Section 930.ILLUSTRATION A Slow Sand Filter Water Treatment Plant
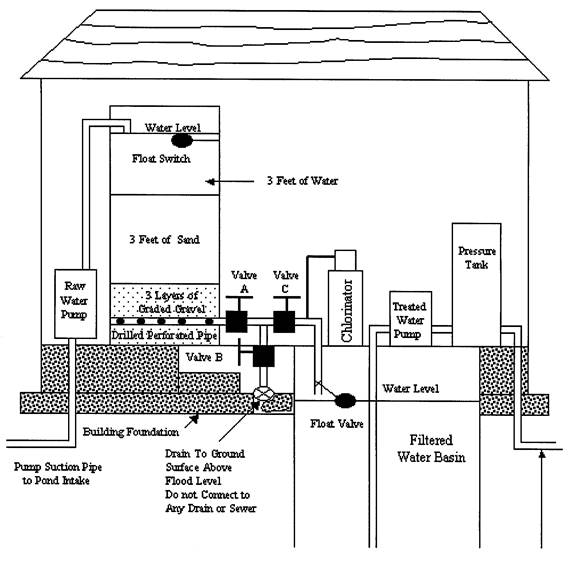
(Source: Amended at 27 Ill. Reg. 15998, effective October 1, 2003)
TITLE 77: PUBLIC HEALTH
|
AUTHORITY: Implementing and authorized by Section 9 of the Illinois Groundwater Protection Act [415 ILCS 55/9].
SOURCE: Adopted at 10 Ill. Reg. 11116, effective July 1, 1986; amended at 27 Ill. Reg. 15998, effective October 1, 2003.
Section 930.5 Applicability
The rules of this Part are promulgated by the Illinois Department of Public Health to implement Section 9 of the Illinois Groundwater Protection Act [415 ILCS 55]. These rules apply to private, semi-private and non-community public water systems obtaining water from a surface source of water and not regulated by the Illinois Environmental Protection Act or Illinois Environmental Protection Agency.
(Source: Amended at 27 Ill. Reg. 15998, effective October 1, 2003)
Section 930.10 Definitions
"Approved Certification Agency" means an organization that has been accredited by the American National Standards Institute and found to meet the requirements specified in ANSI Z 34.1 (1993), Third Party Certification Program to evaluate drinking water treatment units for compliance with ANSI/NSF Standard 42, ANSI/NSF Standard 53 and ANSI/NSF Standard 55.
"Effective size" means the size of screen opening where 90 percent by weight of a sample of filter media is retained on the screen and 10 percent passes through the screen.
"Intake" means a pipe or other means to withdraw raw water from the surface source.
"Non-Community Water System" means a public water system which is not a community water system, and has at least 15 service connections used by nonresidents, or regularly serves 25 or more nonresident individuals daily for at least 60 days per year.
"Private Water System" means a water system that serves an owner-occupied single family residence or dwelling.
"Public Water System" means a system for the provision to the public of piped water for human consumption, if the system has at least 15 service connections or serves an average of at least 25 individuals daily at least 60 days per year. The term Public Water System includes: any collection, treatment, storage and distribution facilities under control of the operator of the system and used primarily in connection with the system; and any collection or pretreatment storage facilities not under such control that are used primarily in connection with the system.
"Semi-Private Water System" means a water supply which is not a public water system, yet which serves a segment of the public other than an owner-occupied single family residence or dwelling.
"Surface source" means a supply of water which is taken from a reservoir (e.g, pond, lake, or stream).
"Uniformity coefficient" means a number obtained by dividing that size of sand in millimeters of which 60 percent by weight is smaller, by that size of sand in millimeters of which 10 percent by weight is smaller.
