer, automatic |
3 |
2 |
|
Dental unit or cuspidor |
1 |
1¼ |
|
Drinking fountain |
½ |
1 |
|
Dishwasher2, domestic |
2 |
1½ |
|
Floor drains |
See Appendix A, Table F |
2 |
|
Lavatories: |
|
|
|
Lavatory |
1 |
1¼ |
|
Lavatory |
2 |
1½ |
|
Lavatory, barber, beauty parlor |
2 |
1½ |
|
Lavatory, dental |
1 |
1¼ |
|
Lavatory, surgeon's |
2 |
1½ |
|
Laundry tray (1 or 2 compartments) |
2 |
1½ |
|
Type of Fixture
|
D.F.U./Fixture (Load) |
Minimum Size of Trap2 (inches) |
|
|
|
|
|
Shower stall |
3 |
2 |
|
Showers (group) per head2 |
3 |
2 |
Sinks: |
|
|
|
Combination sink and tray |
3 |
1½ |
|
Combination sink and tray with food-disposal unit |
4 Separate Traps |
1½ |
|
Flushing rim (with valve) |
8 |
3 |
|
Kitchen sink, domestic |
2 |
1½ |
|
Kitchen sink, domestic, with food-waste grinder |
3 Separate Traps |
1½ |
|
Pot, scullery, etc.2 |
4 |
1½ |
|
Service (P trap) |
3 |
3 |
|
Service (P trap) |
2 |
2 |
|
Surgeon's |
3 |
1½ |
|
Wash sink2 (circular or multiple), each set of faucets |
2 |
1½ |
|
Urinals: |
|
|
|
Urinal, pedestal, siphon jet, blowout |
8 |
2 |
|
Urinal stall |
3 |
2 |
|
Urinal, wall integral trap |
3 |
2 |
|
Urinal, wall P trap, exposed |
2 |
1½ |
|
Water closets: |
|
|
|
Tank operated |
4 |
3 |
|
Valve-operated |
8 |
3 |
|
1A shower head over a bathtub does not increase the fixture value. |
||
|
2See Appendix A: Table F and Section 890.1330(b) for method of determining unit values of fixtures not listed in this Table or for rating of devices with intermittent flows. |
||
(Source: Amended at 28 Ill. Reg. 4215, effective February 18, 2004)
Section 890.APPENDIX A Plumbing Materials, Equipment, Use Restrictions and Applicable Standards
Section 890.TABLE F Fixtures Not Listed in Table E
|
Fixture Drain or Trap Size |
|
Drainage Fixture Unit Valve (D.F.U.) |
|
1¼ inches and smaller |
|
1 |
|
1½ inches |
|
2 |
|
2 inches |
|
3 |
|
2½ inches |
|
4 |
|
3 inches |
|
5 |
|
4 inches |
|
6 |
Section 890.APPENDIX A Plumbing Materials, Equipment, Use Restrictions and Applicable Standards
Section 890.TABLE G Building Drains
|
Diameter of Pipe (inches) |
|
Maximum Number of Drainage Fixture Units (D.F.U.) That May be Connected to Any Portion of the Building Drain |
|||
|
|
Grade per Foot |
||||
|
|
1/16 Inch |
⅛ Inch |
¼ Inch |
½ Inch |
|
|
4 |
|
− |
180 |
216 |
250 |
|
5 |
|
− |
390 |
480 |
575 |
|
6 |
|
− |
700 |
840 |
1,000 |
|
8 |
|
1,400 |
1,600 |
1,920 |
2,300 |
|
10 |
|
2,500 |
2,900 |
3,500 |
4,200 |
|
12 |
|
3,900 |
4,600 |
5,600 |
6,700 |
|
15 |
|
7,000 |
8,300 |
10,000 |
12,000 |
Section 890.APPENDIX A Plumbing Materials, Equipment, Use Restrictions and Applicable Standards
Section 890.TABLE H Horizontal Fixture Branches and Stacks
|
|
Maximum Number of Drainage Fixture Units (D.F.U.) That May be Connected to: |
|||
|
|
|
|
More than 3 Stories in Height |
|
|
Diameter of Pipe (inches) |
Any Horizontal Fixture Branch |
One Stack of 3 Stories in Height or 3 Intervals |
Total for Stack |
Total at One Story or Branch Interval |
|
1¼ |
1 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
|
1½ |
3 |
4 |
8 |
2 |
|
2 |
6 |
10 |
24 |
6 |
|
2½ |
12 |
20 |
42 |
9 |
|
3 |
201 |
302 |
602 |
161 |
|
4 |
100 |
240 |
500 |
90 |
|
5 |
360 |
540 |
1,100 |
200 |
|
6 |
620 |
960 |
1,900 |
350 |
|
8 |
1,400 |
2,200 |
