AUTHORITY: Implementing the Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Act [430 ILCS 75] and authorized by Sections 2 and 2.1 of the Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Act [430 ILCS 75/2 and 2.1].
SOURCE: Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Act Rules and Regulations adopted at 4 Ill. Reg. 7, p. 126, effective January 31, 1980; codified at 5 Ill. Reg. 10677; amended at 7 Ill. Reg. 6925, effective July 1, 1983; amended at 10 Ill. Reg. 9510, effective July 1, 1985; amended at 11 Ill. Reg. 16587, effective January 1, 1988; amended at 16 Ill. Reg. 6808, effective July 1, 1992; amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993; amended at 19 Ill. Reg. 11904, effective August 15, 1995; amended at 20 Ill. Reg. 9540, effective July 3, 1996; amended at 21 Ill. Reg. 997, effective January 1, 1997; amended at 23 Ill. Reg. 162, effective January 1, 1999; amended at 24 Ill. Reg. 18555, effective December 7, 2000; amended at 25 Ill. Reg. 11914, effective January 1, 2002; amended at 27 Ill. Reg. 518, effective January 01, 2003; emergency amendment at 27 Ill. Reg. 14855, effective September 2, 2003, for a maximum of 150 days; amended at 28 Ill. Reg. 1737, effective January 13, 2004; amended at 28 Ill. Reg. 13509, effective September 24, 2004; amended at 32 Ill. Reg. 17198, effective October 16, 2008; amended at 35 Ill. Reg. 9028, effective July 1, 2011; amended at 37 Ill. Reg. 13424, effective August 1, 2013; amended at 38 Ill. Reg. 18925, effective September 4, 2014; recodified from Chapter I, 41 Ill. Adm. Code 120, to Chapter III, 41 Ill. Adm. Code 2120, at 39 Ill. Reg. 10645; amended at 41 Ill. Reg. 846, effective January 17, 2017; amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 13457, effective July 1, 2018; amended at 44 Ill. Reg. 13968, effective August 13, 2020; amended at 46 Ill. Reg. 6907, effective May 1, 2022; amended at 48 Ill. Reg. 3420, effective February 21, 2024; expedited correction at 48 Ill. Reg. 9121, effective February 21, 2024.
Section 2120.10 Definitions
Act or the Act
− the Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Act [430 ILCS 75].
Alteration −
any change in the item described on the original Manufacturers' Data Report
which affects the pressure containing capability of the boiler or pressure
vessel. Non-physical changes such as an increase in the maximum allowable
working pressure (internal or external) or design temperature of a boiler or
pressure vessel shall be considered an alteration. A reduction in minimum
temperature such that additional mechanical tests are required shall also be
considered an alteration.
API 510 −
the code for the maintenance, inspection, repair, alteration and re-rating of
pressure vessels published by the American Petroleum Institute.
Approved −
approved by the Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Rules.
ASME Code −
the Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code of the American Society of Mechanical
Engineers with revisions, amendments and interpretations made, approved and
adopted by the Council of the Society and approved and adopted by the Board. Copies
of the Code may be obtained from the Society at Three Park Avenue, New York NY
10016-5990.
Authorized
Inspection Agency − one of the following:
A department
or division established by a jurisdiction that has adopted one or more Sections
of the ASME Code and whose inspectors hold valid National Board Commissions;
An insurance company authorized by
the jurisdiction to insure boilers and pressure vessels that employs special
inspectors who have met the requirements of this Part; or
An owner-user
of boilers and pressure vessels who employs owner-user inspectors and maintains
a regularly established inspection department, whose organization and
inspection procedures meet the requirements of this Part.
Authorized
Repairer − a holder of a Certificate of Registration issued pursuant to
the Boiler and Pressure Vessel Repairer Regulation Act.
Board − the
Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Rules created by the Act and empowered to
make, alter, amend and interpret rules and regulations for the safe
construction, installation, inspection, alteration, and repair of boilers and
pressure vessels and for establishing fees.
Boiler −
a vessel intended for use in heating water or other liquids or for generating
steam or other vapors under pressure or vacuum by the application of heat
resulting from the combustion of fuels, electricity, or waste gases.
Certificate
Inspection − an inspection, the report of which is used by the Chief
Inspector as justification for issuing, withholding or revoking the inspection
certificate. The Certificate Inspection shall be an internal inspection when
required; otherwise, it shall be as complete an inspection as possible.
Certificate of
Competency − a certificate issued to a person who has passed the
examination and meets all other requirements of this Part, as prescribed by the
Board.
Certificate of
Registration − a certificate issued by OSFM pursuant to the Boiler and
Pressure Vessel Repairer Regulation Act.
Commission −
the commission issued by OSFM to the chief, deputy, special or owner-user
inspector in accordance with this Part.
Condemned
Boiler or Pressure Vessel − a boiler or pressure vessel that has been
inspected and declared unsafe, or disqualified by legal requirements, by the
Chief or Deputy Inspector.
Division −
the Division of Boiler & Pressure Vessel Safety.
Electric
Boiler − a boiler in which the source of heat is electricity.
Engineer −
a registered professional engineer registered in accordance with the Illinois
Professional Engineering Act [225 ILCS 325] or a person who graduated from an
accredited college or university and either:
holds a
mechanical engineering degree; or
has five years
experience in a related field (e.g., civil engineering, metallurgical
engineering, industrial engineering, design engineering, maintenance
engineering, project engineering or construction, maintenance, repair or
operation of high pressure boilers and pressure vessels).
Existing
Installation − includes:
Any boiler
installed and placed in operation within the State of Illinois before May 1,
1953.
Any hot water
supply boiler installed and placed in operation within the State of Illinois on
or before July 9, 1957.
Any pressure
vessel installed and placed in operation within the State of Illinois on or
before December 31, 1976.
External
Inspection − an inspection made when a boiler or pressure vessel is in
operation, if possible.
Heating Boiler
− a steam boiler operated at pressures not exceeding 15 psig, or a hot
water heating boiler operated at pressures not exceeding 160 psig and/or
temperatures not exceeding 250° F. at or near the boiler outlet.
High Pressure
Boiler − a boiler generating steam at a pressure in excess of 15 psig or
a water boiler operated in excess of 160 psig and/or temperatures in excess of
250° F.
High-Temperature
Water Boiler − a water boiler operating at pressures exceeding 160 psig
and/or temperatures exceeding 250° F. at or near the boiler outlet.
Hot Water
Supply Boiler − a boiler (including fired storage water heater)
furnishing hot water to be used externally to itself at pressures not exceeding
160 psig and/or temperatures not exceeding 250° F. at or near the boiler outlet,
except those exempted pursuant to the Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Act and
this Part.
Inspection
Certificate − a certification issued by the Chief Inspector for the
operation of a boiler or pressure vessel, as required by the Act.
Inspector −
the Chief Inspector or Deputy Inspector or Special Inspector or Owner-User
Inspector.
Chief
Inspector − the Chief Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspector employed under
the Act.
Deputy
Inspector − any inspector employed under the provisions of the Act.
Special
Inspector − an inspector holding an Illinois Certificate of Competency
and who is regularly employed by an insurance company authorized to write
boiler and pressure vessel insurance in this State.
Owner-User
Inspector − an inspector described in Section 2120.1360 continuously
employed as an inspector by an Owner-User Inspection Agency.
Internal
Inspection − as complete an examination as can reasonably be made of the
internal and external surfaces of a boiler or pressure vessel while it is shut
down and manhole plates, handhole plates or other inspection opening closures
are removed as required by the inspector.
Jurisdiction −
a state, commonwealth, county or municipality of the United States or a
province of Canada that has adopted one or more sections of the ASME Code and
maintains a duly constituted Department, Bureau, or Division for the purpose of
enforcement of the Code. In Illinois, the Division of Boiler and Pressure
Vessel Safety is the jurisdiction, except for the City of Chicago.
Lined Potable
Water Heater − a water heater, with a corrosion resistant lining, used to
supply potable hot water.
Low Pressure
Boiler − a steam boiler operated at pressures not exceeding 15 psig or a
hot water boiler operated at pressures not exceeding 160 psig and/or
temperatures not exceeding 250° F.
Miniature
Boiler − any boiler that does not exceed any of the following limits:
16 inches
inside diameter of shell;
20 square feet
heating surface;
5 cubic feet
gross volume, exclusive of casing and insulation;
100 psig
maximum allowable working pressure.
National Board
Inspection Code or NBIC − the Manual for Boiler and Pressure Vessel
Inspectors published by the National Board. The NBIC is developed under the
ANSI consensus process. Copies of the NBIC may be obtained from the National
Board.
National Board
− the National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors, 1055
Crupper Avenue, Columbus, Ohio 43229, whose membership is composed of the Chief
Inspectors of jurisdictions who are charged with the enforcement of the boiler
and pressure vessel laws within their respective jurisdictions.
National Board
Commission − the commission issued by the National Board to a holder of a
Certificate of Competency who desires to make shop inspections or field
inspections in accordance with the National Board bylaws and whose employer
submits the inspector's application to the National Board for the commission.
Nationally Recognized Testing
Agency − an organization concerned with product evaluation that provides
uniform testing, examination, listing and labeling under established,
nationally recognized standards.
New Boiler
Installations − all boilers constructed, installed and placed in
operation within the State of Illinois after May 1, 1953, and all hot water
supply boilers installed and placed in operation after July 9, 1957.
New Pressure
Vessel Installations − pressure vessels installed and placed in operation
within the State of Illinois after December 31, 1976.
Non-Standard
Boiler or Pressure Vessel − a boiler or pressure vessel that does not
bear the ASME Code Symbol Stamp.
Operator −
any individual who has charge of a boiler or pressure vessel as defined by the
Act, and whose duties include operation and maintenance of those devices.
OSFM −
the Office of the State Fire Marshal.
Owner or User −
any person, firm or corporation legally responsible for the safe operation of
any boiler or pressure vessel within the State.
Owner-User −
an owner and user qualified under Section 15 of the Act.
Place of
Public Assembly − a building or specific area, including outdoor areas,
in which persons assemble for civic, educational, religious, social or
recreational purposes or that is provided by a common carrier for passengers
awaiting transportation or in which persons are housed to receive medical,
charitable or other care or treatment, or are held or detained for public,
civic or correctional purposes.
Portable
Boiler − an internally fired boiler primarily intended for temporary
location and the construction and usage of which permits it to be readily moved
from one location to another.