(Source: Amended at 27 Ill. Reg. 15998, effective October 1, 2003)
Section 930.15 Incorporated Materials
a) The following regulations and materials are incorporated or referenced in this Part:
1) Illinois Plumbing Code
(77 Ill. Adm. Code 890)
Illinois Department of Public Health
2) Illinois Water Well Construction Code
(77 Ill. Adm. Code 920)
Illinois Department of Public Health
3) Drinking Water Systems
(77 Ill. Adm. Code 900)
Illinois Department of Public Health
4) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Waste water (1995 Edition − American Public Health Association, 1015 15th Street, N.W., Washington, D.C. 20005)
5) ANSI/NSF Standard 42, Drinking Water Treatment Units – Aesthetic Effects (1997) Published by:
NSF International
P.O. Box 130140
Ann Arbor, Michigan 48113-0140
Referenced in Section 930.20
6) ANSI/NSF Standard 53, Drinking Water Treatment Units – Health Effects (1997) Published by:
NSF International
P.O. Box 130140
Ann Arbor, Michigan 48113-0140
Referenced in Section 930.20
7) ANSI/NSF Standard 55, Ultraviolet Microbiological Water Treatment Systems (1991) Published by:
NSF International
P.O. Box 130140
Ann Arbor, Michigan 48113-0140
Referenced in Section 930.20
8) ANSI Z 34.1 (1993), Third Party Certification Program
American National Standards Institute
11 West 42nd Street
New York NY 10036
b) All incorporations by reference of federal regulations and the standards of nationally recognized organizations refer to the regulations and standards on the date specified and do not include any additions or deletions subsequent to the date specified.
(Source: Amended at 27 Ill. Reg. 15998, effective October 1, 2003)
Section 930.20 Treatment Plant
A non-community water system, semi-private water system, or a private water system which obtains water from a surface source, shall treat water by utilizing a water treatment plant with either slow sand filtration or cartridge filtration, and disinfection.
a) General
1) Raw Water Quality. The turbidity of the source water shall not exceed 50 nephelometric turbidity units. Cartridge filtration shall not be used to treat water obtained from rivers.
2) Intake. A means must be provided to withdraw raw water from the surface source. Intakes shall not incorporate a submerged sand and gravel filter. The intake must be located at a point of deepest water in the pond and must be capable of being raised or lowered for cleaning. A coarse meshed screen with openings not greater than ¼ inch shall be placed over the end of the intake pipe to prevent entrance of fish, dead leaves, and other debris. The intake pipe must be constructed such that it is flexible, will not break when raised, and shall be approved for use as potable water piping in accordance with the Illinois Plumbing Code (77 Ill. Adm. Code 890, Section 890.Appendix A Plumbing Materials, Equipment, Use Restrictions and Applicable Standards) or Table A Approved Materials for Water Service Pipe of this Part. The intake pipe must be kept below any ice, it must be buried in a trench through shallow water, and it must be placed below the frost line at all points.
b) Slow Sand Filtration. The treatment plant shall include the following principal units.
1) Raw Water Pump. A pump shall be required to deliver water from the intake to the filter at a rate which is greater than the filtration rate. The pump must be self-priming or so installed that it will not lose its prime.
A) The pump shall be driven by an electric motor, controlled by a sensing system on top of the filter, and set to start and stop the raw water pump automatically. The system shall be set to allow 10 inch-12 inch fluctuation in the water level in the filter to prevent frequent cycling of the pump.
B) The raw water pump will not be required when the elevation of the filter is below the elevation of the intake pipe. Elevation difference between the pond and the filter must be sufficient to produce the flow rate needed at times of low pond water levels in accordance with the rates set forth in Section 930.30 of this Part. There must be no possibility of flooding the treatment plant by high water which may occur below the pond.
2) Filter Sand. The filter must be designed so that the raw water flows downward by gravity through the filter media.
A) Filter Sand. The filter media shall be a layer of sand at least three feet in depth. The sand shall have an effective size of .25-.35 mm with an ideal size of .30 mm and a uniformity coefficient of 1.4-1.8 with an ideal uniformity coefficient of 1.6. The sand shall be supported by a bed of gravel one foot in depth. A perforated pipe must be installed at the bottom of the filter which will allow water to flow to a water storage tank.
B) Filtration Rate. The maximum permissible filtration rate shall be 2 gallons per minute for each 25 square feet of sand surface area. The amount of water needed per day shall be calculated using Table B.
C) Construction. The filter must be constructed of concrete or a material which will not corrode or deteriorate and the walls and bottom shall be watertight. Examples of materials which will corrode or deteriorate include wood, tin, or steel. The minimum height of the filter shall be 8 feet in order to provide for a 3 foot depth of water above the sand, and a minimum of 1 foot from water level to the top of the filter during operation.