3,600 |
600 |
|
10 |
2,500 |
3,800 |
5,600 |
1,500 |
|
12 |
3,900 |
6,000 |
8,400 |
1,500 |
|
15 |
7,000 |
− |
− |
− |
|
1 Not over two water closets. |
||||
|
2 Not over six water closets, or more than two per branch interval or per floor. |
||||
Section 890.APPENDIX A Plumbing Materials, Equipment, Use Restrictions and Applicable Standards
Section 890.TABLE I Allowed Distance from Fixture Trap to Vent
|
Size of Fixture Drains (Inches) |
|
Maximum Allowed Distance from Trap to Vent |
|
1¼ |
|
2 ft. 6 in. |
|
1½ |
|
3 ft. 6 in. |
|
2 |
|
4 ft. 0 in. |
|
3 |
|
5 ft. 0 in. |
|
4 and larger |
|
6 ft. 0 in. |
Section 890.APPENDIX A Plumbing Materials, Equipment, Use Restrictions and Applicable Standards
Section 890.TABLE J Size of Vent Stacks
|
Number of Bathroom Groups |
|
Diameter of Vent Stacks (Inches) |
|
1 or 2 |
|
2 |
|
3 to 9 |
|
3 |
|
10 to 16 |
|
4 |
Section 890.APPENDIX A Plumbing Materials, Equipment, Use Restrictions and Applicable Standards
Section 890.TABLE K Size and Length of Vents
|
Size of Soil or Waste Stack |
Fixture Units Connected |
Diameter of Vent Required (Inches) |
||||||||
|
1¼ |
1½ |
2 |
2½ |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
8 |
||
|
Maximum Length of Vent (Feet) |
||||||||||
|
1¼ |
2 |
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1½ |
8 |
50 |
150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1½ |
10 |
30 |
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
12 |
30 |
75 |
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
20 |
26 |
50 |
150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2½ |
42 |
|
30 |
100 |
300 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
10 |
|
30 |
100 |
200 |
600 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
30 |
|
|
60 |
200 |
500 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
60 |
|
|
50 |
60 |
400 |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
100 |
|
|
35 |
100 |
260 |
1,000 |
|
|
|
|
4 |
200 |
|
|
30 |
90 |
250 |
900 |
|
|
|
|
4 |
500 |
|
|
20 |
70 |
180 |
700 |
|
|
|
|
5 |
200 |
|
|
|
35 |
80 |
350 |
1,000 |
|
|
|
5 |
500 |
|
|
|
30 |
70 |
300 |
900 |
|
|
|
5 |
1,100 |
|
|
|
20 |
50 |
200 |
700 |
|
|
|
6 |
350 |
|
|
|
25 |
50 |
200 |
400 |
1,300 |
|
|
6 |
620 |
|
|
|
15 |
30 |
125 |
300 |
1,100 |
|
|
6 |
960 |
|
|
|
|
24 |
100 |
250 |
1,000 |
|
|
6 |
1,900 |
|
|
|
|
20 |
70 |
200 |
700 |
|
|
8 |
600 |
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
150 |
500 |
1,300 |
|
8 |
1,400 |
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
100 |
400 |
1,200 |
|
8 |
2,200 |
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
80 |
350 |
1,100 |
|
9 |
3,600 |
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
60 |
250 |
800 |
|
10 |
1,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
75 |
125 |
1,000 |
|
10 |
2,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
100 |
500 |
|
10 |
3,800 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
80 |
350 |
|
10 |
5,600 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
60 |
250 |
Agency Note: Per Section 890.1580(e), no more than 20 percent of the maximum developed length may be installed in the horizontal position. Vent piping serving floor drains shall be installed in such a manner as to minimize horizontal vent distances.