Power Boiler −
a boiler in which steam or other vapor is generated at a pressure of more than
15 psig and includes a high-pressure, high-temperature water boiler.
Pressure
Vessel − a vessel in which pressure is obtained from an external source,
or by the application of heat from an indirect source or from a direct source
other than those boilers defined in this Section.
PSIG − pounds
per square inch gauge.
Reinstalled
Boiler or Pressure Vessel − a boiler or pressure vessel removed from its
original setting and reinstalled at the same location within the State of
Illinois or at a new location without change of ownership.
Relief Valve −
an automatic pressure relieving device actuated by the static pressure upstream
of the valve that opens further with the increase in pressure over the opening
pressure. It is used primarily for liquid service.
Repair −
work necessary to return a boiler or pressure vessel to a safe operating
condition.
Re-rating −
a change in the maximum allowable working pressure or temperature of a boiler
or pressure vessel, regardless of whether physical work is performed on the
boiler or pressure vessel. Re-rating shall be considered an alteration.
Safety Relief
Valve − an automatic pressure actuated relieving device suitable for use
as a safety or relief valve, depending on application.
Safety Valve −
an automatic pressure relieving device actuated by the static pressure upstream
of the valve and characterized by full opening pop action. It is used for gas
or vapor service.
Secondhand
Boiler or Pressure Vessel − a boiler or pressure vessel that has changed
both location and ownership since primary use.
Standard
Boiler or Pressure Vessel − a boiler or pressure vessel that bears the
ASME Code Symbol Stamp.
State Special −
a boiler or pressure vessel of special construction that may not be constructed
in accordance with the ASME Code. See Section 2120.1100 of this Part for the
procedures for granting a State Special.
Welding or Arc
Welding − a group of welding processes in which coalescence is produced
by heating with an arc or arcs, with or without the application of pressure,
and with or without the use of filler metal.
(Source: Amended at 35 Ill.
Reg. 9028, effective July 1, 2011)
Section 2120.20
Incorporation of National Standards
a) Where standards are incorporated by reference in this Part,
the incorporated material does not include any later editions or amendments.
b) The Board hereby adopts the following nationally recognized
standards and addenda:
1) American
Petroleum Institute (API)
1220 L Street, Northwest
Washington DC 20005
API-510, Eleventh Edition, October
2022, Pressure Vessel Inspection Code: In-service Inspection, Rating, Repair,
and Alteration; with Errata 1 (March 2023)
2) American
Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME)
United Engineering Center
Three Park Avenue
New York NY 10017
www.asme.org
A) ASME
Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, 2023 Edition
Section I Rules
for Construction of Power Boilers
Section II Material
Specifications – Part A – Ferrous
Section II Material
Specifications – Part B – Nonferrous
Section II Material
Specifications – Part C – Welding Rods, Electrodes and Filler Metals
Section II Material
Specifications – Part D – Properties (Customary)
Section IV Rules
for Construction of Heating Boilers
Section V Nondestructive
Examination
Section VI Recommended
Rules for the Care and Operation of Heating Boilers
Section VII Recommended
Guidelines for the Care of Power Boilers
Section VIII Pressure
Vessels – Division 1, Rules for Construction of Pressure Vessels (Including
Appendix M)
Section VIII Pressure
Vessels – Division 2 – Alternative Rules
Section VIII Pressure
Vessels – Division 3 – Alternative Rules for Construction of High Pressure
Vessels
Section IX Welding,
Brazing and Fusing Qualifications
Section X Fiberglass-Reinforced
Plastic Pressure Vessels
B) ASME
CSD-1 2021 − Controls and Safety Devices for Automatically Fired Boilers
3) National
Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors (NB)
1055 Crupper Avenue
Columbus OH 43229
www.nationalboard.org
National Board Inspection Code
(NBIC), 2023 Edition
4) National
Fire Protection Association (NFPA)
1 Batterymarch Park
Quincy MA 02269-9101
www.nfpa.org
NFPA 85 Boiler
and Combustion Systems Hazards Code, 2023 Edition
(Source: Amended at 48 Ill. Reg. 3420,
effective February 21, 2024; expedited correction at 48 Ill. Reg. 9121,
effective February 21, 2024)
Section 2120.30 Fees
As authorized by the Boiler and
Pressure Vessel Safety Act, the Board establishes the following fees to be
collected for services rendered:
|
Examinations......................................................................................
|
$30
|
|
|
Commissions
|
|
|
|
New
Issuance.................................................................................
|
$40
|
|
|
Renewal.........................................................................................
|
$25
|
|
|
Chief and Deputy…………………………………………………
|
$0
|
|
|
All Certificates of Inspection..............................................................
|
$70
|
|
|
Inspections Conducted by the
Division
|
|
|
|
High Pressure and High Temperature Water Boilers
|
|
|
|
Boilers
without a manhole........................................................
|
$30
|
|
|
Boilers
with a manhole.............................................................
|
$60
|
|
|
Low
Pressure Steam and Water Boilers
|
|
|
Boilers
without a manhole........................................................
|
$30
|
|
|
Boilers
with a manhole.............................................................
|
$60
|
|
|
Hot water
supply boilers...........................................................
|
$30
|
|
|
|
|
|
No more than $130 shall be
charged for one boiler in any one year.
Pressure
Vessels
Fees are based on the product of
the overall length times the width or diameter of the vessel expressed in
square feet.
|
50 sq. ft.
or less...................................................................
|
$25
|
|
51 sq. ft.
to 150 sq. ft..........................................................
|
$50
|
|
over 150
sq. ft.....................................................................
|
$75
|
No more than $160 shall be
charged for any one pressure vessel in any one year.
|
Annual Statements (Owner-Users)....................................................
|
$35 per vessel
|
Miscellaneous
|
Witness a
hydrostatic test..........................................................
|
$100
|
Joint reviews, audits, shop
inspections, other services
|
½ day..................................................................................
|
$300
|
|
Full day..............................................................................
|
$500
|
Plus expenses, including travel and
lodging.
|
State Special Permits..........................................................................
|
$1,000
|
(Source: Amended at 37 Ill.
Reg. 13424, effective August 1, 2013)
Section 2120.40
Administration
a) Applying State Serial Number. The State serial number on
boilers shall be not less than 5/16" in height and
shall be preceded by the letter "B". The State serial number on
pressure vessels shall be not less than 5/16" in
height and shall be preceded by the letter "U". The inspector shall
make certain that the correct Illinois State serial number is affixed to the
boiler or pressure vessel at the time of inspection.
b) First Time Inspection. Effective January 1, 1999, all first
time inspections of boilers and pressure vessels shall be performed by the
Chief or a Deputy Inspector employed by the Division.
c) Basis for Extending Certificate of Internal Inspection for
Power Boilers. The Chief Inspector is authorized to extend, for a period not
exceeding one year, or 2 years for power boilers having an output rated at or
above 450,000 lbs/hr, the time within which power boilers are required to be internally
inspected, subject to the following conditions and qualifications:
1) The analysis and treatment of feedwater for power boilers
shall be under the supervision of a person qualified in the field of water
chemistry.
2) The analysis and treatment of the boiler feedwater shall be
for the purpose of controlling and limiting serious deteriorating, encrusting
and sludging factors affecting the safety of the boiler.
3) The owner or user of power boilers must maintain, for
examination by the inspector, accurate records of chemical and physical
laboratory analyses of samples of the boiler water taken at regular intervals
of not more than 24 hours operation and of the treatment applied. These
records must specify dates and times of analyses, by whom analyzed, and the
treatment applied at that time, and should be certified by the responsible
authority. These records will adequately show the conditions of the water and
any constituents or characteristics that are capable of producing corrosion or
other deterioration of the boiler or its parts.
4) The Chief Inspector is authorized to review the qualifications
of the supervisor and the acceptability of supervision in accordance with the requirements
of subsections (c)(1) through (c)(3).
5) An internal inspection must have been performed during a
pre-planned outage allowing appropriate time for a complete and comprehensive
evaluation, including inspections of watersides, furnace area and all gas
passages, with no deficiencies found that would preclude extending the internal
inspection for one year, or 2 years for power boilers having an output rated at
or above 450,000 lbs/hr.
6) At no time shall the period between internal inspections for
boilers having an output rated at or above 450,000 lbs/hr exceed a 36-month
time interval.
7) Application for extension shall be by letter setting forth
facts establishing compliance with the requirements of subsections (c)(1)
through (c)(7) and shall be accompanied by the report of external inspection.
d) Unsafe Boilers or Pressure Vessels. Any boiler or pressure
vessel having been inspected and declared unsafe by an inspector shall have the
Inspection Certificate suspended.
e) Factors of Safety for Existing Installations. An inspector
shall increase the factors of safety if the condition of a boiler or pressure
vessel warrants it. If the owner or user does not concur with the inspector's decision,
the owner or user may appeal to the Board.
f) Frequency of Inspection of Boilers and Pressure Vessels
1) Power boilers and high temperature water boilers shall receive
a certificate inspection annually, which shall be an internal inspection where
conditions permit unless authorization is granted by the chief inspector to
extend the internal inspection as permitted in subsection (c). The boilers
shall also be inspected externally annually while under representative
operating conditions, if possible, except that a power boiler having an output rated
at or above 450,000 lbs/hr may forgo the external inspection for the year the
internal inspection is conducted.
2) Low pressure steam and hot water heating boilers and hot water
supply boilers shall receive a certificate inspection every 2 years. Groups of
heating and hot water supply boilers connected together shall be registered as
one unit and receive one Inspection Certificate when the following conditions
are met:
A) No
unit exceeds 400,000 BTU input;
B) All units being considered in the assembled modular unit are
connected to a common header or manifold; and
C) No more than 8 units can be grouped together and registered as
one unit.
3) Inspection of the flame safeguard equipment shall be in
conjunction with the regular inspections of boilers.
4) Pressure vessels subject to internal corrosion shall receive a
certificate inspection every 3 years. This inspection shall be external and
internal where conditions permit. However, owner-users qualified in accordance
with Section 15 of the Act shall have the option of using API-510 or the NBIC
for inspection intervals.
5) Pressure vessels not subject to internal corrosion shall
receive a certificate inspection every 3 years. However, owner-users qualified
in accordance with Section 15 of the Act shall have the option of using API-510
or the NBIC for inspection intervals.
g) Inspection and Inspection Certificate Fees
1) If a boiler or pressure vessel shall, upon inspection, be
found to be suitable and to conform to this Part, the owner or user will be
invoiced the fees established by the Board for each boiler and pressure vessel
inspected. The fee must be paid before an Inspection Certificate will be
issued.