D) Underdrain Pipe. A perforated underdrain pipe, 1¼ inches inside diameter or larger, shall be installed horizontally at 2 inches above the bottom of the filter tank. One end of the pipe shall be capped within the filter to prevent the entrance of gravel. The other end shall pass through the filter wall, and a valve shall be installed to regulate the flow of water leaving the filter. See Illustration A. Forty -50 holes in the underdrain pipe shall be drilled in 2 rows at a 90o angle to each other on the bottom side of the pipe. The holes shall be ¼ inch in diameter and shall be uniformly spaced. One separate underdrain pipe shall be installed for each 75 square feet of filter area.
E) Gravel. Clean, washed gravel shall be placed in three graded layers in the filter, the coarsest gravel being on the bottom. The bottom layer shall be placed to a depth of 6 inches, and shall consist of stones ½-¾ inches in diameter. The top of the pipe shall be 2 inches below the top of this layer. The second or middle layer shall be 3 inches in depth and shall consist of stones ¼-½ inches in diameter. The third or top layer shall be 3 inches in depth and consist of stones ⅛-¼ inches in diameter.
F) Filter Valves. The piping which carries the water from the filter is to be valved as shown in Illustration B. The filter to waste pipe shall discharge at least 6 inches above the floor drain to permit checking the clarity of the filtered water and to measure the flow rate of filtered water. The floor drain shall not be located over the filtered water storage tank nor shall any portion of the waste drain piping pass through any part of the water storage tank. The filtered water shall be stored in the storage tank and a float valve shall be installed at the end of the filtered water pipe within the storage tank to shut off the flow when the tank is filled to approximately 6 inches from the top. (See Illustration A for exact location.) Solenoid valves controlled by a float switch may also be used. A manhole shall be installed in the top of the storage tank. The manhole shall have a raised curb and be provided with a cover of the overhanging type. The float valve is to be located to one side of the manhole so that it may be reached for any adjustment, without entering the storage tank. The floor drain which receives filtered water and discharges to waste shall discharge at ground level, at least 15 feet horizontally and downgrade from the plant and above any floodwater level. This drain shall not be connected to any other drain or sewer.
G) Filtered Water Storage Tank. A watertight and pollution-proof reservoir must be provided to receive the filtered water. Its capacity shall be at least equal to the amount of water which will be used in one day. This amount is obtained by using Table B. The top of the storage tank shall not be higher than the bottom of the filter, and shall not be located where it can be subject to flooding. Sources of pollution shall not be located closer to buried water storage tanks than indicated in Section 920.50 of the Illinois Water Well Construction Code (77 Ill. Adm. Code 920.50).
H) Filtered Water Pump and Pressure Tank. An electrically driven pump shall be provided to remove water from the storage tank. The water distribution system shall be designed to maintain a minimum positive pressure of 20 pounds per square inch (p.s.i.) in all parts of the system at all times. Water pipe shall conform to applicable specifications and standards of the Illinois Plumbing Code (77 Ill. Adm. Code 890, Section 890.1150) for the type of pipe to be used.
I) Filter Building. A building or structure shall be provided to enclose the filter and pumps. If the system is to be operated through the winter months, heating must be provided to prevent freezing.
c) Cartridge Filtration. The treatment plant shall include the following principal units.
1) Raw Water Pump. The pump shall be driven by an electric motor and be controlled by a pressure switch set to turn on the pump at a pressure of no less than 20 pounds per square inch. The pump shall be protected against excessive cycling by the installation of a hydropneumatic tank. The volume of water that can be drawn from the hydropneumatic tank between pump cycles shall be at least equal to the volume of water pumped in 30 seconds. The hydropneumatic tank shall be installed upstream of the filters and disinfection system.
2) Particulate Reduction Filter. Particulate reduction shall be accomplished using a filter certified to comply with ANSI/NSF Standard 42 − Drinking Water Treatment units − Aesthetic Effects, for particulate reduction, class I or II and be listed as such by an approved certification agency. The design flow rate in the particular application in which the filter is utilized shall not exceed the rated service flow rate for which the filter was certified. An official certification label from the certifying agency shall be permanently affixed to the filter. When treating turbid waters, an additional filter may be needed prior to the particulate reduction filter.