Section 890.APPENDIX A Plumbing Materials, Equipment, Use Restrictions and Applicable Standards
Section 890.TABLE L Horizontal Circuit and Loop Vent Sizing Table
|
Line |
Soil or waste pipe diam. (in.) |
Fixture Units (max. number |
Diameter of circuit or loop vent (in.) |
|||||
|
1½ |
2 |
2½ |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|||
|
Maximum Horizontal Length (ft.) |
||||||||
|
1 |
1½ |
10 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
2 |
12 |
15 |
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
2 |
20 |
10 |
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
3 |
10 |
|
20 |
40 |
100 |
|
|
|
5 |
3 |
30 |
|
|
40 |
100 |
|
|
|
6 |
3 |
60 |
|
|
16 |
80 |
|
|
|
7 |
4 |
100 |
|
7 |
20 |
52 |
200 |
|
|
8 |
4 |
200 |
|
6 |
18 |
50 |
180 |
|
|
9 |
4 |
500 |
|
|
14 |
36 |
140 |
|
|
10 |
5 |
200 |
|
|
|
16 |
70 |
200 |
|
11 |
5 |
1,100 |
|
|
|
10 |
40 |
140 |
Section 890.APPENDIX A Plumbing Materials, Equipment, Use Restrictions and Applicable Standards
Section 890.TABLE M Load Values Assigned to Fixtures
|
Fixture |
Occupancy |
Type of Supply Control |
Load Values in Water (Supply Fixture Units) |
||
|
Cold |
Hot |
Total |
|||
|
Water Closet |
Public/Private |
Flush Valve |
10 |
– |
10 |
|
Water Closet |
Public/Private |
Flush Tank |
3 |
– |
3 |
|
Urinal |
Public |
1" Flush Valve |
10 |
– |
10 |
|
Urinal |
Public |
¾" Flush Valve |
5 |
– |
5 |
|
Urinal |
Public |
Flush Tank |
3 |
– |
3 |
|
Lavatory |
Public |
Faucet |
1 |
1 |
2 |
|
Bathtub |
Public |
Faucet |
3 |
3 |
4 |
|
Shower Head |
Public |
Mixing Valve |
2 |
2 |
3 |
|
Service Sink |
Offices, etc. |
Faucet |
2 |
2 |
3 |
|
Kitchen Sink |
Hotel/Restaur. |
Faucet |
3 |
3 |
4 |
|
Drinking Fountain |
Office, etc. |
3/8" Valve |
0.25 |
– |
0.25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lavatory |
Private |
Faucet |
0.75 |
0.75 |
1 |
|
Bathtub |
Private |
Faucet |
1.5 |
1.5 |
2 |
|
Shower Stall |
Private |
Mixing Valve |
1 |
1 |
2 |
|
Kitchen Sink |
Private |
Faucet |
1.5 |
1.5 |
2 |
|
Laundry Trays (1 to 3) |
Private |
Faucet |
2 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dishwashing Machine |
Private |
Automatic |
|
-1 |
1 |
|
Laundry Machine (8 lb) |
Private |
Automatic |
1.5 |
1.5 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Laundry Machine (16 lb) |
Public/ General |
Automatic |
3 |
3 |
4 |
Agency Notes: For fixtures not listed, loads shall be assumed by comparing the fixtures to one listed using water in similar quantities and at similar rates. The assigned loads for fixtures with both cold and hot water supplies are given for separate cold and hot water loads and for total load.
Where a unit of local government or the community public water supply does not require separate water service lines for irrigation or similar systems that are likely to impose continuous demands (e.g., lawn sprinkler or air conditioning systems), the following rule applies: estimate the continuous demand (in gallons per minute) for outlets/systems separately from the intermittent demand from the fixtures listed in this table, and add this amount to the demand of the fixtures (in gallons per minute).
Fire sprinkler systems are exempt from this table.
(Source: Amended at 38 Ill. Reg. 9940, effective April 24, 2014)
Section 890.APPENDIX A Plumbing Materials, Equipment, Use Restrictions and Applicable Standards
Section 890.TABLE N Water Supply Fixture Units (WSFU) for a Supply System with Flush Tanks Water Closets
|
|
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
WSFU |
Demand (GPM) |
Pipe Size (Inches) |
Pressure Loss (PSI/100' of Pipe) |
Velocity (Ft./Sec.) |
Meter Size (Inches) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
2 |
½" |
4.2 |
2.7 |
⅝" |
|
4 |
3 |
½" |
8.7 |
4.2 |
⅝" |
|
6 |
5 |
½" |
22.5 |
7.0 |
⅝" |
|
8 |
6.5 |
¾" |
6.3 |
4.3 |
⅝" |
|
10 |
8 |
¾" |
9.0 |
5.4 |
¾" |
|
12 |
9.2 |
¾" |
11.5 |
6.1 |
¾" |
|
14 |
10.4 |