2) If the owner or user of each boiler or pressure vessel
required to be inspected refuses or fails to allow an inspection to be made or
refuses or fails to pay the appropriate fees, the Inspection Certificate, if it
has not expired, shall be suspended by the Chief Inspector until the owner or
user complies with the requirements.
3) The owner or user who causes a boiler or pressure vessel to be
operated without a valid Inspection Certificate shall be guilty of a Class B
misdemeanor and each day shall be deemed a separate offense in accordance with
Section 12 of the Act.
h) Inspectors to Have No Other Interests. It is prohibited for
any employee of the Division of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety to accept any
compensation or remuneration from any source for acting as a consultant,
engineer, safety engineer, safety specialist, etc., or under any other title. Employees
of this Division shall not be engaged in the sale of any article or device that
is related to boilers or pressure vessels and shall devote their full time to
inspection work.
i) Installing Used or Second-hand Boilers or Pressure Vessels.
A certificate inspection shall be made of all used or second-hand boilers or
pressure vessels prior to operation in this State. When a boiler or pressure
vessel is moved and reinstalled, the fittings and appurtenances shall be
upgraded to comply with the rules for new installations.
j) Inspectors to Notify Chief Inspector of Defective Boilers and
Pressure Vessels. If an inspector finds that a boiler or pressure vessel or
any of the appurtenances are in an unsafe condition, the inspector shall
immediately notify the Chief Inspector and submit a report of the defects.
k) Insurance Agencies to Notify the Chief Inspector of New,
Cancelled or Suspended Risks. All insurance agencies shall notify the Chief
Inspector within 30 days of all boiler or pressure vessel risks written,
cancelled, not renewed or suspended in Illinois.
l) Manufacturers Data Reports to be Filed. Effective January 1,
1974, Manufacturers Data Reports on boilers and, as amended December 31, 1976,
for pressure vessels, that are to be installed in the State of Illinois (unless
otherwise exempted by this Part) shall be filed with the Chief Inspector
through the National Board. Each boiler and pressure vessel for which a report
is filed should be assigned a National Board number.
m) Boilers and Pressure Vessels without ASME Stamping. If the
boiler or pressure vessel does not bear the ASME stamp, then the drawings, data
and material showing all details of construction shall be submitted to the
Chief Inspector and the Chief Inspector's approval shall be obtained before installation
in this State. The Chief Inspector shall grant approval if the construction,
materials and inspection requirements meet the rules, except for ASME stamp.
n) Notification of Inspection. The owner or user shall prepare
each boiler or pressure vessel for internal inspection and shall prepare for
and apply a hydrostatic test whenever necessary, on the date specified by an
inspector, which shall be not less than 7 days after the date of notification.
o) Owner to Notify Chief Inspector in Case of Accident. Any
owner or user, which includes any person, firm, partnership, corporation, or
governmental entity, that knowingly fails to notify the Chief Inspector within
24 hours, or on the next business day, of an accident, explosion, event, or
incident that serves to render a boiler or pressure vessel inoperative because
of damage or failure or that involves any bodily injury or death to any person
is guilty of a Class B misdemeanor, if a natural person, or a business offense
punishable by a fine of not less than $501 and not more than $10,000, if a
corporation or governmental entity.
p) Penalties. Any person, firm, partnership or corporation
violating any of the provisions of this Part shall be subject to the penalties
provided in the Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Act.
q) Registration of Boilers and Pressure Vessels. All owners or
users of boilers and pressure vessels subject to the Act now in use or
installed ready for use in the State of Illinois shall notify the Chief
Inspector in writing giving the location, type, capacity, age and date of
installation.
r) Removal of Safety Appliances
1) No person, except under the direction of an inspector, shall
attempt to remove or shall do any work upon safety appliances required by this
Part while a boiler or pressure vessel is in operation. Should any of these
appliances be repaired during an outage of a boiler or pressure vessel, they
must be reinstalled and in proper working order before the object is again
placed in service.
2) No person shall in any manner load the safety valve or valves
to maintain a working pressure in excess of that stated on the Inspection
Certificate.
s) Stamping of Boilers and Pressure Vessels. Each boiler or pressure
vessel subject to the Act shall be identified by a serial number of the State
of Illinois. The number will be assigned by the Chief Inspector and applied to
the boiler or pressure vessel by the inspector at the time of inspection. Also,
the Code required stamping shall be kept free of paint and lagging so that it
will be plainly visible and easily read by the inspector.
t) Inspections and Inspection Reports
1) Inspection Reports shall be submitted within 10 days from the
date of inspection.
2) All Inspection Reports shall be completed with all pertinent
information as required, including location and actual conditions observed.
3) The
Chief or a Deputy Inspector employed by the Division, and Special Inspectors,
shall have up to 90 days after the expiration of the Inspection Certificate to
conduct his or her inspection. An Inspection Certificate shall remain valid
beyond the expiration date noted on the certificate until the boiler or
pressure vessel is reinspected by the authorized inspecting authorities or
until the certificate is suspended by the Chief Inspector, provided that the
owner or user of the boiler or pressure vessel makes it available for inspection
at reasonable times. [430 ILCS 75/11(b)]
4) Validity of Inspection Certificate. The Chief Inspector may
at any time suspend an Inspection Certificate when the boiler or pressure
vessel for which it was issued may not continue to be operated without menace
to public safety, or when the boiler or pressure vessel is found not to comply
with this Part. A Special Inspector shall have authority to request suspension
of an Inspection Certificate for boilers or pressure vessels insured by the
employing company. Suspension of an Inspection Certificate shall continue in
effect until the boiler or pressure vessel has been made to conform to this
Part.
u) For
all boiler systems installed after December 1, 2014, the intake and exhaust
points for all boiler ventilation piping shall be located outside of the
building served and at least 36 inches above grade.
(Source: Amended at 41 Ill.
Reg. 846, effective January 17, 2017)
Section 2120.50 Inspectors,
Examinations, Certificate of Competency and Commission.
a) Examinations
1) Examinations for Certificate of Competency and Commission as
an Inspector of Boilers and Pressure Vessels shall be held the first Wednesday
of the months of March, June, September and December. Special examinations
will be held when considered necessary by the Board. A passing score on the
examination for a National Board Commission issued through the National Board
shall satisfy the examination requirement for an Inspector Commission issued by
OSFM under this Part and Section 9 of the Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Act
[430 ILCS 75/9].
2) Applicants for examination for a Special Inspector shall have
3 years experience in the construction, maintenance, repair or operation of
high pressure boilers and pressure vessels. A credit of 2 years of the required
experience will be given to applicants holding a Mechanical Engineering degree
from a college of engineering and one year's credit will be given for all other
types of engineering degrees.
3) Application for examination for Certificate of Competency and
Commission shall be written upon a form to be furnished by OSFM stating the
educational background of the applicant, a list of employers, period of
employment and position held with each employer. Applications containing
willful falsification or untruthful statements shall be rejected. If the
applicant's education and experience meet the requirements of the Board, the
applicant shall be given the written examination dealing with the construction,
installation, operation, maintenance and repair of boilers, pressure vessels
and their appurtenances. If the applicant is successful in meeting the
requirements of the Board, a Certificate of Competency and Commission will be
issued by OSFM. An applicant who fails to pass the examination will be notified
and permitted to take another written examination.
b) Commissions
1) A Commission as an Inspector and an identifying commission
card shall be issued by the State Fire Marshal as provided in the Act.
2) Commissions issued to inspectors in the employ of insurance
companies or of owner-users shall be held at the office of the employing
company. The Commission and the identifying commission card shall be returned
to the Chief Inspector when suspended or revoked or the inspector to whom the
Commission was issued is no longer employed by the insurance company or self-insurer.
3) A Commission issued to an Inspector may be suspended or
revoked by the State Fire Marshal as provided in the Act.
4) Reciprocal Commissions. A Reciprocal Commission as an
Inspector may be issued by the State Fire Marshal as provided in the Act.
(Source: Amended at 46 Ill.
Reg. 6907, effective May 1, 2022)
Section 2120.100 New
Installations of Boilers, Miniature Boilers, Heating Boilers and Hot Water
Supply Boilers
No boiler, except those exempted
by the Act, or by this Part, shall be installed in this State unless it has
been constructed and inspected in conformity with the applicable section of the
ASME Code and is inspected and registered in accordance with the requirements
of these Rules. Existing non-standard boilers may not be installed or
reinstalled in a different location.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.200 New
Installations of Pressure Vessels
No Pressure Vessel, except those
exempted by the Act or this Part shall be installed in this State unless it has
been constructed and inspected in conformity with the applicable section of the
ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, and inspected and registered in
accordance with the requirements of this Part. Existing non-standard pressure
vessels may not be installed or reinstalled in a different location.
Section 2120.300 Existing
Installations of Power Boilers
Maximum Allowable Working
Pressure for Standard Boilers. The maximum allowable working pressure for
standard boilers shall be determined in accordance with the applicable
provisions of the edition of the ASME Code under which they were constructed
and stamped. Existing installations of non-standard power boilers and
miniature boilers shall comply with this Section.
a) Maximum Allowable Working Pressure for Nonstandard Boilers.
1) The maximum allowable working pressure on the shell of a
nonstandard boiler shall be determined by the strength of the weakest section
of the structure, computed from the thickness of the plate, the tensile
strength of the plate, the efficiency of the longitudinal joint or tube
ligaments, the inside diameter of the weakest course and the factor of safety
permitted below.
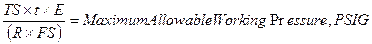
Where:
TS = ultimate tensile strength of shell plates, psi.
t = minimum thickness of shell plate, in weakest course, inches.
E = efficiency of longitudinal joint:
For Fusion-Welded and Brazed Joints:
Single lap welded ............................................................... 40
Double lap welded............................................................... 60
Single butt welded............................................................... 60
Double butt welded............................................................. 75
Forge welded....................................................................... 70
Brazed steel......................................................................... 80
For riveted
construction, E shall be determined by the rules given in Section I, Part PR,
of the 1971 Edition ASME Code.
For
seamless construction, E shall be considered 100 percent.
R =
inside radius of the weakest course of the shell, in inches.
FS =
factor of safety permitted.