3) Turbidity Reduction and Cyst Reduction. Turbidity reduction and cyst reduction shall be accomplished utilizing either separate filters for each process or one filter for both processes. The turbidity and cyst reduction filters shall be located downstream of the particulate reduction filter.
A) Turbidity Reduction Filter. Turbidity reduction shall be accomplished using a filter certified to comply with ANSI/NSF Standard 53 − Drinking Water Treatment units − Health Effects, for turbidity reduction and be listed as such by an approved certification agency. The design flow rate in the particular application in which the filter is utilized shall not exceed the rated service flow rate for which the filter was certified. An official certification label from the certifying agency shall be permanently affixed to the filter.
B) Cyst Reduction Filter. Cyst reduction shall be accomplished using a filter certified to comply with ANSI/NSF Standard 53 − Drinking Water Treatment units − Health Effects, for cyst reduction and be listed as such by an approved certification agency. The design flow rate in the particular application in which the filter is utilized shall not exceed the rated service flow rate for which the filter was certified. An official certification label from the certifying agency shall be permanently affixed to the filter.
4) Flow Control. A flow control valve and a flow rate meter shall be installed downstream of the filters. The flow rate meter shall have a range which will permit the measurement of the rated service flow rate for the filters, and shall have an accuracy of ± 10% over the full scale.
d) Disinfection.
1) A disinfection system shall be installed with calcium or sodium hypochlorites or gas chlorine or other disinfecting agents approved by the Department. Proposals for the use of disinfecting agents other than those specifically listed in this Section must be approved by the Department prior to preparation of final plans and specifications. The Department will grant approval when all available information establishes that the chemical to be used as a disinfecting agent meets the following conditions: the residual levels created by the use of the chemical will not jeopardize the health of the user of the water, testing procedures for residual elements are recognized in "Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater" (1995 Edition − American Public Health Association) (see Section 930.15) and the chemical will destroy bacteria in the water supply. Ultraviolet disinfection may only be used in water treatment plants utilizing cartridge filtration.
2) Chlorination. Disinfection using chlorine shall include feeding equipment, a retention tank and testing equipment.
A) Chlorination Equipment. The chlorinator shall be designed to provide a free chlorine residual of at least two milligrams per liter (mg/l) in the water. The equipment shall be designed so that it will operate accurately over the desired feeding range. Where flow is uniform, actuation of a constant volume feeder by the pump circuit is required. Where flow is variable, automatic flow proportioning is required.
i) Hypochlorinator. Positive displacement pumps shall be provided to inject hypochlorite solution. The pump shall be of variable flow type and shall be of sufficient capacity to feed the required amount of disinfectant. If calcium hypochlorite is used, the concentration of calcium hypochlorite in the solution shall not exceed 5 percent. The solution container shall have a minimum capacity equal to the volume of solution required per day. The chlorine pump shall be controlled by a float switch located in the filtered water storage tank. Chlorine shall be pumped whenever water is flowing into the storage tank.
ii) Gas Chlorinators. Any gas chlorination system shall meet the requirements of Section 900.40(n)(5) of the Drinking Water Systems Code (77 Ill. Adm. Code 900.40(n)(5)).
B) Contact Time and Point of Application. Chlorine shall be applied after the filter and prior to the filtered water storage tank, and in a manner that will provide a free chlorine residual of at least 2 milligrams per liter in the water after thorough mixing and a contact time of at least 30 minutes at maximum flow rates. The pipe carrying water from the filter shall terminate at or above the water surface of the storage tank. Water shall be withdrawn from a solid pipe at a point not more than 3 inches above the bottom of the water storage tank.
C) Testing Equipment. Chlorine residual test equipment capable of measuring free chlorine residual shall be provided and shall be capable of measuring residuals to the nearest 0.1 mg/L in the range below 0.5 mg/L, to the nearest 0.3 mg/L between 0.5 and 1.0 mg/L, and to the nearest 0.5 mg/L between 1.0 mg/L and 2.0 mg/L.