¾" |
15.0 |
6.9 |
¾" |
|
16 |
11.6 |
¾" |
18.0 |
7.7 |
¾" |
|
20 |
14 |
1" |
7.2 |
5.6 |
¾" |
|
25 |
17 |
1" |
10.0 |
6.6 |
¾" |
|
30 |
20 |
1" |
13.6 |
8.0 |
1" |
|
35 |
22.5 |
1¼" |
5.8 |
5.7 |
1" |
|
40 |
25 |
1¼" |
7.0 |
6.3 |
1" |
|
45 |
27 |
1¼" |
8.2 |
6.9 |
1" |
|
50 |
29 |
1¼" |
9.5 |
7.4 |
1" |
|
60 |
32 |
1½" |
5.0 |
5.8 |
1½" |
|
70 |
35 |
1½" |
6.2 |
6.4 |
1½" |
|
80 |
38 |
1½" |
7.0 |
7.2 |
1½" |
|
90 |
41 |
1½" |
8.0 |
7.5 |
1½" |
|
100 |
43.5 |
1½" |
8.7 |
7.8 |
2" |
|
120 |
48 |
2" |
2.7 |
5.0 |
2" |
|
140 |
52.5 |
2" |
3.1 |
5.4 |
2" |
|
160 |
57 |
2" |
3.6 |
5.8 |
2" |
|
180 |
61 |
2" |
3.9 |
6.1 |
2" |
|
200 |
65 |
2" |
4.5 |
6.6 |
2" |
|
225 |
70 |
2" |
5.2 |
7.1 |
2" |
|
250 |
75 |
2" |
6.0 |
7.7 |
3" |
|
275 |
80 |
2½" |
2.6 |
5.5 |
3" |
|
300 |
85 |
2½" |
2.9 |
5.8 |
3" |
|
350 |
95 |
2½" |
3.5 |
6.5 |
3" |
|
400 |
105 |
2½" |
4.2 |
7.1 |
3" |
|
450 |
115 |
2½" |
5.0 |
8.0 |
3" |
|
500 |
125 |
3" |
2.3 |
5.9 |
3" |
|
600 |
145 |
3" |
3.1 |
6.8 |
4" |
|
750 |
170 |
3" |
4.0 |
8.0 |
4" |
|
1000 |
208 |
4" |
1.5 |
5.7 |
4" |
|
1250 |
240 |
4" |
1.9 |
6.4 |
4" |
|
1500 |
267 |
4" |
2.3 |
7.0 |
4" |
|
1750 |
294 |
4" |
2.8 |
7.8 |
4" |
|
2000 |
320 |
6" |
0.36 |
3.7 |
6" |
|
|
|||||
|
Agency Notes: |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Where a unit of local government or the community public water supply does not require separate water service lines for irrigation or similar systems that are likely to impose continuous demands (e.g., lawn sprinkler or air conditioning systems), the following rule applies: estimate the continuous demand (in gallons per minute) for outlets/systems separately from the intermittent demand from the above fixtures, and add this amount to the demand of the fixtures (in gallons per minute). |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Meter and meter yoke sizes shown in this table shall apply only to those jurisdictions or governmental units where local ordinances or community public water supply requirements do not prescribe specific sizes of meters or meter yokes. Where local ordinances or community public water supply requirements cover sizing, those requirements shall be followed. |
|||||
(Source: Amended at 38 Ill. Reg. 9940, effective April 24, 2014)
Section 890.APPENDIX A Plumbing Materials, Equipment, Use Restrictions and Applicable Standards
Section 890.TABLE O Water Supply Fixture Units (WSFU) for a Supply System with Flushometer Water Closets
|
|
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
WSFU |
Demand (GPM) |
Pipe Size (Inches) |
Pressure Loss (PSI/100' of Pipe) |
Velocity (Ft./Sec.) |
Meter Size (Inches) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
27 |
1¼" |
8.3 |
6.8 |
¾" |
|
12 |
28.6 |
1¼" |
9.2 |
7.2 |
¾" |
|
14 |
30.2 |
1¼" |
10 |
7.9 |
¾" |
|
16 |
31.8 |
1¼" |
11 |
8.0 |
¾" |
|
20 |
35 |
1½" |
6.0 |
6.4 |
¾" |
|
25 |
38 |
1½" |
7.0 |
6.9 |
1" |
|
30 |
41 |
1½" |
8.0 |
7.4 |
1" |
|
35 |
43.8 |
1½" |
8.8 |
8.0 |
1" |
|
40 |
46.5 |
2" |
2.5 |
4.7 |
1" |
|
45 |
49 |
2" |
2.7 |
5.1 |
1" |
|
50 |
51.5 |
2" |
2.9 |
5.4 |
1½" |
|
60 |
55 |
2" |
3.4 |
5.8 |
1½" |
|
70 |
58.5 |
2" |
3.7 |
6.0 |
1½" |
|
80 |
62 |
2" |
4.0 |
6.2 |
1½" |
|
90 |
64.8 |
2" |
4.6 |
6.5 |
1½" |
|
100 |
67.5 |
2" |
5.0 |
6.8 |
1½" |
|
120 |
72.5 |
2" |
5.6 |
7.2 |
2" |
|
140 |
77.5 |
2" |
6.3 |
8.0 |
2" |
|
160 |
82.5 |
2½" |
2.7 |
5.7 |
2" |
|
180 |
87 |
2½" |
3.0 |
6.1 |
2" |
|
200 |
91.5 |
2½" |
3.4 |
6.4 |
2" |
|
225 |
97 |
2½" |
3.7 |
6.8 |
2" |
|
250 |
101 |
2½" |
4.0 |
7.1 |
3" |
|
275 |
106 |
2½" |
4.2 |
7.3 |
3" |
|
300 |
110 |
2½" |
4.6 |
7.6 |
3" |
|
350 |
119 |
3" |
2.1 |
5.5 |
3" |
|
400 |
126 |
3" |
2.3 |
5.9 |
3" |
|
450 |
138 |
3" |
2.7 |
6.3 |
3" |
|
500 |
145 |
3" |
3.0 |
6.8 |
3" |
|
600 |
160 |
3" |
3.6 |
7.4 |
4" |
|
750 |
178 |
4" |
1.1 |
4.7 |
4" |
|
1000 |
208 |
4" |
1.5 |
5.6 |
4" |
|
1250 |
240 |
4" |
1.9 |
6.4 |
4" |
|