2) Tensile Strength. When the tensile strength of steel or
wrought iron shell plates is not known, it shall be taken as 55,000 psi for
steel and 45,000 psi for wrought iron.
3) Bearing Strength of Mild Steel. The resistance to crushing of
mild steel shall be taken at 95,000 psi of cross-sectional area.
4) Factors of Safety. The following factors of safety shall be
increased by the Inspector if the condition and safety of the boiler demand it:
The lowest factor of safety permissible on existing installations shall be 5,
except for horizontal return tubular boilers having continuous longitudinal lap
seams more than 12 ft. in length, when the factor of safety shall be 8; when
this latter type of boiler is removed from its existing setting, it shall not
be reinstalled for pressures in excess of 15 psig. Reinstalled or second-hand
boilers shall have a minimum factor of safety of 6 when the longitudinal seams
are of lap riveted construction, and a minimum factor of safety of 5 when the
longitudinal seams are of butt and double-strap construction.
b) Repairs and Renewals of Boiler Fittings and Appurtenances.
Whenever repairs are made to fittings or appurtenances or it becomes necessary
to replace them, including burners and all associated controls, the work shall comply
with current ASME/National Board Code requirements or the requirement of the
ASME Codes in effect at the time of construction.
c) Recommendations for Operation. It is recommended that the
applicable Section of the ASME Code, Section VI, Recommended Rules for the Care
of Heating Boilers or Section VII, Recommendations and Rules for the Care of
Power Boilers be used as a guide for proper and safe operating practices.
d) Conditions not Covered by this Part. All cases not
specifically covered by this Part shall be treated as new installations.
Existing standard and non-standard boilers shall be governed by current
ASME/National Board Code requirements or the requirement of the ASME Codes in
effect at the time of construction. Questions concerning existing nonstandard
boilers may be referred to the Chief Inspector. Appeal of a decision of the
Chief Inspector may be made to the Board.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.400 Operation
of Boilers and Pressure Vessels
a) Designation of Operators. Owners of boilers and pressure
vessels as defined in the Act shall designate an operator to discharge the
duties of operation and maintenance of such devices.
b) Maintenance Requirements. Owners of boilers and pressure
vessels shall maintain such devices in accordance with manufacturers
specifications and this Part pertinent to such devices.
c) Operational Requirements. Owners of boilers and pressure
vessels shall perform periodic checks and operational maintenance of such devices
to ensure the structural and technical integrity of the device. Frequency of
checks and operational maintenance shall be determined by the manufacturer of
the device and this Part. Depending on the size and use of a boiler or
pressure vessel, checks and maintenance must be made at designated intervals by
the operator. The designated interval and checks shall be as prescribed by,
but need not be limited to, the manufacturers specification(s) and ASME CSD 1
(Controls and Safety Devices for Automatically Fired Boilers). Operators
responsible for the maintenance and operation of boilers and pressure vessels
shall have the skills necessary to perform those tasks at the level to ensure
the safe operation of regulated devices. It is recommended that all operators
of boilers and pressure vessels obtain training in the proper operation and
maintenance of such devices; training may be obtained through local community
colleges, mechanical insurers, trade associations, trade unions, and
manufacturers and distributors of such devices.
d) Recordkeeping. Owners of boilers and pressure vessels shall
maintain records of operation and maintenance of devices and make such records
available upon request of the inspector. Such records shall include, but not
be limited to, the following information:
1) Maintenance history of the device.
2) Operational check and maintenance logs.
3) Permits, licenses and other regulatory compliance information.
4) Problems and operational disruptions due to failure of the
device or a device accessory.
Appendix A
contains examples of operational and maintenance logs. Records shall be
maintained for a period of no less than 3 years from the date of recording.
(Source: Added at 23 Ill. Reg. 162, effective January 1, 1999)
Section 2120.500 Existing
Installation of Pressure Vessels
Maximum Allowable Working
Pressure for Standard Pressure Vessels. The maximum allowable working pressure
for standard pressure vessels shall be determined in accordance with the
applicable provisions of the ASME Code under which they were constructed and stamped.
a) Maximum Allowable Working Pressure for Nonstandard Pressure
Vessels.
1) For Internal Pressure. The maximum allowable working pressure
on the shell of a nonstandard pressure vessel shall be determined by the
strength of the weakest course computed from the thickness of the plate, the
tensile strength of the plate, the efficiency of the longitudinal joint, the
inside diameter of the course and the factor of safety set by this Part.


Where:
TS = ultimate tensile strength of shell plates, psi. When the tensile
strength of steel plate is not known, it shall be taken as 55,000 psi for
temperature not exceeding 650F.
t = minimum thickness of shell plate of weakest course, inches.
E = efficiency of longitudinal joint, depending upon construction.
Use the following values:
For Fusion-Welded and Brazed Joints:
Single lap welded ................................................ 40
Double lap welded................................................ 60
Single butt welded................................................ 60
Double butt welded.............................................. 75
Forge welded........................................................ 70
Brazed steel.......................................................... 80
For riveted
joints − calculate riveted joint efficiency in accordance with rules
given in Section I, Part PR, of the 1971 Edition ASME Code.
R = inside radius for weakest course of shell, inches, provided the
thickness does not exceed 10 percent of the radius. If the thickness if over 10
percent of the radius, the outer radius shall be used.
FS = factor of safety permitted shall be a minimum of 5.0.
2) For External Pressure. The maximum allowable working pressure
for cylindrical nonstandard pressure vessels subjected to external or
collapsing pressure shall be determined by the Rules in Par. UG-27 and UG-28 of
Section VIII of the ASME Code.
3) Factors of Safety. The minimum factor of safety may be
increased when deemed necessary by the Inspector to assure the operation of the
vessel within safe limits. The condition of the vessel and the particular
service to which it is subject will be determining factors.
4) End Closures. The maximum allowable working pressure permitted
for formed heads under pressure shall be determined by using the appropriate
formulas from Par. UG-32, UG-33, or UG-35 of Section VIII, ASME Code and the
tensile strength and factors of safety given above.
b) Repairs and Renewals of Fittings and Appurtenances. Whenever
repairs are made to fittings and appurtenances or it becomes necessary to
replace them, the work must comply with the requirements for new installations.
c) Conditions Not Covered by This Part. All cases not
specifically covered by this Part shall be treated as new installations.
Existing standard and non-standard pressure vessels shall be governed by
current ASME/National Board Inspection Code requirements or the requirement of
the ASME Codes in effect at the time of construction. Questions concerning
existing non-standard pressure vessels may be referred to the Chief Inspector.
Appeal of a decision of the Chief Inspector may be made to the Board.
(Source: Amended at 19 Ill. Reg. 11904, effective August 15, 1995)
Section 2120.1000 Repairs
and Alterations to Boilers and Pressure Vessels by Welding
a) Introduction. This Subpart covers rules for repairs and
alterations to boilers and pressure vessels by welding. Where applicable rules
for a repair or alteration are not given, it is intended that, subject to
approval of the Inspector, details of design and construction, insofar as
practicable, will be consistent with the rules of the ASME Code or the rules
for repairs contained in the National Board Inspection Code or the Code to
which the item was originally constructed.
b) General Requirements for Repairs and Alterations. The
requirements of this Subpart apply to all repairs and alterations to boiler and
pressure vessel pressure retaining parts, except that an owner-user of pressure
vessels qualified in accordance with Section 15 of the Act shall have the
option of using the provisions of API-510 for the inspection, repair,
alteration, or rerating of pressure vessels. Organizations authorized in
accordance with the Boiler and Pressure Vessel Repairer Regulation Act need not
meet the requirements of Section 2120.1010, 2120.1020, 2120.1030 or 2120.1040.
c) All boilers and pressure vessels covered by the Act and
repaired after July 31, 1997, must be repaired by one of the following:
1) By an organization holding a valid Certificate of Registration
issued by the State Fire Marshal.
2) An organization authorized by the Division of Boiler and
Pressure Vessel Safety pursuant to this Subpart to repair boilers or pressure
vessels for their own use.
d) All boilers and pressure vessels covered by the Act altered
after July 31, 1997, shall be altered in accordance with Section 2120.1041(b).
(Source: Amended at 21 Ill. Reg. 997, effective January 1, 1997)
Section 2120.1010
Authorization to Repair Boilers and Pressure Vessels
Realizing the importance of the
proper repair of boilers and pressure vessels, the Board of Boiler and Pressure
Vessel Rules authorized the development of procedures and rules for the
issuance and use of the Certificate of Authorization for repair for those
organizations requesting authorization for their own use to repair boilers and
pressure vessels under Section 2120.1000(c)(2). The Division shall review the
repair organization's Quality Control Manual and shall require a demonstration
of the repair organization's Quality Control System as described in this
Subpart.
(Source: Amended at 21 Ill. Reg. 997, effective January 1, 1997)
Section 2120.1020 Issuance
and Renewal of the Certificate
Authorization to repair boilers
and pressure vessels will be granted by the Division of Boiler and Pressure
Vessel Safety, Office of the State Fire Marshal, pursuant to the provisions of
the following administrative procedures and rules:
a) A Certificate of Authorization will be issued for a period of
three years. The certificate shall indicate authorization to repair either
boilers or pressure vessels or both, as covered by the repair organization's
Quality Control Manual. The Certificate will be signed by the Chief Inspector.
b) The applicant shall apply to the Division for renewal of
authorization and reissuance of the Certificate at least six (6) months prior
to the date of expiration.
c) Before issuance or renewal of the Certificate of Authorization,
the repair organization shall demonstrate its Quality Control System to a
representative of the Division.
d) It is the responsibility of the repair organization to make
arrangements for this review. Certificates cannot be issued nor renewed until the
Division has completed this review.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1030 Changes to
Certificates of Authorization
When an organization authorized
by the Division to repair boilers and pressure vessels for their own use
changes location and/or ownership or name, the Office of the State Fire
Marshal, Division of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety shall be notified. When
a repair organization changes location, name or ownership, a review of its
Quality Control System is required.
(Source: Amended at 21 Ill. Reg. 997, effective January 1, 1997)
Section 2120.1040 Quality
Control Requirements
a) General
1) Before issuance or renewal of a Certificate of Authorization,
the repair organization must meet all requirements including an acceptable
Quality Control System, outlined in a written Quality Control System Manual,
which shall include material control, fabrication, welding, nondestructive
examination, testing and inspection.
2) The Quality Control System Manual shall also include
provisions for making revisions, posting and dating changes in the program
enabling the System to be kept current as required.