3) Ultraviolet Disinfection. Where ultraviolet disinfection is used, it shall be accomplished using an ultraviolet disinfection system certified to comply with ANSI/NSF Standard 55 − Ultraviolet Microbiological Water Treatment Systems − Class A Systems. The design flow rate for the ultraviolet disinfection equipment shall be at least equal to the rated service flow rate for any of the filters. The ultraviolet disinfection equipment shall be installed downstream of the filters.
(Source: Amended at 27 Ill. Reg. 15998, effective October 1, 2003)
Section 930.30 Treatment Plant Operation
a) Slow sand filtration plants shall comply with the following.
1) Disinfection of Storage Tank. The walls and bottom of the storage tank must be free of dirt and debris prior to operation. The side and bottom must then be washed with a chlorine solution of 100 parts per million.
2) Prior to operation, the filter must be disinfected with a solution of 100 parts per million. The effluent valve is to be closed, and this solution must remain in the filter for at least 24 hours.
3) Before water is allowed to flow to the filter, a clean piece of wood, fiberglass or a metal plate 2 feet square must be placed on the surface of the sand in order to prevent the initial water from disturbing the sand. After the filter has reached operating level, the plate must be removed.
4) Filtration Rate. The filtration rate shall not exceed 2 gallons per minute for each 25 square feet of sand filter area.
b) Cartridge filtration treatment plants shall comply with the following.
1) The flow rate shall not exceed the maximum design flow rate for any of the filters or disinfection system.
2) The water pressure shall be maintained at 20 pounds per square inch or greater downstream of the treatment plant.
c) Disinfection shall comply with the following.
1) If chlorine disinfection is used, a minimum free chlorine residual of at least 0.2 mg/L shall be maintained at distant points in the water distribution system and a minimum free chlorine residual of 0.4 mg/L shall be maintained in the water storage tank.
2) If ultraviolet disinfection is used, the ultraviolet disinfection equipment shall be kept in continuous operation 24 hours per day.
(Source: Amended at 27 Ill. Reg. 15998, effective October 1, 2003)
Section 930.40 Treatment Plant Maintenance
a) Slow sand filtration treatment plants shall be maintained as follows:
1) Cleaning. Whenever the design flow can no longer be achieved the filter must be cleaned. In order to clean the filter, the water level must be lowered to 2 to 3 inches below the top of the sand. The filter must not be drained. The accumulated mud and slime along with ½ inch of the top of the sand surface must be removed.
2) Proper Filter Depth. After 6 inches of sand has been removed due to repeated cleaning, additional sand which shall comply with the design criteria specified in Section 930.20(c) must be added so the filter is restored to the original depth of 3 feet.
b) Cartridge filtration treatment plants shall be maintained as follows:
1) Cartridge filters shall be cleaned or replaced according to the manufacturer’s recommendation.
2) Replacement cartridges shall be equal to the original equipment.
c) Ultraviolet disinfection equipment shall be maintained as follows:
1) The ultraviolet equipment lamp shall be cleaned or replaced when the equipment has a lamp intensity failure. The lamp shall be replaced when the equipment has a lamp failure.
2) The ultraviolet lamp shall be replaced at intervals specified by the manufacturer, but no less often than annually.
3) Replacement ultraviolet equipment lamps shall be equal to the original equipment.