1500 |
267 |
4" |
2.3 |
7.0 |
4" |
|
1750 |
294 |
4" |
2.8 |
7.8 |
4" |
|
2000 |
321 |
6" |
0.4 |
3.7 |
6" |
|
|
|||||
|
Agency Notes: |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Where a unit of local government or the community public water supply does not require separate water service lines for irrigation or similar systems that are likely to impose continuous demands (e.g., lawn sprinkler or air conditioning systems), the following rule applies: estimate the continuous demand (in gallons per minute) for outlets/systems separately from the intermittent demand from the above fixtures, and add this amount to the demand of the fixtures (in gallons per minute). |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Meter and meter yoke sizes shown in this table shall apply only to those jurisdictions or governmental units where local ordinances or community public water supply requirements do not prescribe specific sizes of meters or meter yokes. Where local ordinances or community public water supply requirements cover such sizing, those requirements shall be followed. |
|||||
(Source: Amended at 38 Ill. Reg. 9940, effective April 24, 2014)
Section 890.APPENDIX A Plumbing Materials, Equipment, Use Restrictions and Applicable Standards
Section 890.TABLE P Demand at Individual Water Outlets
Demand at Individual Water Outlets
|
Type of Outlet |
Demand (g.p.m.) |
|
Ordinary Lavatory Faucet |
2.0 |
|
Self Closing Lavatory Faucet |
2.5 |
|
Sink Faucet, ⅜" or ½" |
4.5 |
|
Sink Faucet, ¾" |
6.0 |
|
Bath Faucet, ½" |
5.0 |
|
Shower Head, ½" |
5.0 |
|
Laundry Faucet, ½" |
5.0 |
|
Ballcock in Water Closet Flush Tank |
3.0 |
|
1" Flush Valve (25 psi flow pressure) |
35.0 |
|
1" Flush Valve (15 psi flow pressure) |
27.0 |
|
¾" Flush Valve (15 psi flow pressure) |
15.0 |
|
Drinking Fountain Jet |
0.75 |
|
Dishwashing Machine (domestic) |
4.0 |
|
Laundry Machine (8 to 16 pounds) |
4.0 |
|
Aspirator (operating room or laboratory) |
2.5 |
(Source: Amended at 22 Ill. Reg. 21540, effective December 1, 1998)
Section 890.APPENDIX A Plumbing Materials, Equipment, Use Restrictions and Applicable Standards
Section 890.TABLE Q Allowance in Equivalent Length of Pipe for Friction Loss in Valves and Fittings
The following applies to all types of material approved for potable water distribution:
|
Equivalent Feet of Pipe for Various Pipe Sizes |
||||||||
|
Valve or Fitting |
½" |
¾" |
1" |
1¼" |
1½" |
2" |
2½" |
3" |
|
45º ell (wrought) |
0.5 |
0.5 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
3.0 |
4.0 |
|
90º ell (wrought) |
0.5 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
3.0 |
|
Tee, Run (wrought) |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
2.0 |
− |
|
Tee, Branch (wrought) |
1.0 |
2.0 |
3.0 |
4.0 |
5.0 |
7.0 |
9.0 |
− |
|
45º ell (cast) |
0.5 |
1.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
3.0 |
5.0 |
8.0 |
11.0 |
|
90º ell (cast) |
1.0 |
2.0 |
4.0 |
5.0 |
8.0 |
11.0 |
14.0 |
18.0 |
|
Tee, Run (cast) |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
1.5 |
1.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
|
Tee, Branch (cast) |
2.0 |
3.0 |
5.0 |
7.0 |
9.0 |
12.0 |
16.0 |
20.0 |
|
Compression Stop |
13.0 |
21.0 |
30.0 |
− |
− |
− |
− |
− |
|
Globe Valve |
− |
− |
− |
53.0 |
66.0 |
90.0 |
− |
− |
|
Gate Valve |
− |
− |
1.0 |
1.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
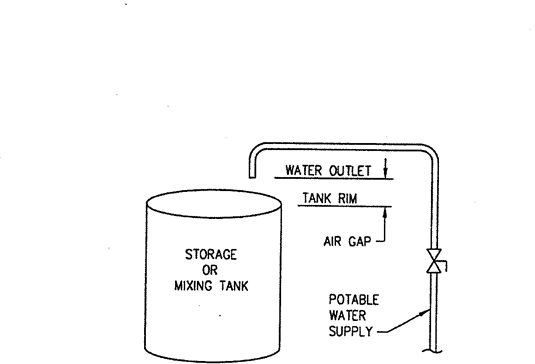 |
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION A Air Gap Drawing #1
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Air Gap.")
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION B Air Gap Drawing #2
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Air Gap.")
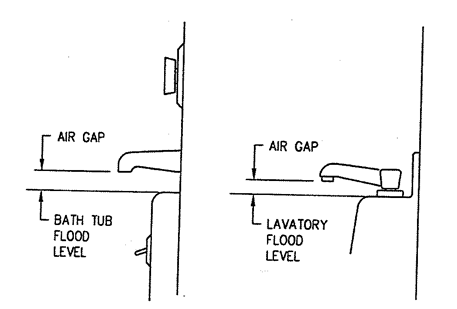 |
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION C Battery of Fixtures
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Battery of Fixtures.")