3) The description and information relating to the System may be
brief or voluminous, depending upon the circumstances.
4) In general, the Quality Control System Manual shall describe
and explain what documents and procedures the repair firm will use to validate
a repair.
5) A review of the repair organization's Quality Control System
and Manual will be performed by a representative of the Division. The review
will include a demonstration of the implementation of the provisions of the
repair organization's Quality Control System.
6) Each repair organization to which a Certificate of
Authorization is issued shall maintain thereafter an up-to-date copy of its
accepted Quality Control System Manual and keep a current copy on file with the
Division. Revisions to the Manual shall not be implemented until such
revisions are accepted by the Division.
b) The following sets the minimum requirements for a Quality
Control System for repairs of boilers and pressure vessels. Each repair
organization shall develop its own Quality Control System which is designed to
meet the requirements of the organization. Requirements for the individual
Quality Control System Manuals include:
1) Title Page – The title page shall include the name and address
of the repair organization to which the Certificate of Authorization is to be
issued. It shall also list the Sections of the ASME Code to which the repairs
apply.
2) Revision Log – A revision log is required to assure control
over revisions in the Quality Control System Manual. The log shall contain
sufficient space for date, description and section of revision, repair
organization approval and Division acceptance.
3) Contents Page – The contents page shall list and reference, by
paragraph and page number, the subjects and exhibits contained within the
System.
4) Statement of Authority and Responsibility – A statement of
authority and responsibility shall appear on organization letterhead, dated and
signed by an officer of the organization:
A) Directing that disagreements in the implementation of the
written Quality Control System shall be referred to a higher authority in the
organization for resolution; and
B) Listing the title of the individual authorized to approve
revisions to the written Quality Control System Manual and the method by which
such revisions are to be submitted to the Division for acceptance before
implementation.
5) Organizational Chart – The organizational chart shall include
all departments or divisions within the repair organization that perform
functions affecting the quality of the repair and show the relationship.
6) Scope of Work – The scope of work section shall clearly
indicate the scope and type of repairs the organization is capable of and
intends to perform. The scope can be limited by engineering, machine tools,
welding processes, heat treatment facilities, testing facilities,
nondestructive examination (NDE) techniques or qualified personnel.
7) Drawings and Specification Control – The drawings and
specification control system shall provide procedures assuring that the latest
applicable drawings, specifications and instructions required are used for
repair, inspection and testing.
8) Material Control – The material control section shall describe
procurement of material with request for mill test certification as required.
It shall describe receiving, storage and issuance, as well as the following:
A) The title of the individual responsible for the procurement of
all material.
B) The title of the individual responsible for certification and
other records as required.
C) Procedures for checking all incoming material and parts for
conformance with the purchase order and, where applicable, the material
specifications or drawings. The material section shall indicate how the
material or part is identified and how identity is maintained by the Quality
Control System.
9) Repair and Inspection Program – The repair and inspection
program section shall include reference to a document (such as a report,
traveler or checklist) which outlines the specific repair and inspection
procedures used in the repair. The document shall be retained for a period of
at least five years. The document shall include the material check and a
description of items such as the welding procedure specifications (WPS),
fit-ups, NDE technique, heat treatment, and hydrostatic/pneumatic pressure test
methods used. There shall be a space for "sign-offs" at each operation
to verify that each step has been properly performed.
10) Welding, NDE and Heat Treatment – The Quality Control System
Manual shall indicate the title of the person(s) responsible for the
development and approval of the welding procedure, specifications, and their
qualifications as well as the qualifications of welders and welding operators.
Welding procedure, specifications, welders and welding operators shall be
qualified under the requirements specified in the ASME Boiler and Pressure
Vessel Code, Section IX. Similarly, NDE and heat treatment techniques must be
described in the Quality Control System Manual. When outside services are
used, the contracted service provider shall perform in accordance with the
Quality Control System Manual and shall meet the requirements of the applicable
section of the ASME Code.
11) Calibration of Measurement and Test Gauges – The calibration
of measurement and test gauges system shall include the periodic (indicate time
schedule) calibration of measuring instruments and pressure gauges.
A) Pressure gauges are to be checked periodically by the person
authorized (indicate title). The method of gauge testing is to be indicated
and results recorded.
B) Periodically, all master instruments shall be calibrated,
preferably but not necessarily, to measuring equipment that is traceable to the
National Bureau of Standards.
12) Nonconformities – The system shall establish measures for the
identification, documentation, evaluation, segregation and disposition of
nonconformities. A nonconformity is a condition of any material, item, product
or process in which one or more characteristics do not conform to the
established requirements. These may include, but are not limited to, data
discrepancies, procedural and/or documentation deficiencies or material
defects. Also, the title(s) of the individual(s) involved in this process
shall be included.
13) Controlled Copy – An up-to-date copy of the written Quality
Control Systems Manual shall be submitted to the Division for review and
acceptance. Revisions shall also be submitted for acceptance prior to being
implemented.
14) Sample Forms – Forms used in the Quality Control System shall
be included in the Manual with a written description. Forms exhibited shall be
marked "SAMPLE" and completed in a manner typical of actual repair
procedures.
15) Individuality Important – It is extremely important that the
Quality Control System and Manual be tailored to the operations of the
individual repair organization while meeting the requirements of this Subpart.
(Source: Amended at 23 Ill. Reg. 162, effective January 1, 1999)
Section 2120.1041 Repair and
Alteration Requirements
a) Repairs. Except as permitted for low pressure boilers, no
repair to a pressure vessel or high pressure boiler shall be initiated without
the authorization of the Inspector who shall be satisfied that the welding
procedures and welders are qualified and that the repair methods are
acceptable. The Inspector may give prior approval for repairs of a routine
nature. In every case, however, the Inspector shall be advised of each repair
under such prior agreement.
b) Alterations. Except as permitted for owner-users in Section 2120.1000(b),
alterations to boilers and pressure vessels shall be performed by an authorized
repairer. No alteration to a boiler or pressure vessel shall be initiated
without the authorization of the Inspector who shall be satisfied that the
alteration methods and calculations are acceptable. If the Inspector considers
it necessary, the Inspector shall make an inspection of the object before
granting such authorization.
c) Welded Repairs to Low Pressure Boilers. All welded repairs to
low pressure boilers shall be performed by an authorized repairer and shall
comply with all the rules as required by the Board, except no third party
inspection is required. Prior to the start of any low pressure boiler repair,
the authorized repairer shall contact the Division and request a low pressure
boiler repair permit authorization number and inform the Division of the
physical location of the boiler to be repaired. Upon completion of the repair,
the authorized repairer will submit a completed "Low Pressure Boiler
Repair Form" (LP-1) to the Division.
d) Acceptance of Repairs and Alterations. Provided that repairs
or alterations are acceptable to the Authorized Inspection Agency responsible
for the boiler or pressure vessel, acceptance of repairs and alterations may be
made by an Inspector employed by any of the following:
1) The Division.
2) The Inspection Agency of record of the organization making the
repair or alteration.
3) The Authorized Inspection Agency, provided the work was not performed
by the Agency employing the Inspector, except as provided in subsection (f) of
this Section.
e) Acceptance Inspection. It shall be the responsibility of the
organization making the repair or alteration to coordinate the acceptance
inspection of the repair or alteration. Except for repairs of a routine
nature, a completed record of welding repairs shall be submitted to the
Division by those organizations authorized under Section 2120.1000(c)(2).
Authorized repairers shall submit the appropriate National Board Form to the
Division upon completion of repairs or alterations.
f) Owner-User Acceptance Inspection of Repairs. An Owner-User
Inspector may perform acceptance inspections of repairs and alterations to
boilers and pressure vessels when such repairs and alterations have been
performed by the Inspector's employer, provided the repair organization and
inspection procedures have the Division's specific approval. Such acceptance
inspection procedures shall be subject to the concurrence of the Authorized
Inspection Agency responsible for the boiler or pressure vessel.
g) Replacement Pressure Parts. In general, replacement pressure
parts may be classified as follows:
1) Replacement parts subject to internal or external pressure
that consist of materials which may be formed or assembled to the required
shape by bending, forging or other forming methods, but on which no shop
fabrication welding is performed may be supplied as material. Material and
part identification shall be supplied in the form of bills of material and
drawings with ASME Code compliance.
2) Replacement parts subject to internal or external pressure
that are fabricated preassembled by welding, but on which shop inspection is
not required by the ASME Code, shall have the welding performed in accordance
with Section IX and other applicable Sections of the ASME Code. The
replacement part assembly identification shall be supplied in the form of bills
of material and drawings. The supplier or manufacturer shall certify that the
material, design and fabrication are in accordance with the applicable Section
of the ASME Code.
3) Replacement parts subject to internal or external pressure
fabricated by welding which require shop inspection by an Authorized Inspector
shall be fabricated by a manufacturer having an ASME Certificate of
Authorization and the appropriate Code Symbol Stamp. A Manufacturer's Partial
Data Report shall be supplied by the manufacturer.
h) Pressure Tests
1) Repairs. The Inspector may require a pressure test after the
completion of a repair to a boiler or pressure vessel when in the Inspector's
judgment one should be conducted.
2) Alterations. A pressure test in accordance with the National
Board Inspection Code shall be applied to the boiler or pressure vessel on the
completion of an alteration.
i) Repair Methods. Repair methods in this Section shall be used
in conjunction with the general requirements in Section 2120.1000(b) of this
Part.
j) Defect Repairs
1) General. A repair of a defect, such as a crack in a welded
joint or base material, shall not be made until the defect has been removed. A
suitable nondestructive method shall be used to assure its complete removal.
If the defect penetrates the full thickness of the material, the repair shall
be made with a complete penetration weld such as double butt weld or a single
butt weld with or without backing. Before repairing a cracked area, care shall
be taken to investigate its cause and to determine its extent.
2) Unstayed Boiler Furnace Cracks. Cracks at the knuckle or at
the turn of the flange of the furnace opening require immediate replacement of
the affected area or specific approval of repairs by the Authorized Inspection
Agency.
3) Rivet or Staybolt Hole Cracks. Cracks radiating from rivet or
staybolt holes may be repaired if the plate is not seriously damaged. If the
plate is seriously damaged, it shall be replaced.
4) Minor Defects. Minor cracks, isolated pits, and small plate
imperfections shall be examined to determine the extent of the defect and
whether welding is required. When welding is required, these defects shall be
prepared for welding by removing to solid metal. Liquid penetrant or magnetic
particle examination may be used before and/or after welding.