(Source: Amended at 27 Ill. Reg. 15998, effective October 1, 2003)
Section 930.ILLUSTRATION A Slow Sand Filter Water Treatment Plant

(Source: Amended at 27 Ill. Reg. 15998, effective October 1, 2003)
Section 930.ILLUSTRATION B Filter Valving

(Source: Amended at 27 Ill. Reg. 15998, effective October 1, 2003)
Section 930.TABLE A Approved Materials for Water Service Pipe
|
|
Material |
Standard |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1) |
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) Pipe |
ASTM D 1527-1988 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM D 2282-1988 |
|
|
|
Joints |
ASTM D 2235-1988 |
|
|
|
Solvent Cement (1) |
ASTM D 2235-1988 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2) |
Brass Pipe |
ASTM B 43-1988 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3) |
Cast Iron (ductile iron) |
ASTM A 377-1984 |
|
|
|
Water Pipe |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4) |
Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC) Pipe |
ASTM D 2846-1988 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM F 441-1988 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM F 442-1988 |
|
|
|
Joints |
ASTM D 2846-1988 |
|
|
|
Solvent Cement (orange) (1) |
ASTM F 493-1988 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5) |
Copper/Copper Alloy Pipe |
ASTM B 42-1988 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM B 302-1988 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6) |
Copper/Copper Alloy Tubing |
ASTM B 88-1988 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7) |
Polyethylene (PE) Pipe |
ASTM D 2239-1988 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8) |
Polyethylene (PE) Tubing |
ASTM D 2737-1988 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9) |
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Pipe |
ASTM D 1785-1988 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM D 224l-1988 |
|
|
|
|
ASTM D 2672-1988 |
|
|
|
Joints |
ASTM D 2855-1983 |
|
|
|
Primer |
ASTM F 656-1988 |
|
|
|
Solvent Cement (1) |
ASTM D 2564-1988 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1) |
Solvent cement must be handled in accordance with ASTM F 402-1988. |
||
(Source: Added at 27 Ill. Reg. 15998, effective October 1, 2003)
Section 930.TABLE B Daily Water Requirements
TYPE OF ESTABLISHMENT
FARM HOME:
|
Each person................. |
50 gals. |
Each hog.................... |
5 gals. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Each beef cow............ |
15 gals. |
Each sheep................. |
3 gals. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Each milk cow........... |
35 gals.* |
Each 100 chickens..... |
10 gals. |
Multiply the total in gallons by 365 to obtain the estimated water need for a year. Add to this any irrigation or other sizable needs, such as spraying of large orchards.
*Includes allowance for dairy barn and milk house sanitation.
|
PERMANENT DWELLINGS: |
GALLONS PER PERSON PER DAY |
|
|
|
|
Apartments – multiple family |
75 |
|
Boarding Houses |
50 |
|
Additional per non-resident border |
10 |
|
Boarding Schools |
100 |
|
Residential Institutions (per bed) |
125 |
|
Single Family Homes and Condominiums |
100 |
|
Mobile Home Parks (per space) |
250 |
|
Rooming Houses |
40 |
|
|
|
|
TRAVEL AND RECREATIONAL FACILITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
Airports (per passenger) |
5 |
|
Campgrounds with flush toilets and showers (per space) |
20 |
|
Campgrounds with flush toilets, no showers (per space) |
15 |
|
Cottages and small dwellings with single occupancy |
75 |
|
Country Clubs (per member present) |
25 |
|
Day Camps (children – no meals) |
25 |
|
Highway Rest Areas |
5 |
|
Hotels and Motels (per bed space) |
50 |
|
Picnic Parks with flush toilets |
5 |
|
Places of Public Assembly |
5 |
|
Swimming Pools, Bathing Beaches and Bathhouses (bather load |
10 |
|
as defined in 77 Ill. Adm. Code 820.10) |
|
|
Theaters |
|
|
Movie (per auditorium seat) |
5 |
|
Drive-In (per car space) |
10 |
|
Travel Trailer Park with water and sewer hookups (per space) |
30 |
|
Travel Trailer Park without water and sewer hookups (per space) |
10 |
|
|
|
|
COMMERCIAL, INDUSTRIAL AND MISCELLANEOUS: |
|
|
|
|
|
Churches |
5 |
|
Construction Camps or Sites |
50 |
|
Factories (gallons per person per shift, exclusive of industrial needs) |
35 |
|
Hospital (per bed space) |
250 |
|
Laundries – self-service (gallons per wash, i.e., per customer) |
50 |
|
Offices and other day workers |
15 |
|
Restaurants (per meal) |
10 |
|
Additional for bars and cocktail lounges |
2 |
|
Schools without gyms, cafeterias or showers |
15 |
|
Schools with gyms, cafeterias and showers |
25 |
|
Schools with cafeterias, but without gyms and showers |
20 |
|
Service stations (per vehicle served) |
5 |
|
Shopping Centers (per 1000 ft.2 floor area) |
250 |
|
Stores (per toilet room) |
400 |
(Source: Added at 27 Ill. Reg. 15998, effective October 1, 2003)
Section 930.EXHIBIT A Daily Water Requirements (Repealed)
(Source: Repealed at 27 Ill. Reg. 15998, effective October 1, 2003)