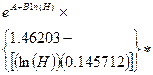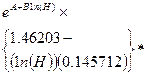SUBTITLE C: WATER POLLUTION
CHAPTER I: POLLUTION CONTROL BOARD
PART 302 WATER QUALITY STANDARDS
SECTION 302.208 NUMERIC STANDARDS FOR CHEMICAL CONSTITUENTS
Section 302.208 Numeric Standards for Chemical Constituents
a) The acute standard (AS) for the chemical constituents listed in subsection (e) must not be exceeded at any time except for those waters for which a zone of initial dilution (ZID) has been approved by the Agency under Section 302.102.
b) The chronic standard (CS) for the chemical constituents listed in subsection (e) must not be exceeded by the arithmetic average of at least four consecutive samples collected over any period of at least four days, except for those waters in which the Agency has approved a mixing zone or in which mixing is allowed under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 302.102. The samples used to demonstrate attainment or lack of attainment with a CS must be collected in a manner that assures an average representative of the sampling period. For the chemical constituents that have water quality-based standards dependent upon hardness, the chronic water quality standard will be calculated according to subsection (e) using the hardness of the water body at the time the sample was collected. To calculate the attainment status of chronic standards, the concentration of the chemical constituent in each sample is divided by the calculated water quality standard for the sample to determine a quotient. The water quality standard is attained if the mean of the sample quotients is less than or equal to one for the duration of the averaging period.
c) The human health standard (HHS) for the chemical constituents listed in subsection (f) must not be exceeded when the streamflow is at or above the harmonic mean flow under Section 302.658, nor must an annual average, based on at least eight samples collected in a manner representative of the sampling period, exceed the HHS except for those waters in which the Agency has approved a mixing zone or in which mixing is allowed under Section 302.102.
d) The standard for the chemical constituents of subsections (g) and (h) must not be exceeded at any time except for those waters in which the Agency has approved a mixing zone or in which mixing is allowed under Section 302.102.
e) Numeric Water Quality Standards for the Protection of Aquatic Organisms
|
Constituent |
AS (µg/L) |
CS (µg/L) |
|
Arsenic (trivalent, dissolved) |
360 x 1.0* = 360 |
190 x 1.0* = 190 |
|
|
|
|
|
Boron (total) |
40,100 |
7,600 |
|
|
|
|
|
Cadmium (dissolved) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
where A = -2.918 and B = 1.128 |
where A = -3.490 and B = 0.7852 |
|
|
|
|
|
Chromium (hexavalent, total) |
16 |
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
Chromium (trivalent, dissolved) |
where A = 3.688 and B = 0.8190 |
where A = 1.561 and B = 0.8190 |
|
|
|
|
|
Copper (dissolved) |
where A = -1.464 and B = 0.9422 |
where A = -1.465 and B = 0.8545 |
|
|
|
|
|
Cyanide** |
22 |
5.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
Fluoride (total) |
|
|
|
where A = 6.7319 and B = 0.5394 |
where A = 6.0445 and B = 0.5394 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lead (dissolved) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
where A = -1.301 and B = 1.273 |
where A = -2.863 and B = 1.273 |
|
|
|
|
|
Manganese (dissolved) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
where A = 4.9187 and B = 0.7467 |
where A = 4.0635 and B = 0.7467 |
|
|
|
|
|
Mercury (dissolved) |
2.6 x 0.85* = 2.2 |
1.3 x 0.85* = 1.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nickel (dissolved) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
where A = 0.5173 and B = 0.8460 |
where A = -2.286 and B = 0.8460 |
|
|
|
|
|
TRC |
19 |
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
Zinc (dissolved) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
where A = 0.9035 and B = 0.8473 |
where A = -0.4456 and B = 0.8473 |
|
|
|
|
|
Benzene |
4200 |
860 |
|
Ethylbenzene |
150 |
14 |
|
Toluene |
2000 |
600 |
|
Xylene(s) |
920 |
360 |
|
where: |
|||
|
|
µg/L |
= |
microgram per liter |
|
|
ex |
= |
base of natural logarithms raised to the x-power |
|
|
ln(H) |
= |
natural logarithm of hardness (in mg/L as CaCO3) |
|
|
* |
= |
conversion factor multiplier for dissolved metals |
|
|
** |
= |
standard to be evaluated using either of the following USEPA approved methods, incorporated by reference at 35 Ill. Adm. Code 301.106: Method OIA-1677, DW: Available Cyanide by Flow Injection, Ligand Exchange, and Amperometry, January 2004, Document Number EPA-821-R-04-001 or Cyanide Amenable to Chlorination, Standard Methods 4500-CN-G (40 CFR 136.3) |
f) Numeric Water Quality Standard for the Protection of Human Health
|
Constituent |
|
(µg/L) |
|
Mercury (total) |
|
0.012 |
|
Benzene |
|
310 |
|
where: |
|||
|
|
µg/L |
= |
micrograms per liter |
g) Single-value standards apply at the following concentrations for these substances:
|
Constituent |
Unit |
|
Standard |
|
Barium (total) |
mg/L |
|
5.0 |
|
Chloride (total) |
mg/L |
|
500 |
|
Iron (dissolved) |
mg/L |
|
1.0 |
|
Phenols |
mg/L |
|
0.1 |
|
Selenium (total) |
mg/L |
|
1.0 |
|
Silver (total) |
µg/L |
|
5.0 |
|
where: |
|||
|
|
mg/L |
= |
milligram per liter and |
|
|
µg/L |
= |
microgram per liter |
(Source: Amended at 47 Ill. Reg. 4437, effective March 23, 2023)