5) Defective Bolting. Defective bolting material shall not be
repaired but shall be replaced with suitable material which meets the
specifications of the applicable Section of the ASME Code.
k) Wasted Areas
1) Shells, Drums, Headers. Wasted areas in stayed and unstayed
shells, drums and headers may be built up by welding provided that in the
judgment of the Inspector the strength of the structure will not be impaired.
Where extensive weld build-up is employed, the Inspector may require an
appropriate method of NDE (nondestructive examination) for the complete surface
of the repair. For repairs of minor defects see Section 2120.1041(j)(4) of
this Part.
2) Access Openings. Wasted areas around access openings may be
built up by welding or they may be repaired. In boilers, the area to be so
repaired shall not be closer than 2 inches (50.8mm) from any knuckle.
3) Flanges. Wasted flange faces may be cleaned thoroughly and
built up with weld metal. They should be machined in place if possible to a
thickness not less than that of the original flange or that required by
calculations in accordance with the provisions of the applicable Section of the
ASME Code. Wasted flanges may also be remachined in place without building up
with weld metal provided the metal removed in the process does not reduce the
thickness of the flange to a measurement below that calculated above. Flanges
which leak because of warpage or distortion and which cannot be remachined
shall be replaced with new flanges which have at least the dimensions
conforming to the applicable Section of the ASME Code.
4) Tubes. Wasted ares on tubes may be repaired by welding
provided that in the judgment of the Inspector the strength of the tube will
not be impaired.
5) Corrosion, Grooving.
A) Localized corrosion that produced a groove, especially along or
immediately adjacent to a joint, could be more serious than a similar amount of
corrosion on solid plate away from the joint. Grooving and cracks along
longitudinal joints are especially significant as they are likely to occur
where the material is more highly stressed. Severe corrosion is likely to
occur at points where the circulation of the corrosive fluid is poor; such
places shall be examined most carefully.
B) For the purposes of estimating the effect of corrosion or other
defects upon the strength of a shell, comparison shall be made with the
efficiency of the longitudinal joint of the boiler or pressure vessel, the
strength of which is always less than that of a solid sheet.
C) All flanging shall be inspected thoroughly, particularly the
flanges of heads that are not stayed. Internal grooving in the fillets of such
heads and external grooving in the outer surfaces of heads concave to pressure
are very common since there is a slight movement in heads of this character
which produces this kind of defect. Some types of boilers or pressure vessels
have the ogee or reversed-flange construction in a few of their parts that may
be inaccessible to the eye, but the conditions shall be determined by the
insertion of a borescope, fiber optics or a mirror which, at a proper angle,
will reflect back to the eye the condition of such a part.
D) On new vessels and on vessels for which service conditions are
being changed, one of the following methods shall be employed to determine the
probable rate of corrosion from which the remaining wall thickness at the time
of the next inspection can be estimated:
i) The corrosion rate as established by accurate data collected
by the owner or user on vessels in the same or similar service.
ii) If accurate data for the same or similar service are not
available, the probable corrosion rate as estimated from the Inspector's
knowledge and experience on vessels in similar service.
iii) If the probable corrosion rate cannot be determined by either
of the above mentioned methods, thickness determinations shall be made after
approximately 1000 hours of service, or one normal run if longer than this;
subsequent sets of thickness measurements shall be taken after additional
similar intervals until the corrosion rate is determined by this method; the
corrosion data indicated by the first inspection may be used as a first
approximation of the corrosion rate but shall be excluded from all subsequent
computations of the corrosion rate, since attack on the initial surfaces may
not be indicative of subsequent attack on corroded surfaces.
l) Seal Welding
1) Seal Welding of Tubes. Tubes may be seal welded provided the
ends of the tubes have sufficient wall thickness to prevent burn through and
the requirements of the appropriate Sections of the ASME Code are satisfied.
2) Seal Welding of Riveted Joints. Edges of butt straps, plate
laps and nozzles, or of connections attached by riveting may be restored to
original dimensions by welding. Seal welding of riveted joints, butt straps or
rivets shall require the approval of the Authorized Inspection Agency.
m) Re-Ending or Piecing Pipes and Tubes. Re-ending or piecing
pipes and tubes is permitted provided the thickness of the remaining tube or
pipe is not less than 90 percent of that required by the applicable Section of
the ASME Code.
n) Patches
1) Flush Patches. The weld around a flush patch shall be a full
penetration weld and the accessible surfaces shall be ground flush where
required by the applicable Section of the ASME Code. Flush welded patches
shall be subjected to an appropriate nondestructive examination which shall be
consistent with the original construction requirements.
2) Tube Patches. In some situations it is necessary to weld a
flush patch on a tube, such as when replacing tube sections and accessibility
around the complete circumference of the tube is restricted or when it is
necessary to repair a small bulge. This is referred to as a window patch.
3) Stays. Threaded stays may be replaced by welded-in stays
provided that, in the judgment of the Inspector, the plate adjacent to the
staybolt has not been materially weakened by deterioration or wasting away.
All requirements of the applicable Section of the ASME Code governing welded-in
stays shall be met.
o) Alteration Methods. Alteration methods shall comply with the
general requirements of Section 2120.1000(b) of this Part.
p) Replacement Drums and Shells. Major replacement of pressure
parts, including drums and shells, which are fabricated by welding and for
which a Manufacturer's Data Report is required by the applicable Code Section
shall be fabricated by a manufacturer having an ASME Certificate of
Authorization and the appropriate Code Symbol Stamp. The item shall be
inspected, stamped with the applicable Code Symbol and the word
"PART", and reported on the appropriate Manufacturer's Partial Data
Report.
q) Replaced Stamping. When a repair or alteration requires
removal of that part of a boiler or pressure vessel containing the Code
Stamping, the Inspector shall, subject to the approval of the jurisdiction,
witness the making of a facsimile of stamping, the obliteration of the old
stamping and the transfer of the stamping to the new part. When the stamping
is on a nameplate, the Inspector is to witness the transfer of the nameplate to
the new part. The Code Symbol is not to be restamped.
r) Rerating of a Boiler or Pressure Vessel. Rerating of a
boiler or pressure vessel by increasing the maximum allowable working pressure
(internal or external) or temperature, or decreasing the minimum temperature
such that additional mechanical tests are required, shall be considered an
alteration and shall be done only after the following requirements have all
been met to the satisfaction of the Authorized Inspection Agency:
1) Revised calculations verifying the new service conditions
shall be required from the original manufacturer for review and acceptance by
the Authorized Inspection Agency. When such calculations cannot be obtained
from this source, they may be prepared by an Engineer and forwarded for review
and acceptance by the Authorized Inspection Agency.
2) All reratings shall be established in accordance with the
requirements of the Code to which the boiler or pressure vessel was built or by
computation using the appropriate formulas in the latest edition of the ASME
Code if all essential details are definitely known to comply with the edition
of the Code to which the object was built.
3) Current inspection records verify that the boiler or pressure
vessel is satisfactory for the proposed service conditions.
4) The boiler or pressure vessel has been pressure tested for the
rerated condition as required by subsection (h)(2) of this Section.
s) Suggestions
1) The Inspector should be well informed of the natural and
neglectful causes of defects and deterioration of boilers and pressure
vessels. The Inspector should be conscientious and extremely careful in
observing, taking sufficient time to make the examinations thorough in every
way, taking no one's statement as final as to conditions not personally
observed, and, in the event of inability to make thorough inspections, the
Inspector should note it in the report and not accept the statements of others.
2) The Inspector shall make a general observation of the
conditions of the boiler room and apparatus, as well as of the attendants, as a
guide in forming an opinion of the general care of the equipment.
3) The Inspector shall weigh very carefully the condition of any
defects in order to determine their relation to, or influence upon, the safety
of the inspected boiler or pressure vessel. The Inspector shall question
responsible employees as to the history of old boilers or pressure vessels,
their peculiarities and behavior; ascertain what, if any, repairs have been
made; ascertain the character of repairs; and investigate and determine whether
repairs were made properly and safely.
(Source: Amended at 21 Ill. Reg. 997, effective January 1, 1997)
Section 2120.1200
Authorization for Repair of Safety & Safety Relief Valves
All National Board capacity
certified ASME Code Section I, "V" stamped and Section VIII,
"UV" stamped safety and safety relief valves that are repaired after
January 1, 1987, must be repaired by one of the following:
a) The manufacturer of the valve who is in possession of a valid
ASME "V" or "UV" Certificate of Authorization.
b) By an organization in possession of a valid "VR"
Certificate of Authorization issued by the National Board of Boiler and
Pressure Vessel Inspectors.
c) An organization authorized by the Division of Boiler and
Pressure Vessel Safety to repair safety and safety relief valves pursuant to
this Subpart.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1210
Authorization to Repair ASME and National Board Stamped Safety and Safety
Relief Valves
Realizing the importance of the
proper repair of safety and safety relief valves, the Board of Boiler and
Pressure Vessel Rules authorized the development of procedures and rules for
the issuance and use of the Certificate of Authorization for Valve Repair for
those organizations requesting authorization to repair safety and safety relief
valves under Section 2120.1200(c). The Division shall review the repair
organization's Quality Control System Manual and shall require a demonstration
of the repair organization's Quality Control System as described in this
Subpart.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1220 Issuance
and Renewal of the Certificate
Authorization to repair all ASME
Section I and Section VIII safety and safety relief valves will be granted by
the Division of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety, Office of the State Fire
Marshal, pursuant to the provisions of the following administrative procedures
and rules:
a) A Certificate of Authorization will be issued expiring on the
triennial anniversary date. The certificate shall indicate authorization to
repair either Section I or Section VIII valves or both, as verified by testing
and as covered by the repair organization's Quality Control System Manual. The
Certificate will be signed by the Chief Inspector;
b) The applicant should apply to the Division for renewal of
authorization and reissuance of the Certificate at least six (6) months prior
to the date of expiration;
c) Before issuance or renewal of the Certificate of Authorization
for Valve Repair, the repair organization and its facilities demonstrate its
Quality Control System to a representative of the Division;
d) It is the responsibility of the valve repair organization to
make arrangements for this review. Certificates cannot be issued nor renewed
until the Division has completed this review;
e) Before the Certificate of Authorization for Valve Repair will
be issued or renewed, two valves which have been repaired by the applicant at
his repair facility, and selected at random by a representative of the
Division, must successfully complete operational verification tests prior to
issuance or renewal. The valve selection (one steam and one air or gas where
steam and gas valves are repaired) shall be such as to cause a minimum
disruption to the repair organization. However, the valves shall be typical of
those repaired by the organization. Tests conducted must be witnessed by a representative
of the Division. The purpose of the tests is to ensure that the repairs have
been satisfactorily carried out and the function and operation of the valves
meet the requirements of the Section of the ASME Code to which they were
manufactured.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1240 Changes to
Certificates of Authorization
When a valve repair organization
changes, location and/or ownership or name, the Office of the State Fire
Marshal, Division of Boiler & Pressure Vessel Safety shall be notified.