(Source: Amended at 38 Ill. Reg. 9940, effective April 24, 2014)
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION D Branch
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Branch.")
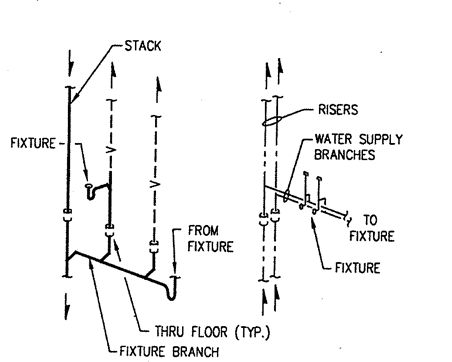 |
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION E Branch Vent
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of “Branch Vent.”)
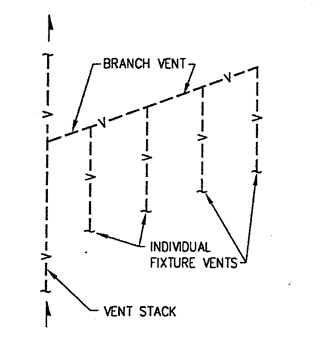 |
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION F Building Drain
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Building Drain.")
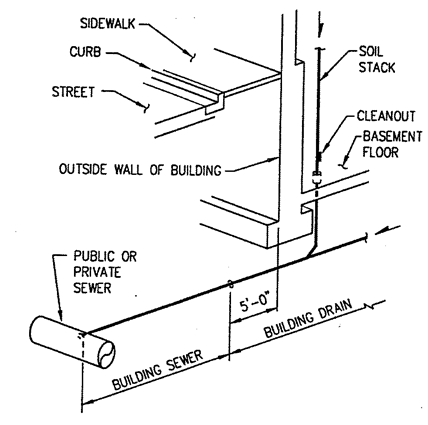 |
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION G Building Sub-Drain
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Building Sub-Drain.")

(Source: Amended at 38 Ill. Reg. 9940, effective April 24, 2014)
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION H Circuit Vent
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Circuit Vent.")
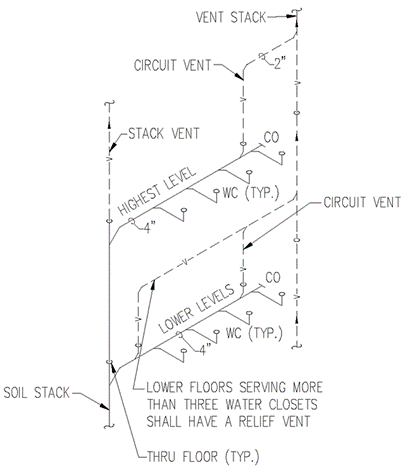
(Source: Amended at 38 Ill. Reg. 9940, effective April 24, 2014)
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION I Common Vent
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Common Vent.")

(Source: Amended at 38 Ill. Reg. 9940, effective April 24, 2014)
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION J Continuous Vent
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Continuous Vent.")
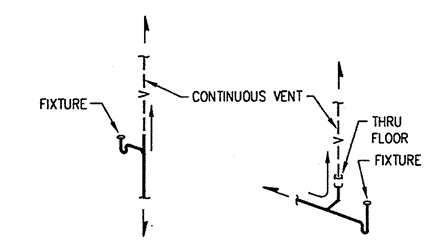 |
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION K Dead End
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Dead End.")
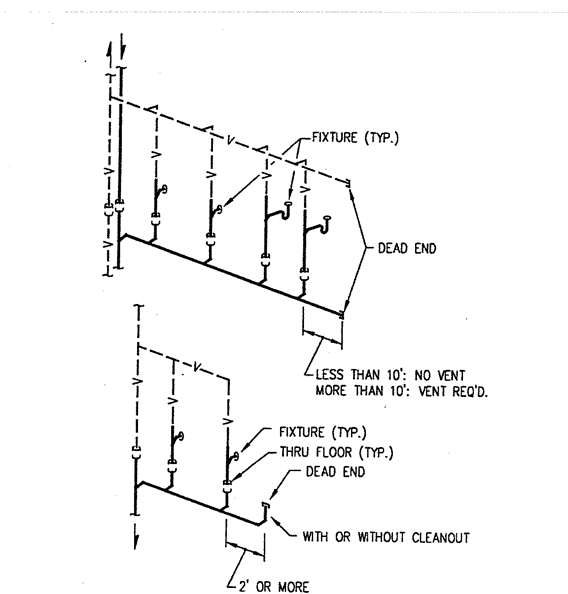 |
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION L Drain
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Drain.")