When a valve repair organization changes location, name or ownership, a review
of its facilities and Quality Control System Manual shall be required.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1250 Repairs to
Safety and Safety Relief Valves
a) Repair of a safetyor safety relief valve is considered to be
the replacement, remachining or cleaning of any critical part as described in 2120.1260(b)(8)(D),
lapping of seat and disc or any other operation which may affect the flow
passage, capacity, function or pressure retaining integrity. Disassembly,
reassembly and/or adjustments which affect the safety or safety relief valve
function are also considered a repair. The initial installation, testing and
adjustments of a new safety valve or a safety relief valve on a boiler or
pressure vessel are not considered a repair.
b) The Division shall authorize properly trained and qualified
employees of boiler or pressure vessel users or their designees (see Section 2120.1285)
to make adjustments to set pressure provided the adjusted settings and the date
of the adjustment are recorded on a metal tag secured to the seal wire. All
external adjustments shall be resealed showing the identification of the
organization making the adjustments.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1260 Quality
Control System
a) General
1) Before issuance or renewal of the Certificate of
Authorization, the applicant must meet all requirements, including an
acceptable written Quality Control System that shall include, but not be
limited to, material control, fabrication, welding, nondestructive examination,
testing and inspection.
2) The written Quality Control System shall also include provisions
for making revisions, posting and dating changes in the program, enabling the
system to be kept current as required.
3) The description and information of the system may be brief or
voluminous, depending upon:
A) whether
the organization's quality control manual accurately describes who is
responsible for maintaining quality control; and
B) the
size of the company holding the authorization and the number of employees
assigned specific quality control duties.
4) In general, the Quality Control System shall describe and
explain what documents and procedures the repair firm will use to validate a
valve repair.
5) A review of the applicant's Quality Control System will be
performed by a representative of the Division. The review will include a demonstration
of the implementation of the provisions of the applicant's Quality Control System.
6) Each applicant to whom a Certificate of Authorization is
issued shall maintain thereafter an up to date copy of its accepted Quality
Control System Manual with the Division. Revisions to the Quality Control
System Manual shall not be implemented until the revisions are accepted by the
Division.
b) The following are the minimum requirements of the Division for
a written Quality Control System for repairs of ASME safety and safety relief
valves. It is essential that each valve repair organization develop its own
Quality Control System that meets the requirements of its organization. For
this reason, it is not possible to develop one Quality Control System that
could apply to more than one organization. Some of these requirements are:
1) Title Page – The title page shall include the name and address
of the company to which the Certificate of Authorization is to be issued. It
shall also list the Sections of the ASME Code to which the repairs will apply.
2) Revision Log – A revision log is required to assure revision
control of the Quality Control System Manual. The log shall contain sufficient
space for date, description and section of revision, company approval and
Division acceptance.
3) Contents Page – The contents page shall list and reference, by
paragraph and page number, the subjects and exhibits contained in the manual.
4) Statement of Authority and Responsibility – A statement of
authority and responsibility shall appear on company letterhead, dated and
signed by an officer of the company verifying the following:
A) If there is a disagreement in the implementation of the written
Quality Control System, the matter is referred to a higher authority in the
company for resolution; and
B) The title of the individual authorized to approve revisions to
the written Quality Control System and the method by which revisions are to be
submitted to the Division for acceptance before implementation.
5) Organizational Chart – The organizational chart shall include
all departments or divisions within the company that perform functions
affecting the quality of the valve repair and show the relationship among the
various departments or divisions.
6) Scope of Work – The scope of work section shall clearly
indicate the scope and type of valve repairs the organization is capable of and
intends to carry out, and shall include the type and sizes of valves that can
be repaired. In addition, the testing media (steam, air, water, etc.) and
pressure ranges should be included. The scope can be limited by engineering,
machine tools, welding processes, heat treatment facilities, testing
facilities, non-destructive examination (NDE) techniques or qualified
personnel.
7) Drawings and Specification Control – The drawings and
specification control system shall provide procedures assuring that the latest
applicable drawings, specifications and manufacturer's available instructions
required are used for valve repair, inspection and testing.
A) Specific reference shall be made to the materials used for the
repair of the various valve parts (PG-73.2.3, Section I and UG-136(b)(3),
Section VIII, Division 1 of the ASME Code).
B) Mechanical requirements shall comply with the ASME Code. See
applicable Code Section.
8) Material and Part Control – The material and part control
section shall describe procurement of parts from the original valve
manufacturer or their designated representative, if applicable, and of material
with request for mill test certification as required. It shall also describe
receiving, storage and issuance, as well as the following:
A) State the title of the individual responsible for the
procurement of all material and parts.
B) State the title of the individual responsible for certification
and other records as required.
C) All incoming material and parts shall be checked for
conformance with the purchase order and, when applicable, the material specifications
or drawings. Indicate how the material or part is identified and how identity
is maintained by the Quality Control System.
D) All critical parts shall be fabricated by the valve
manufacturer. Critical parts are defined as any part that may affect the flow
passage, capacity, pressure rating or valve function.
9) Repair and Inspection Program – The repair and inspection
program section shall include reference to a document (such as a report,
traveler or checklist) that outlines the specific repair and inspection
procedures to be used in the repair of safety and safety relief valves.
Provisions shall be made to retain this document for a period of at least five
years as a part of quality control traceability documents.
A) Each valve or group of valves shall be accompanied by the
document referred to in subsection (b)(9) for processing through the plant.
B) The document referred to in subsection (b)(9) shall include
material check, reference to items such as the welding procedure specifications
(WPS), fit-ups, NDE technique, heat treatment, and pressure test methods to be
used. There shall be a space for "sign-offs" at each operation to
verify that each step has been properly performed for each valve.
C) The system shall include a method of controlling the repair or
replacement of critical valve parts. The method of identifying each spring
shall be indicated.
10) Welding, NDE and Heat Treatment (when applicable) – When
welded repairs are made by the Certificate holder, the Quality Control System
Manual shall indicate the titles of the persons responsible for the development
and approval of the welding procedure specifications and their qualifications,
and the qualifications of welders and welding operators. Welding procedures
specifications and welders and welding operators shall be qualified under the
requirements of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section IX.
Similarly, NDE and heat treatment techniques must be covered in the Quality
Control System Manual. When outside services are used, the Quality Control
System Manual shall describe the system by which the use of those services meets
the requirements of the applicable Section of the ASME Code.
11) Valve Testing and Setting – The Quality Control System Manual
shall include provisions that each valve shall be tested and set and all
external adjustments sealed according to the requirements of the valve
manufacturer and as required by this Section. The seal shall identify the
repair organization. Abbreviations or initials are permitted.
12) Valve Repair Nameplates – An effective valve stamping system
shall be established to ensure proper stamping of each valve as required by
Section 2120.1270. The Quality Control System Manual shall include a
description or a drawing of the nameplate.
13) Calibration of Measurement and Test Gauges – The calibration
of the measurement and test gauges system shall include the periodic
calibration of measuring instruments and pressure gauges.
A) Pressure gauges used for setting valves are to be checked
periodically (indicate time schedule) by the person authorized (indicate
title). The method of gauge testing is to be indicated and results recorded.
B) Periodically, all master instruments shall be calibrated
preferably, but not necessarily, to measuring equipment traceable to the
National Bureau of Standards.
14) Controlled Copy – An up to date copy of the written Quality
Control System Manual shall be submitted to the Division for review and
acceptance. Revisions shall also be submitted for acceptance prior to being
implemented.
15) Nonconformities – The system shall establish measures for the
identification, documentation, evaluation, segregation and disposition of
nonconformities. A nonconformity is a condition of any material, item, product
or process in which one or more characteristics do not conform to the
established requirements. These may include, but are not limited to, data
discrepancies, procedural and/or documentation deficiencies, or material
defects. Also, the titles of the individuals involved in this process shall be
included.
16) Sample Forms – Forms used in the Quality Control System shall
be included in the manual with a written description. Forms exhibited shall be
marked "SAMPLE" and completed in a manner typical of actual valve
repair procedures.
17) Individuality Important – It is extremely important that the
manual describe and the operation implement the system of each repair
organization firm while meeting the requirements of this Subpart.
(Source: Amended at 32 Ill.
Reg. 17198, effective October 16, 2008)
Section 2120.1270 Nameplates
a) When a safety or safety relief valve is repaired, a metal
repair nameplate stamped with the information required by subsection (b) shall
be attached and sealed by wire and lead or metal seal stamped to the valve
either above, adjacent to or below the original stamping. See Section 2120.1250(b)
for exception.
b) As a minimum, the information on the valve repair nameplate
shall include the name of the repair organization and the date of repair. If
set pressure has been changed, then the new pressure setting, as well as the
blowdown (for "V" stamped valves), and new capacity shall be
indicated. The original nameplate or stamping shall be marked out but left
legible. The new capacity shall be based on that for which the valve was
originally certified.
c) Illegible or Missing Nameplates
1) When the information on the original manufacturer's or
assembler's nameplate or stamping is illegible, the nameplate or stamping shall
be augmented or replaced by a nameplate stamped "duplicate" that
contains all information that originally appeared on the nameplate or valve, as
required by the applicable Section of the ASME Code, except the "V"
or "UV" symbol and the National Board mark. The repair
organization's nameplate and other required data specified in subsection (b)
will make the repair organization responsible to the owner and the Division for
the information on the duplicate nameplate being correct.
2) When the original valve nameplate is missing, the repair
organization is not authorized to perform repairs to the valve under the
program unless positive identification can be made to that specific valve and
verification that the valve was originally stamped with a "V" or
"UV" stamp. Valves that can be positively identified shall be equipped
with a duplicate nameplate as described in subsection (c)(1), in addition to
the repair organization stamped nameplate. The repair organization
responsibilities for accurate data as defined in subsection (c)(1) shall apply.
3) When a duplicate nameplate is affixed to a valve as required
by subsection (c)(1) or (c)(2), it shall be marked "Sec I" or
"Sec VIII", as applicable, to indicate the original ASME Code
stamping.
(Source: Amended at 32 Ill.
Reg. 17198, effective October 16, 2008)
Section 2120.1275 Field
Repair
a) Field repairs are defined as any repair conducted outside a
fixed repair shop location. Field repairs may be conducted with the aid of
mobile facilities with repair capabilities with or without testing
capabilities. Field repairs may be conducted in user facilities without use of
mobile facilities as described above.
b) Organizations that obtain certification for in-shop/plant
repairs may also perform field repairs to safety and safety relief valves
provided that:
1) Technicians trained as required by Section 2120.1285 in the
employ of the certificate holder perform such repairs;
2) Quality Control System meeting Section 2120.1260 with
procedures for field repairs is maintained;
3) All functions affecting the quality of the repaired valves are
supervised from the location where the certification is issued;
4)
A) Periodic audits of the work carried out in the field are made
by quality control personnel of the Certificate holder to ensure that the
requirements of the quality control system are met; this audit shall include
but not be limited to testing by the Certificate holder of sample valves which
were repaired in the field. Sample valves shall be tested using the
Certificate holder's in-shop/plant testing facilities.
B) Provided the above provisions are met, verification testing of
field repaired valves shall not be required.
C) Organizations that only perform field repairs must demonstrate
field repair capabilities to representatives of the Division. Two valves, one
steam and one air as applicable, must be repaired in the field and tested for
verification. A Quality Control System Manual must be prepared describing all
field repair activities that affect the performance of the repaired valves as
specified in Section 2120.1260(b).
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1280 Performance
Testing of Repaired Valves
Repaired
valves shall meet the performance criteria equivalent to the standard for new
valves.
a) Valves marked for steam service or having special internal
parts for steam service shall be tested on steam. Valves marked for general
service may be tested with air or gas. Each valve shall be tested to
demonstrate set pressure, response to blowdown, if required, and seat tightness
in accordance with the requirements of the applicable Sections of the ASME
Code.
b) When valves are repaired by the owner for the owner's own use
and not for resale, valves for steam service may be tested on air or nitrogen
for set pressure and, if possible, blowdown adjustment, provided manufacturer's
corrections for differential in set pressure between steam and testing medium
are applied to the set pressure.
c) A hydraulic or pneumatic device may be used to apply an
auxiliary lifting load on the spring of a repaired valve which has been
installed on a boiler or pressure vessel to establish the set pressure of the
valve in lieu of the tests required in subsection (a) and (b) above, provided
calibrated testing equipment and testing procedures are followed. In such
cases, the manufacturer's recommendations shall be used to establish blowdown.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1285 Training
of Valve Repair Personnel
It is
essential that valve repair organizations insure that their personnel making
repairs to safety and safety relief valves are knowledgeable and qualified. The
repair organization shall provide for documented in-house training for these
persons.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1290 ASME
"V", "UV" or National Board "VR" Certificate
Holders
a) A manufacturer, assembler or other organization in possession
of a valid ASME "V" or "UV" Code Symbol Stamp or an
organization in possession of a National Board Certificate of Authorization for
use of a National Board "VR" Stamp for the repair of ASME-National
Board stamped safety and safety relief valves are authorized by these rules to
repair such valves in accordance with these rules and such repairs must be
within the scope of the organization's Certificate of Authorization whether
issued by the ASME or the National Board.
b) A manufacturer or repair firm may perform field repairs of
safety and safety relief valves covered by his Certificate of Authorization
provided that:
1) Technicians are trained as required by Section 2120.1285 in
the employ of the manufacturer or repair firm perform such repairs;
2) Quality Control System meeting Section 2120.1260 with
procedures for field repairs is maintained;
3) All functions affecting the quality of the repaired valves are
controlled from the location for which the certificate was issued;
4) Periodic audits of work carried out in the field are made by
quality control personnel of the manufacturer or repair firm to ensure that the
requirements of the Quality Control System are met; this audit may include, but
not be limited to, witnessing the test of field repaired valves.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1300
Introduction
The Illinois State Fire Marshal
shall authorize as Owners-Users only those firms which meet all the
requirements of Section 15 of the Act, and who have a written Quality Control
System acceptable to the Chief Inspector. The applicant shall apply to the
Division of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety for Owner-User status. After the
Chief Inspector has reviewed the applicant's Quality Control System, he will
submit a recommendation to the Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Rules for
their consideration. Upon review of the Chief Inspector's recommendation, the
Board will make a determination for acceptance or rejection of the applicant's
status as an Owner-User. After acceptance as an Owner-User, the Division of
Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety shall provide for an annual audit of the
program. This Subpart is a guide to the features which must be covered in the
written description of the Quality Control System Manual.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1301 Authority
and Responsibility
The authority and responsibility
of those in charge of the inspection department shall be established. Persons
performing inspection functions shall have sufficient and well defined
responsibility, authority, and the organizational freedom to identify problems
and to initiate, recommend and provide solutions.
(Source: Added at 11 Ill. Reg. 16587, effective January 1, 1988)
Section 2120.1305
Organization
a) An organization chart showing the relationship between
management, engineering, purchasing, manufacturing, and inspection, is required
to reflect the actual organization. The purpose of this chart is to identify
and associate the various organizational groups with the particular function
for which they are responsible. This requirement does not intend to encroach
on the Owner-User's right to establish, and from time to time, alter whatever
form of organization the Owner-User considers appropriate for its work.
b) The inspector(s) shall be under the supervision of one or more
regularly employed engineer(s).
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1310 Inservice
Inspection Program
The Owner-User Quality Control
System shall include provisions to ensure that inspections are carried out in
accordance with written procedures. These procedures must delineate all sources
and references of pertinent information to be furnished by the Inspector.
Included should be a statement that other sources of qualified help will be
made available to the Inspector. These procedures shall highlight the degree
of inspection required for the types of vessels involved. As a minimum these
procedures shall include provisions for reporting the following:
a) Internal or external inspection.
b) Location and thickness of sample areas.
c) Location and extent of corrosion, bulging, blistering or
cracks in shells, head, welding seams, and/or weld heat affected zones.
d) Type and extent of non-destructive examination employed.
e) Setting and condition of safety valve, safety relief valve, or
rupture disks.
f) Provisions for complying with the report requirements of the
Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Act.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1320 Drawings,
Design Calculations and Specification Control
The Owner-User Quality Control
System shall provide procedures which will ensure that the latest applicable
drawings, design calculations, specifications, and instructions required, as
well as authorized changes, are used for inspection and repair.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1325 Material
Control
The Owner-User shall include a
system of material receiving control that requires verification that the
material received conforms to order requirements and that the identification of
the materials corresponds to the material certifications or material test
reports. The system shall ensure that only the intended material is used in
repairs.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1330
Examination and Inspection Program
The Owner-User Quality Control
System shall describe the repair operations, including examinations,
sufficiently to permit the inspector to determine at what stages specific
inspections are to be performed. The system shall include a checklist,
traveler or process sheet which lists important stages in the repair procedure
which will allow the inspector to designate his desired inspections. As a
minimum the stages shall permit the inspector to indicate his verification of
the following:
a) Calculations are available.
b) Materials used comply with the ASME Code.
c) Welding procedures have been qualified in accordance with
Section IX, ASME Code.
d) Welders and welding operators have been qualified in
accordance with Section IX, ASME Code.
e) Heat treatment, including post weld heat treatment, as
applicable, has been performed.
f) Material imperfections have been acceptably repaired.
g) Weld defects have been acceptably repaired.
h) Nondestructive examinations have been performed and results
are acceptable.
i) Material identification markings have been properly
transferred.
j) There are no material or dimensional imperfections.
k) Performance of internal and/or external inspections and
witnessing hydrostatic or pneumatic test.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1335 Correction
of Nonconformities
There shall be a system agreed
upon with the inspector for correction of nonconformities. A nonconformity is
any condition which does not comply with the applicable provisions of this
Part. Nonconformities must be corrected or eliminated in some way before the
completed component can be considered to comply.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1340 Welding
The Quality Control System shall
include provisions for indicating that welding conforms to requirements of
Section IX, of the ASME Code.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1345
Nondestructive Examination
The Quality Control System shall
include provisions for identifying nondestructive examination procedures which
will apply. Procedures utilized and personnel performing nondestructive
examinations shall meet the requirements of Section V, ASME Code.
(Source: Added at 11 Ill. Reg. 16587, effective January 1, 1988)
Section 2120.1350
Calibration of Measurement and Test Equipment
The Owner-User Quality Control
System shall include provisions for the calibration of examination, measuring,
and test equipment used in fulfillment of requirements.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1355 Records
The Owner-User Quality Control
System shall describe the procedures to be followed to ensure the following
records are maintained for the life of the pressure vessel or boiler.
a) Inservice Inspection Records:
1) ASME data reports if applicable
2) Date object was placed in service
3) Record of inservice inspections including inspector's
signature
b) Repair Record:
1) Calculations
2) Material test reports
3) Traveler
4) Welding procedure specifications
5) Welding procedure qualification records
6) Welder qualification records
7) Heat treat procedure
8) Time-temperature charts
9) NDE procedures
10) NDE examination reports including NDE technician signature
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
Section 2120.1360 Inspectors
The Quality Control System shall
include a definition of inspector. The inspector as referenced in this Subpart
D, Owner-User Quality Control Requirements shall meet the requirements of
Section 8 and pass an examination in accordance with Section 9 of the Boiler
and Pressure Vessel Safety Act. The inspector must carry out his duties in
complete compliance with this Division. The inspector must have the authority
to take necessary action if an unsafe condition is found.
a) The Owner-User inspector must:
1) Be a full-time employee of the Owner-User.
2) Be provided with the necessary tools and equipment to properly
conduct his inspection duties.
3) Be provided with adequate space and necessary office
equipment.
4) Be provided with proper and adequate training in order that he
may effectively perform his duties. Provisions shall be made for additional
training if needed in order to assure effective performance of his duties.
b) The Owner-User inspector shall not perform inspections on
equipment for which he has operation or maintenance responsibilities.
(Source: Amended at 17 Ill. Reg. 14917, effective September 1, 1993)
![]()
![]()
![]()