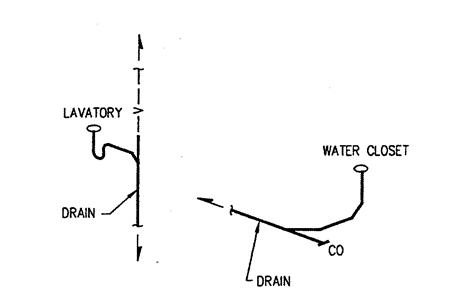 |
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION M Fixture Drain
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Fixture Drain.")
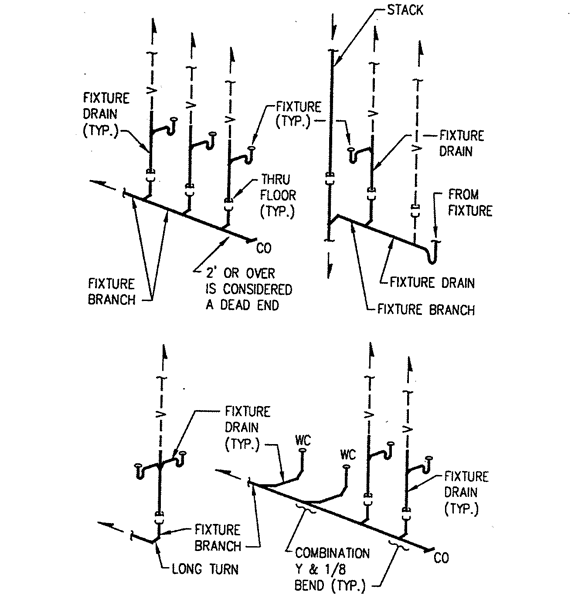 |
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION N Flush Valve (Repealed)
(Source: Repealed at 28 Ill. Reg. 4215, effective February 18, 2004)
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION O Grade
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Grade.")
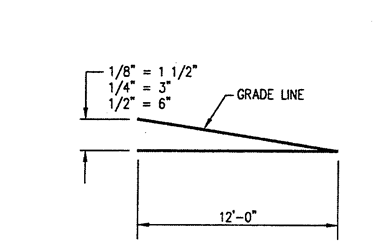 |
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION P Horizontal Branch
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Horizontal Branch.")
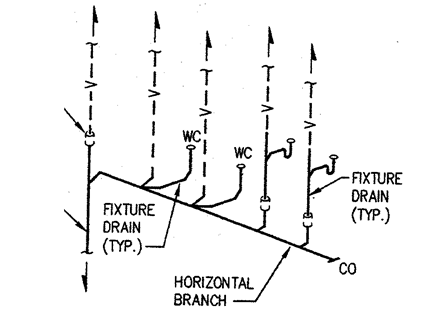 |
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION Q Main Vent
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Main Vent.")

(Source: Amended at 38 Ill. Reg. 9940, effective April 24, 2014)
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION R Quarter Bend (Repealed)
(Source: Repealed at 28 Ill. Reg. 4215, effective February 18, 2004)
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION S Relief Vent
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Relief Vent.")
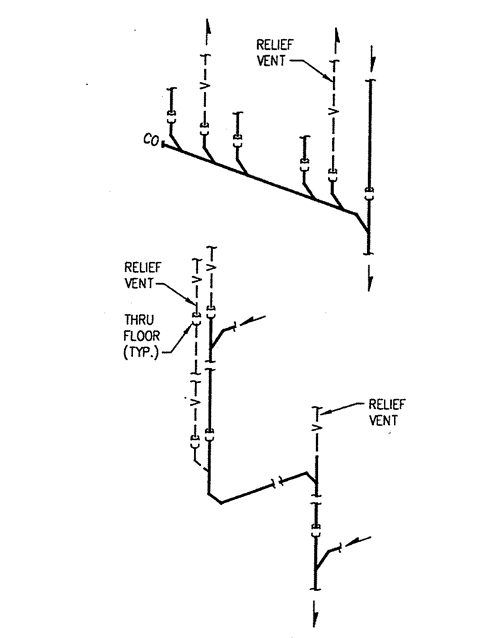 |
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION T Return Offset (Repealed)
(Source: Repealed at 28 Ill. Reg. 4215, effective February 18, 2004)
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION U Revent Pipe
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Revent Pipe.")
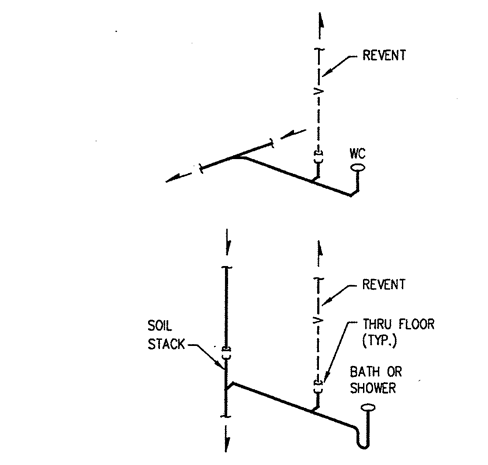
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION V Stack Vent
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Stack Vent.")
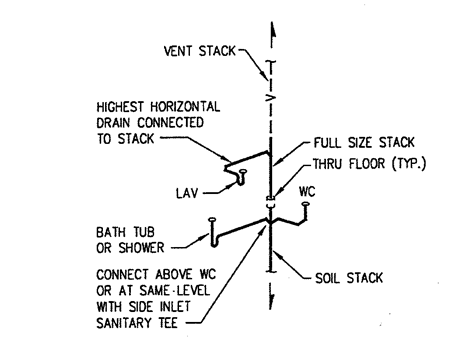 |
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION W Trap
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Trap.")
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Trap Seal.")
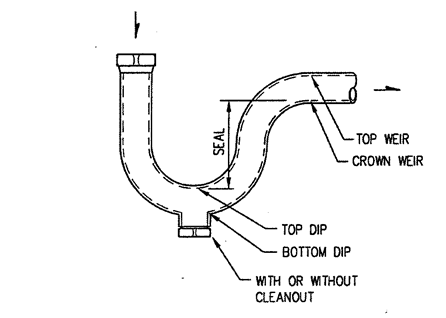 |
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION X Vent Stack (Repealed)
(Source: Repealed at 38 Ill. Reg. 9940, effective April 24, 2014)
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION Y Wet Vent
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Wet Vent.")

(Source: Amended at 38 Ill. Reg. 9940, effective April 24, 2014)
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION Z Yoke Vent
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Yoke Vent.")
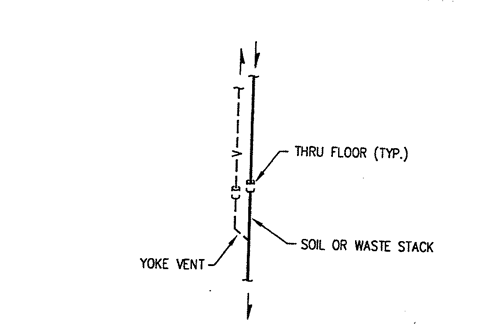 |
(Source: Amended at 38 Ill. Reg. 9940, effective April 24, 2014)
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION AA Sleeves
(Referenced in Section 890.180(c) and (d))
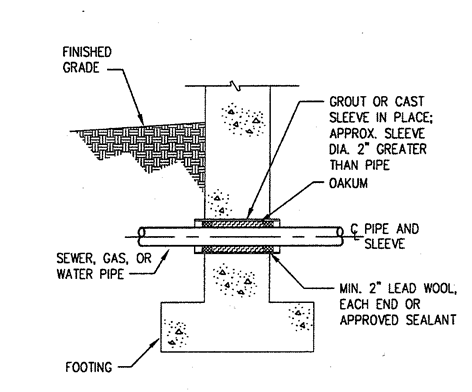
(Source: Amended at 38 Ill. Reg. 9940, effective April 24, 2014)
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION BB Buried Piping Parallel to Footing
(Referenced in Section 890.180(e) and (f))
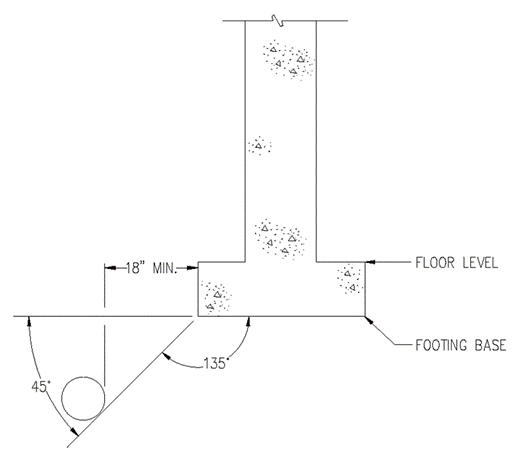
(Source: Added at 38 Ill. Reg. 9940, effective April 24, 2014)
Section 890.APPENDIX B Illustrations for Subpart A
Section 890.ILLUSTRATION CC Individual Dry Vent
(Referenced in Section 890.120, Definition of "Individual Dry Vent.")
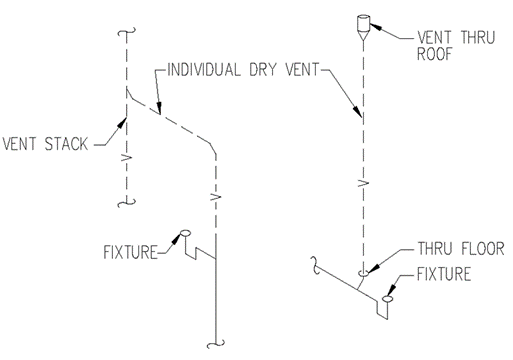
(Source: Added at 38 Ill. Reg. 9940, effective April 24, 2014)